Artificial intelligence has evolved from simple rule-based systems into models that learn, adapt, and generate content. But a newer category of AI goes even further — Cognitive AI.
Cognitive AI focuses on enabling machines to reason, remember, understand context, and make decisions in ways that more closely resemble human thinking.
If you already understand concepts like machine learning, deep learning, or generative AI, Cognitive AI represents the next layer in AI evolution.
In this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll learn:
- what Cognitive AI is (in simple terms)
- how it differs from traditional AI
- how Cognitive AI “thinks”
- real-world examples
- limitations and risks
- how beginners can use it safely
No technical background required.
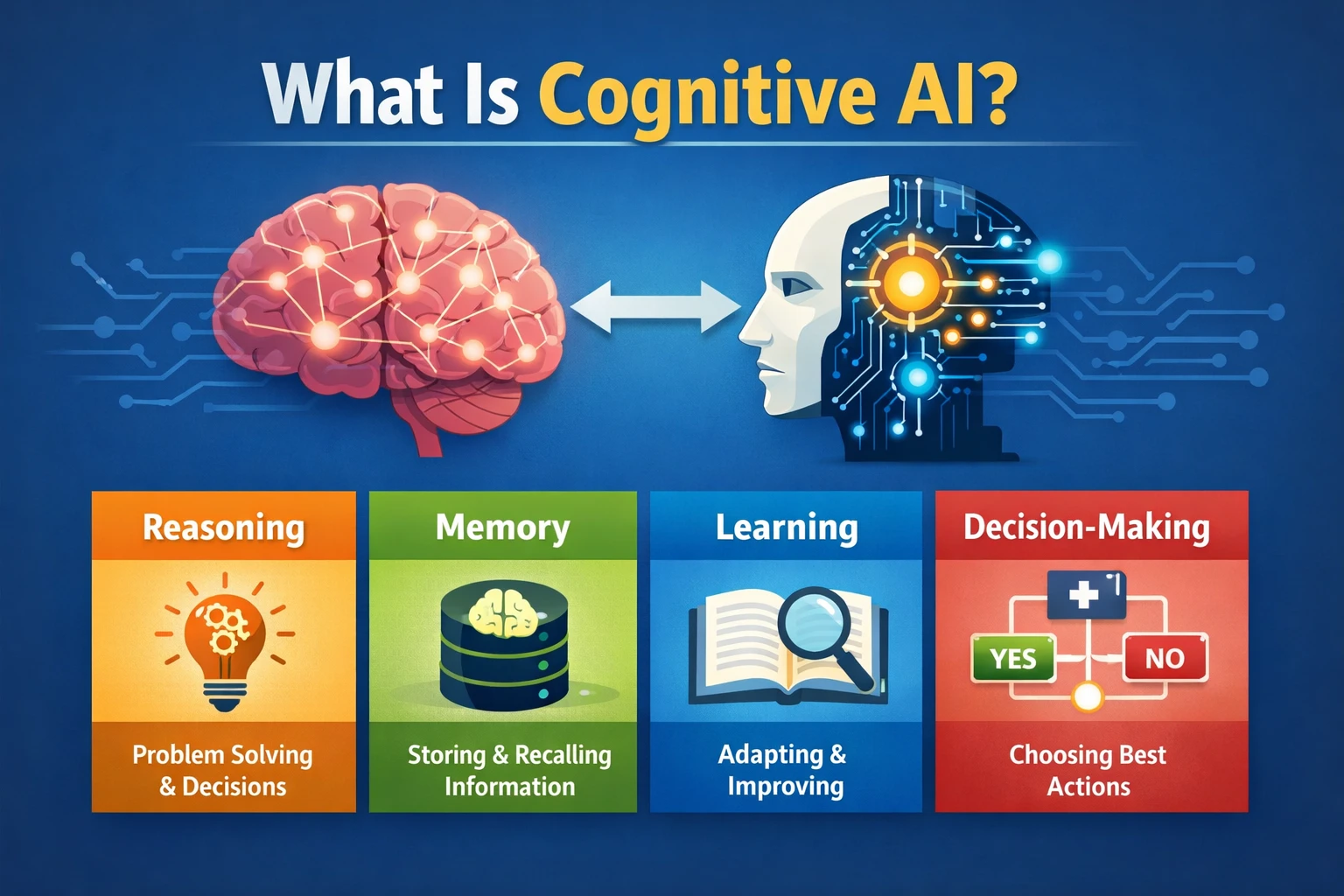
What Is Cognitive AI?
Cognitive AI is a type of artificial intelligence designed to simulate aspects of human cognition — such as reasoning, memory, learning, and decision-making — rather than simply following predefined rules.
