AI in Healthcare: How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Medicine

Artificial intelligence is rapidly changing healthcare — not by replacing doctors, but by helping them work faster, more accurately, and more efficiently.
From analyzing medical images to predicting disease risks and automating paperwork, AI is already playing a meaningful role in modern medicine. Hospitals, clinics, and researchers are using AI to improve patient outcomes, reduce burnout, and make better decisions with data.
In this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll learn:
- what AI in healthcare actually means
- how AI is being used in medicine today
- real-world healthcare AI examples
- the benefits and risks of medical AI
- whether AI can replace doctors
- and what the future of AI in healthcare looks like
No medical or technical background required.
What Is AI in Healthcare?
AI in healthcare refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to assist medical professionals with diagnosis, treatment planning, patient care, and operational tasks.
Instead of relying only on human judgment, these systems analyze large amounts of medical data to identify patterns, generate insights, and support decision-making.
Importantly, AI in healthcare is built to support doctors and clinicians — not replace them.
If you’re new to the topic, it helps to start with the fundamentals in What Is Artificial Intelligence?
How AI Is Used in Healthcare Today
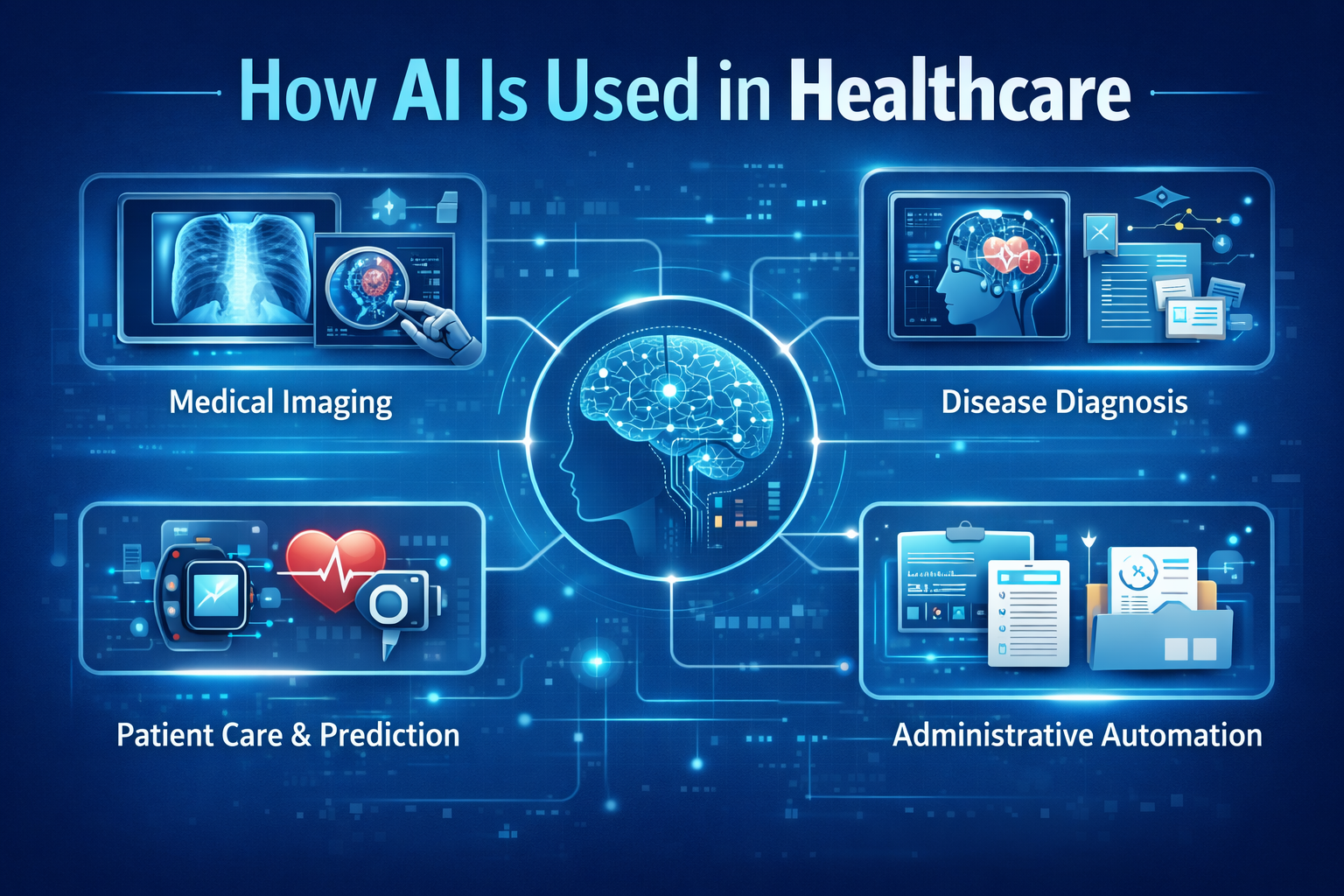
AI is already embedded across many areas of healthcare. Below are the most impactful use cases.
