
What is artificial intelligence, and why is it transforming nearly every industry?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making.
In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll explain what artificial intelligence is, how artificial intelligence works, the main types of artificial intelligence, and real-world AI applications — all in simple terms without technical jargon.
No math. No technical jargon. Just clear explanations.
What Is Artificial Intelligence? (Simple Definition)
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
These tasks include:
- Learning from data
- Recognizing patterns
- Understanding language
- Making decisions
- Solving problems
In simple terms:
AI is the goal of making machines behave intelligently.
AI is not a single technology. It is a broad field that includes many different methods and approaches.
How Artificial Intelligence Works (Step-by-Step)
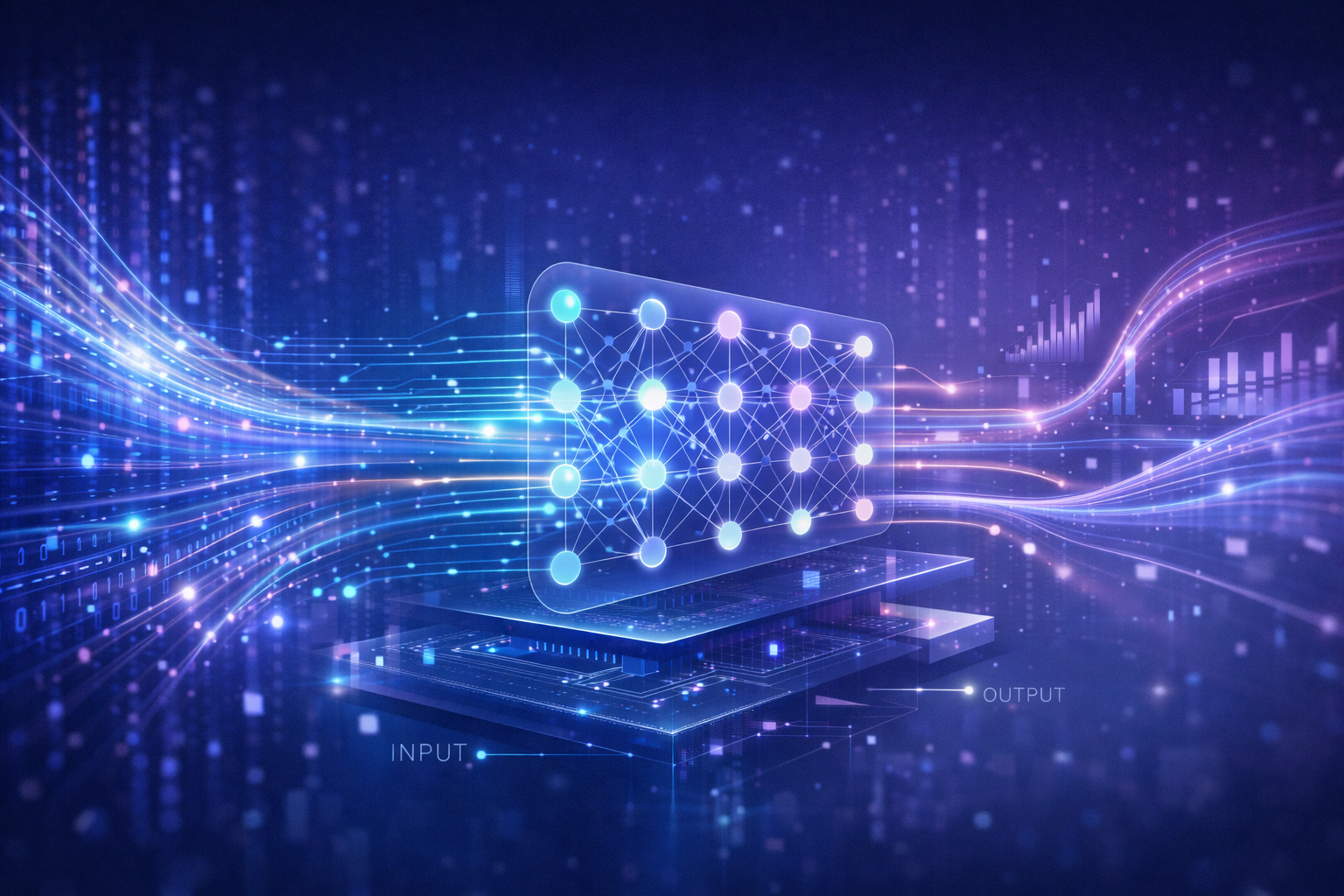
At a high level, most modern AI systems work in three main steps.