A simple way to think about it:
- Traditional AI follows instructions
- Generative AI creates content
- Cognitive AI makes decisions using context, memory, and reasoning
Instead of asking “What rule should I follow?”, Cognitive AI asks:
“What’s happening now, what do I remember, and what’s the best decision?”
Cognitive AI builds on the foundations of machine learning, which we explain in depth in Machine Learning Explained (Simple Guide for Beginners)
How Cognitive AI Is Different From Traditional AI
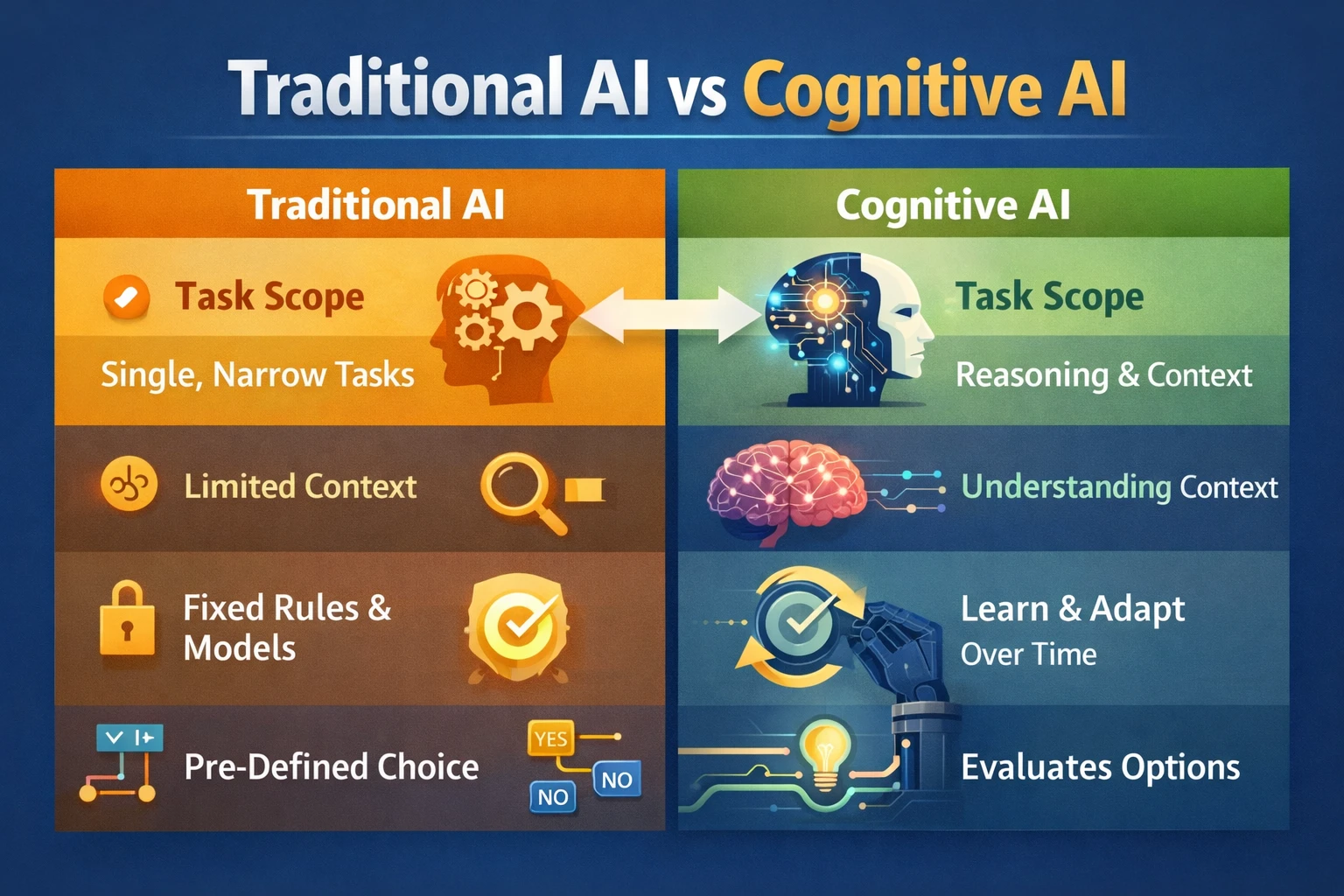
Traditional AI systems are typically built for narrow, predefined tasks, such as:
- detecting spam
- classifying images
- following scripted workflows
They work well in predictable environments — but struggle when conditions change.
Cognitive AI, on the other hand, is designed for dynamic, real-world situations, where:
- information is incomplete
- context shifts over time
- decisions must improve through experience
If you’re new to the broader AI landscape, our beginner guide, What Is Artificial Intelligence? explains where Cognitive AI fits within AI as a whole.
Cognitive AI systems combine:
- machine learning
- memory systems
- reasoning layers
- contextual awareness
This makes them more flexible — and more powerful — than traditional AI.