Medical Imaging & Diagnostics
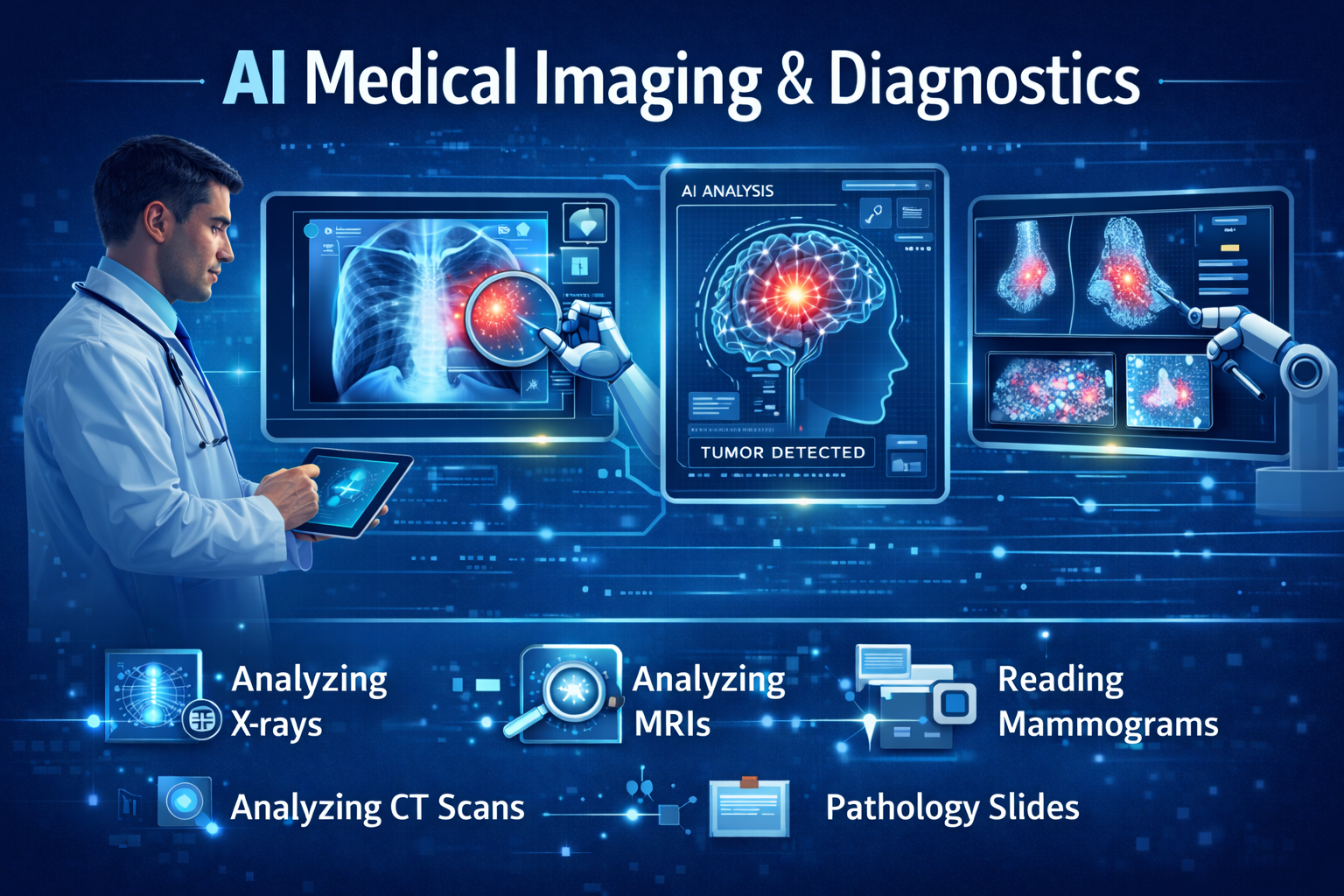
One of the strongest applications of AI in healthcare is medical imaging.