Step 1 — Data Input
AI systems learn from data.
This data can include:
- Images
- Text
- Audio
- Numbers
- User behavior
The more relevant and high-quality data an AI system receives, the better it can learn.
Step 2 — Pattern Learning (Machine Learning Basics)
Using algorithms, AI systems analyze data to find patterns.
This process is called machine learning.
Instead of being manually programmed with rules, machine learning models improve automatically as they are exposed to more data.
If you want a deeper explanation, see our full guide on Machine Learning Explained.
Step 3 — Predictions, Decisions, and Actions
After learning patterns, AI systems can:
- Make predictions
- Classify information
- Generate content
- Recommend products
- Automate decisions
For example:
- A spam filter predicts whether an email is spam.
- A streaming platform recommends shows.
- A medical AI system identifies signs of disease in scans.
AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
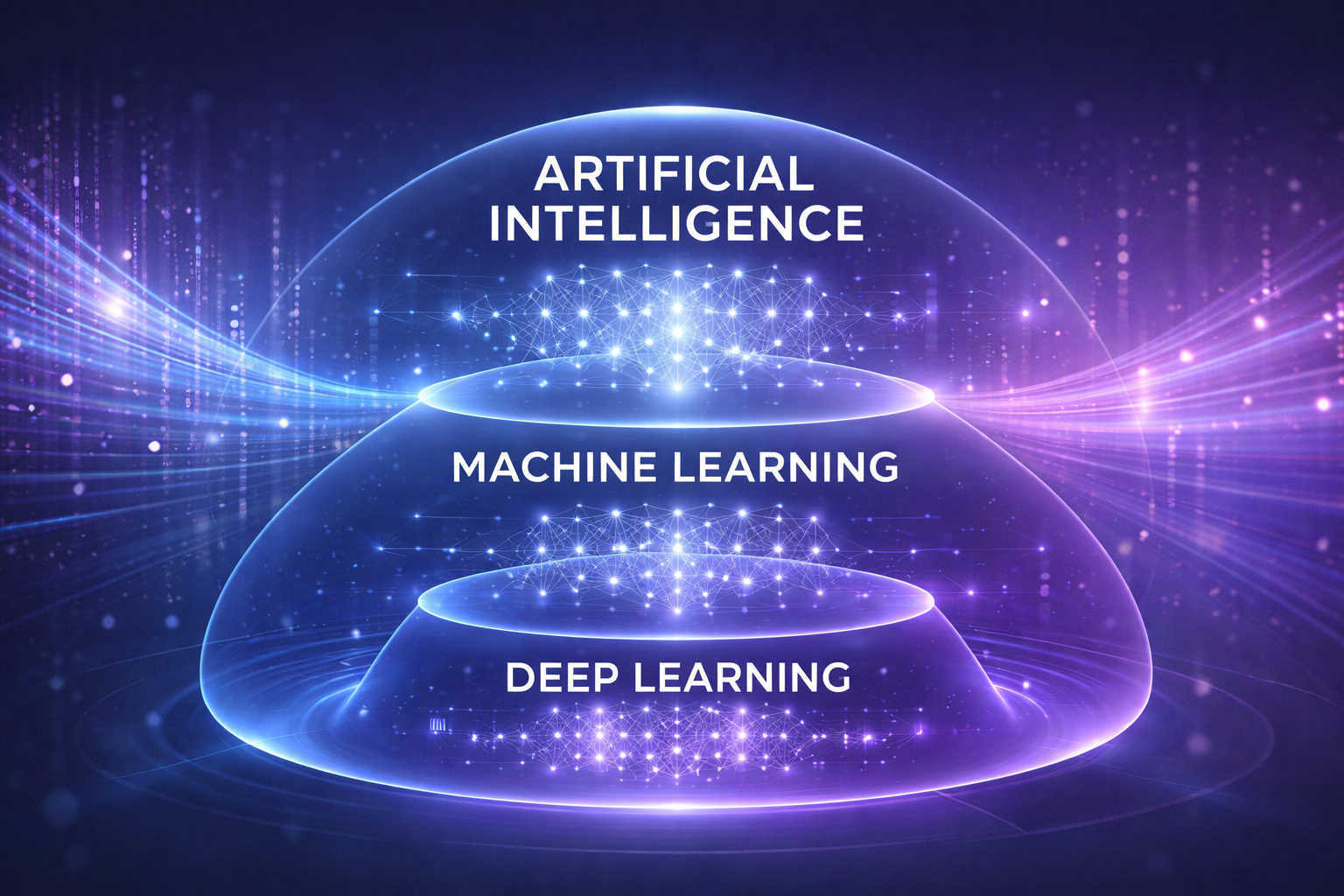
These terms are often used interchangeably — but they are not the same.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad goal of making machines intelligent.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that learns from data.
- Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses layered neural networks.
Think of it like this:
- AI is the umbrella
- Machine learning is one branch
- Deep learning is a deeper branch within that
For a full comparison, read our detailed guide on AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning.
Types of Artificial Intelligence

AI can be categorized into different types based on capability.
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
This is the only type of AI that exists today.
Narrow AI is designed for a specific task, such as:
- Voice assistants
- Recommendation systems
- Image recognition
- Fraud detection
It cannot operate outside its programmed domain.
General AI (Strong AI)
General AI would be able to perform any intellectual task that a human can do.
This level of AI does not exist yet and remains theoretical.
Superintelligent AI
This refers to AI that surpasses human intelligence in all areas.
This concept is speculative and often discussed in long-term AI ethics and safety debates.
Key AI Technologies Explained Simply
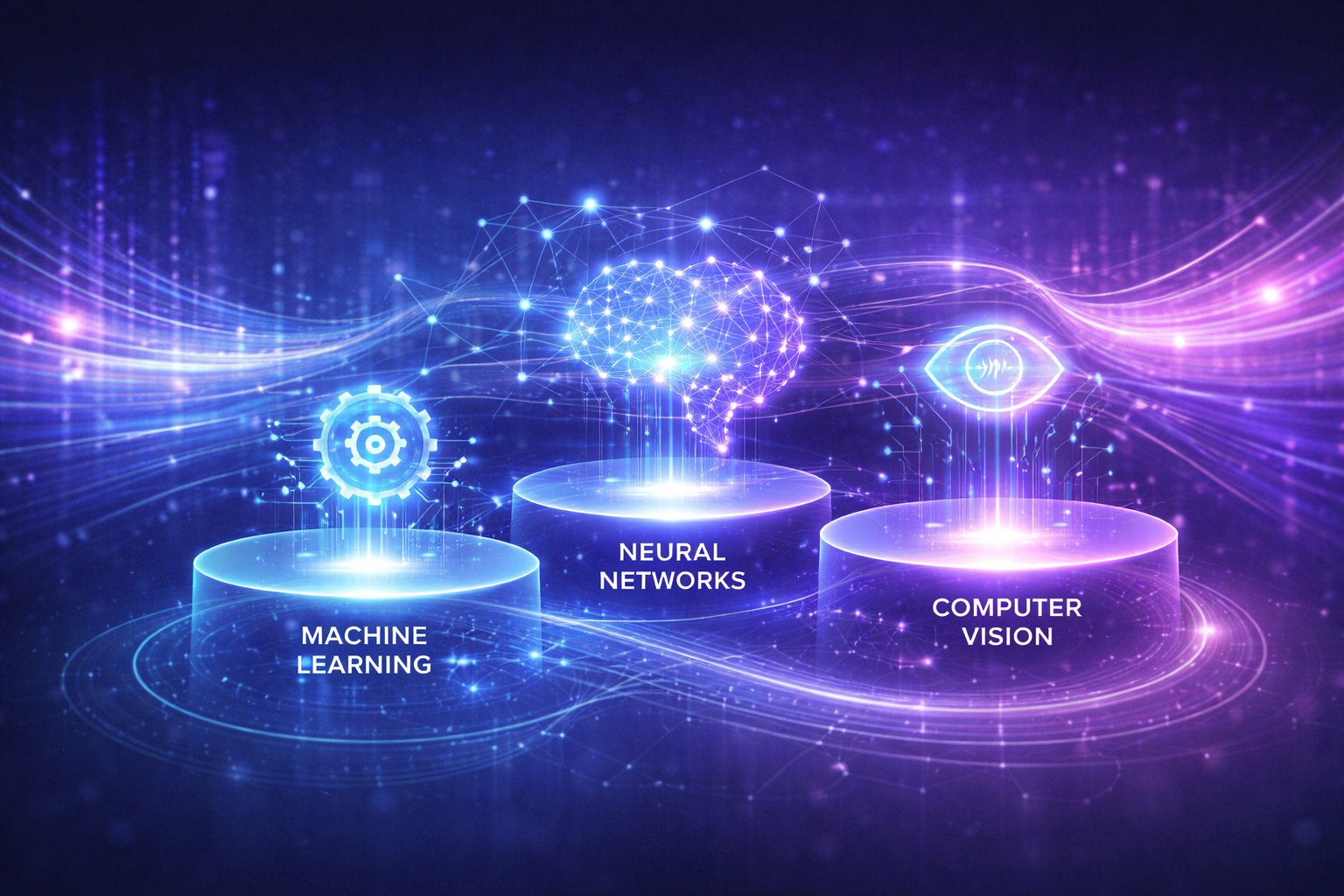
Artificial intelligence includes several major technologies.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning allows systems to learn patterns from data without being explicitly programmed.
Learn more in our Machine Learning Explained guide.
Neural Networks & Deep Learning
Deep learning uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn complex patterns.
It is especially powerful for:
- Image recognition
- Speech processing
- Generative AI
See our full article on Deep Learning 101 for more.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows machines to understand and generate human language.
It powers:
- Chatbots
- Translation tools
- AI writing assistants
Read our full guide on Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Generative AI.