How Cognitive AI “Thinks” (Simplified)
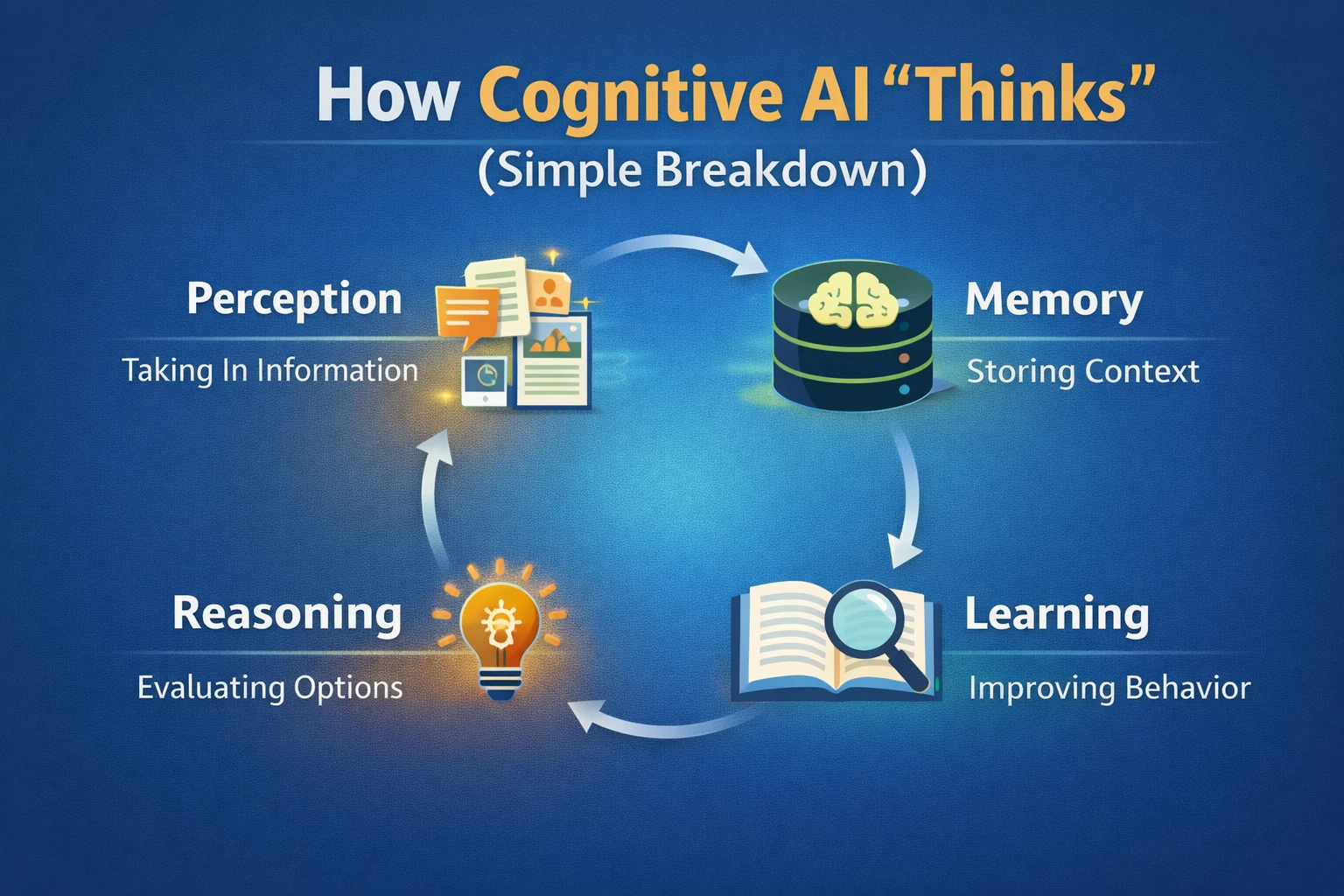
Cognitive AI doesn’t think like a human brain, but it simulates human-like reasoning through structured processes.
The Cognitive AI Decision Loop
At a high level, Cognitive AI follows this cycle:
- Perception — gathers input (text, images, signals, data)
- Understanding — interprets meaning and context
- Memory — recalls relevant past information
- Reasoning — evaluates possible actions
- Decision — selects the best response
- Learning — improves through feedback
Much of this capability relies on neural networks, which are explained in Deep Learning 101.
Decision improvement often uses Reinforcement Learning , where systems learn from rewards and outcomes.
This loop allows Cognitive AI to adapt instead of repeating static behavior.
Cognitive AI vs Other Types of AI
Cognitive AI doesn’t replace other AI approaches — it orchestrates them together.