AI systems are trained to analyze:
- X-rays
- MRIs
- CT scans
- mammograms
- pathology slides
These systems help identify tumors, fractures, abnormalities, and early signs of disease — often faster than traditional workflows.
This capability is powered by computer vision, which allows AI to interpret visual data. Learn how this works in Computer Vision Explained.
AI for Disease Detection & Diagnosis
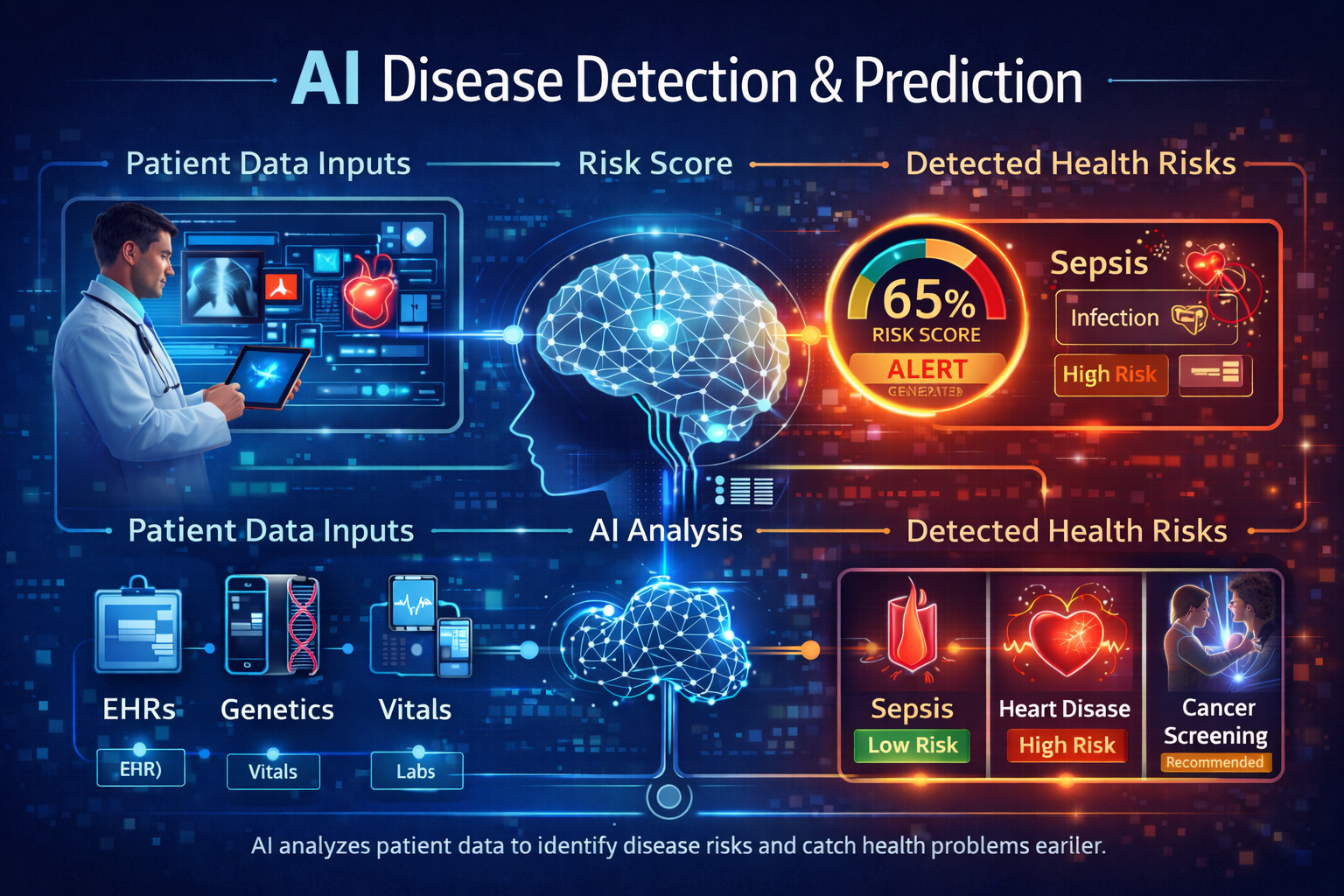
AI is increasingly used to detect diseases earlier and more accurately.