Computer Vision
Computer vision enables machines to interpret and analyze images and video.
It is used in:
- Facial recognition
- Medical imaging
- Autonomous vehicles
Explore more in Computer Vision Explained.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning trains AI systems through trial and error using rewards and penalties.
It is commonly used in:
- Robotics
- Game-playing AI
- Autonomous systems
Real-World Examples of Artificial Intelligence
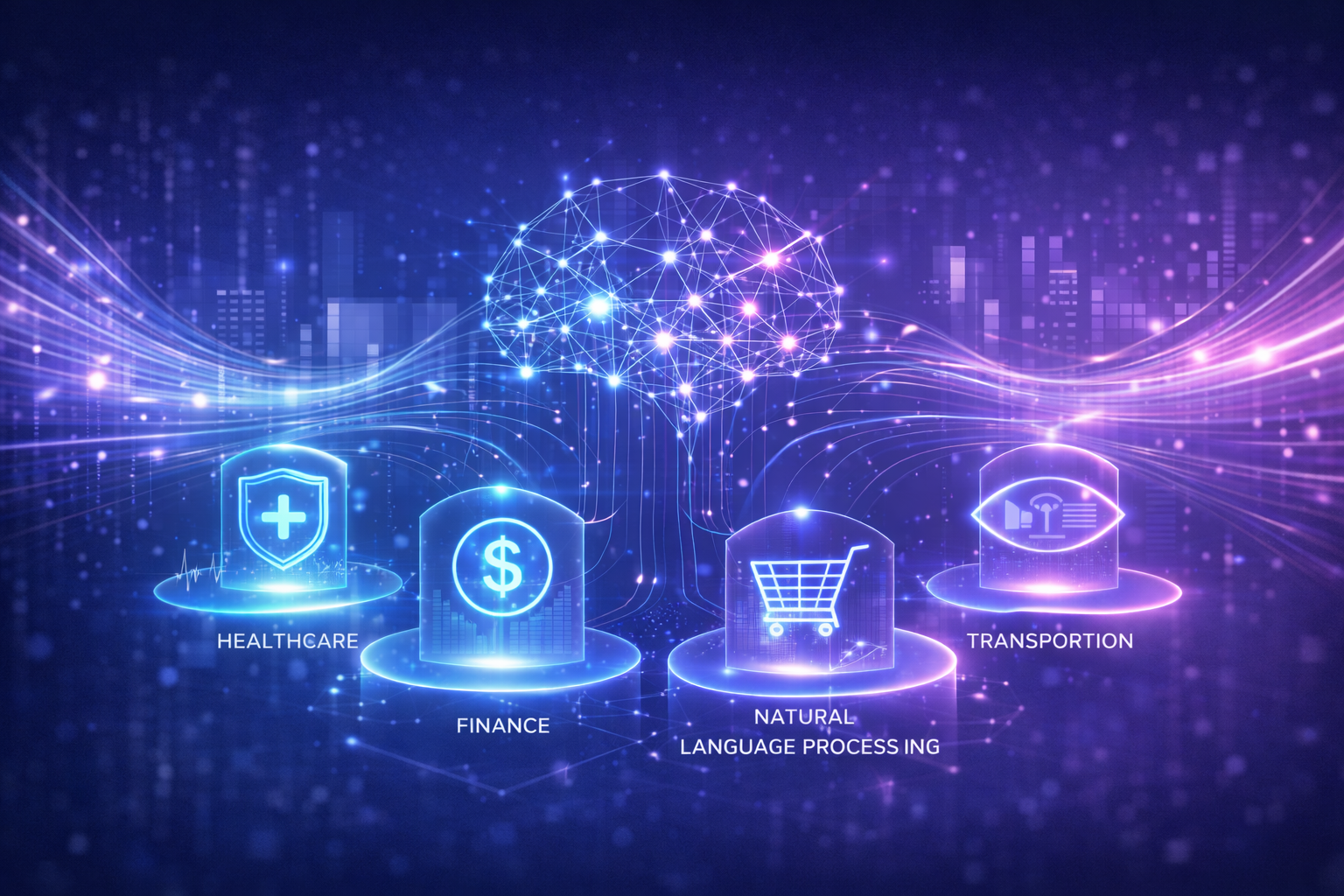

AI is already embedded in many industries:
- Healthcare — diagnosing diseases and analyzing scans
- Finance — detecting fraud and managing risk
- Retail — recommending products
- Transportation — autonomous vehicles
- Education — personalized learning systems
- Social media — content recommendations
AI applications continue to expand rapidly.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
When used responsibly, AI provides major advantages:
- Faster decision-making
- Automation of repetitive tasks
- Improved accuracy
- Personalized user experiences
- Innovation in science and technology
AI can increase efficiency and unlock new possibilities across industries.
Challenges and Limitations of AI
Despite its benefits, AI also presents challenges:
- Bias in training data
- Privacy concerns
- Lack of transparency
- Job disruption
- Ethical concerns
Understanding these risks is essential for building responsible AI systems.
Explore more in our AI Ethics & Responsible Artificial Intelligence section.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence

AI is evolving rapidly.
Future developments may include:
- More advanced generative AI systems
- Multimodal AI combining text, image, and audio
- Smarter AI agents
- Improved regulation and ethical standards