- Machine Learning → pattern recognition
- Deep Learning → perception and complexity
- Natural Language Processing → language understanding
- Computer Vision → visual interpretation
- Reinforcement Learning → decision optimization
Language-based reasoning often relies on NLP, while visual reasoning uses Computer Vision.
Some Cognitive AI systems also integrate content creation models, which we cover in What Is Generative AI?.
The key difference:
Cognitive AI uses context and memory to decide how and when to apply these tools.
Real-World Examples of Cognitive AI

Cognitive AI is already being applied across industries.
Customer Support
AI assistants that remember conversation context, interpret intent, and adapt responses instead of repeating scripts.
Healthcare
Systems that summarize patient history, track clinical context, and assist with decision support (always with human oversight).
Fraud Detection
Platforms that analyze behavior patterns and adapt to new fraud tactics in real time.
Business Operations
Decision-support tools that reason across data and recommend actions, not just dashboards.
Autonomous Systems
Robots and agents that adjust behavior based on environment, memory, and feedback.
Why Cognitive AI Matters Now
Modern problems are complex and unpredictable.
They involve:
- uncertainty
- incomplete information
- rapidly changing conditions
- trade-offs rather than simple answers
Cognitive AI exists because rule-based automation is no longer enough.
As AI continues to evolve, Cognitive AI is expected to play a growing role in shaping the Future of Artificial Intelligence.
Limitations and Risks of Cognitive AI

Cognitive AI is powerful, but it has limitations.
Hallucinations
Systems may produce confident but incorrect conclusions.
Bias
Training data can influence reasoning in unintended ways.
Overconfidence
Outputs may sound authoritative even when uncertainty exists.
No True Understanding
Cognitive AI simulates reasoning — it does not possess consciousness or emotions.
Safety Concerns
High-stakes decisions must always involve human oversight.
Key takeaway: Cognitive AI should assist decisions — not replace human judgment.
How Beginners Can Start Using Cognitive AI Safely

You don’t need to build Cognitive AI systems from scratch.
Beginner Best Practices
- use AI as a decision assistant, not an authority
- verify important outputs
- avoid sensitive data
- keep humans in the loop
- apply constraints and context
Treat Cognitive AI as a thinking partner, not a decision-maker.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cognitive AI
What is Cognitive AI in simple terms?
Cognitive AI is AI that uses context, memory, and reasoning to make better decisions instead of following fixed rules.
Is Cognitive AI the same as machine learning?
No. Machine learning learns patterns; Cognitive AI combines learning with reasoning and memory.
How is Cognitive AI different from generative AI?
Generative AI creates content. Cognitive AI focuses on reasoning and decision-making.
Does Cognitive AI think like humans?
No. It simulates aspects of human thinking but does not have consciousness.
Is Cognitive AI safe?
It can be, when used responsibly with human oversight.
Continue Learning: Build Your AI Foundation
If you want to deepen your understanding of AI systems, explore these next:
• What Is Artificial Intelligence? (Beginner’s Guide)
• Reinforcement Learning Explained
Each article builds on the concepts introduced here.
Conclusion
Cognitive AI represents a shift in artificial intelligence — from systems that follow rules or generate content to systems that reason, remember, and adapt.
It doesn’t replace human intelligence, but it brings AI closer to thinking through decisions instead of executing instructions.
The key takeaway:
Cognitive AI is a powerful assistant — not a substitute for human judgment.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What is Cognitive AI in simple terms?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Cognitive AI is a type of artificial intelligence that uses context, memory, and reasoning to make decisions instead of simply following fixed rules.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “How is Cognitive AI different from traditional AI?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Traditional AI follows predefined rules and workflows, while Cognitive AI adapts to changing situations by using reasoning, memory, and contextual understanding.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Is Cognitive AI the same as machine learning?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “No. Machine learning focuses on learning patterns from data, while Cognitive AI combines machine learning with reasoning, memory, and decision-making systems.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “How is Cognitive AI different from generative AI?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Generative AI creates content like text or images, while Cognitive AI focuses on understanding context and making decisions. Generative models may be used as part of a Cognitive AI system.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Does Cognitive AI actually think like humans?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “No. Cognitive AI simulates aspects of human thinking such as reasoning and memory, but it does not have consciousness, emotions, or true understanding.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What are real-world examples of Cognitive AI?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Real-world examples include customer support assistants, fraud detection systems, healthcare decision-support tools, business intelligence platforms, and autonomous systems.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Is Cognitive AI safe to use?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Cognitive AI can be safe when used responsibly, but important decisions should always involve human oversight due to risks like bias, hallucinations, and overconfidence.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What are the limitations of Cognitive AI?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Limitations include incorrect conclusions, bias from training data, lack of true understanding, and the need for verification in high-stakes situations.”
}
}
]
}