Examples include:
- identifying early cancer risk
- predicting heart disease or stroke
- detecting diabetic complications
- flagging high-risk patients
These systems rely on machine learning models trained on large datasets. To understand how this learning works, see Machine Learning Explained.
Natural Language Processing in Healthcare
Healthcare generates massive amounts of text — clinical notes, patient records, reports, and forms.
Natural language processing (NLP) allows AI to:
- summarize clinical notes
- extract key medical information
- automate documentation
- improve patient communication
This reduces administrative burden and allows clinicians to focus more on patient care. NLP is explained in detail in NLP Explained.
Personalized Treatment & Predictive Care
AI supports personalized medicine by analyzing how individual patients respond to treatments.
Use cases include:
- recommending treatment plans
- predicting patient outcomes
- optimizing medication dosing
- identifying preventive care opportunities
Some systems use reinforcement learning to improve decisions over time. Learn more in Reinforcement Learning Explained.
Real-World Examples of AI in Healthcare
AI in healthcare is already being used in practice, including:
- AI-assisted radiology tools
- hospital systems optimizing scheduling
- virtual health assistants
- AI-supported drug discovery
- early warning systems for patient deterioration
These tools scale medical expertise while maintaining human oversight.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare

Faster Diagnosis
AI analyzes data quickly, helping clinicians act sooner.
Improved Accuracy
When paired with human expertise, AI can reduce errors and improve consistency.
Reduced Doctor Burnout
Automation of documentation and repetitive tasks lowers administrative load.
Better Patient Outcomes
Earlier detection and personalized treatment improve care quality.
Cost & Efficiency Gains
AI helps optimize resources and reduce unnecessary testing.
Risks and Challenges of AI in Healthcare

Bias & Data Quality
Biased or incomplete training data can lead to unfair or inaccurate outcomes.
Privacy & Security
Healthcare data is highly sensitive and must be carefully protected.
Explainability & Trust
Some AI models are difficult to explain — a major concern in medicine.
This challenge is explored further in Symbolic AI vs Neural Networks.
Over-Reliance on AI
AI should support — not replace — human judgment and accountability.
Will AI Replace Doctors?
No.
AI excels at analyzing data and handling repetitive tasks, but it lacks empathy, accountability, and contextual judgment.
The future of healthcare is AI-augmented doctors, not AI-only medicine.
The Future of AI in Healthcare

Looking ahead, AI in healthcare will increasingly focus on:
- preventive and predictive care
- hybrid AI systems that combine learning and reasoning
- continuous patient monitoring
- transparent, explainable decision-support tools
These trends align closely with broader developments discussed in
The Future of AI: Predictions for the Next 10 Years.
How Beginners Can Understand AI in Healthcare
If you’re new to AI:
- focus on core concepts rather than tools
- understand AI’s limitations as well as its strengths
- pay close attention to ethics, bias, and human oversight
Strong fundamentals matter more than specific platforms.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Healthcare
What is AI in healthcare?
AI in healthcare refers to systems that analyze medical data to support diagnosis, treatment planning, patient monitoring, and administrative tasks — while humans remain in control.
Is AI safe to use in healthcare?
AI can be safe when properly tested, regulated, and supervised by medical professionals.
Can AI diagnose diseases on its own?
AI assists diagnosis, but final decisions must always be made by qualified clinicians.
How accurate is AI medical imaging?
AI can be highly accurate for specific tasks, especially when combined with expert human review.
Will AI replace doctors and nurses?
No. AI automates tasks and supports decisions but does not replace human care.
How is patient data protected?
Protection depends on strong security practices, regulatory compliance, and ethical system design.
What are the biggest risks of AI in healthcare?
Bias, lack of transparency, privacy concerns, and over-reliance on automation.
What types of AI are used in healthcare?
Machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing are the most common.
How does AI reduce doctor burnout?
By automating documentation, scheduling, and repetitive administrative work.
What is the future of AI in healthcare?
More personalized, predictive, and transparent systems — with humans firmly in control.
Continue Learning — Build Your AI Foundation
- What Is Artificial Intelligence?
- Machine Learning Explained
- Deep Learning 101
- NLP Explained
- Computer Vision Explained
- Reinforcement Learning Explained
- The Future of AI
Conclusion
AI in healthcare is transforming medicine by improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency — while keeping humans at the center of care.
When used responsibly, AI can improve patient outcomes, reduce burnout, and support better decision-making across the healthcare system.
Understanding how AI works — and where its limits lie — is the key to using it safely, ethically, and effectively in modern medicine.