AI will continue shaping industries, economies, and daily life.
For predictions and trends, see our Future of AI: Trends, Predictions & Innovations guide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is AI the same as machine learning?
No. AI is the broad field of intelligent systems, while machine learning is a method that enables systems to learn patterns from data.
Can AI think like humans?
No. Current AI systems simulate intelligent behavior but do not possess consciousness or true understanding.
What’s the difference between AI and robotics?
AI refers to intelligence in software systems. Robotics involves physical machines. A robot may use AI, but not all robots are AI-powered.
Will AI replace jobs?
AI will automate certain tasks, but it will also create new roles and industries. The impact depends on how societies adapt.
What should beginners learn first about AI?
Start with understanding:
- What AI is
- Basic machine learning concepts
- How data drives intelligent systems
From there, you can explore deep learning, NLP, computer vision, and reinforcement learning.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding AI Matters
Now that you understand what artificial intelligence is and how it works, you have a strong foundation for exploring more advanced AI topics.
Artificial intelligence is no longer science fiction. It is part of everyday life.
Understanding what AI is — and what it is not — helps you:
- Navigate technological change
- Make informed decisions
- Build relevant skills
- Think critically about AI’s role in society
Whether you’re a student, professional, or simply curious about technology, learning the fundamentals of artificial intelligence is a powerful first step.
Normally I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very forced me to try and do so Your writing style has been amazed me Thanks quite great post