AI in Smart Cities is a beacon of innovation and efficiency, aiming to harmonize the use of technology with the needs of its inhabitants and the environment. Central to the evolution of these urban ecosystems is Artificial Intelligence (AI), a dynamic and transformative force reshaping the fabric of city life. AI in intelligent cities represents an integration of advanced technologies and a reimagining of urban living, where data-driven decision-making and intelligent systems contribute to sustainable and resilient communities.
1. Introduction to AI in Smart Cities

Smart cities leverage AI to analyze and synthesize data from many sources, including IoT sensors, traffic systems, energy grids, and more, to improve urban infrastructure, public services, and the overall quality of life.
This intelligent analysis enables cities to respond in real time to challenges such as traffic congestion, energy distribution, public safety, and environmental sustainability.
By embedding AI into the core systems of urban areas, municipalities can optimize resources, reduce carbon footprints, enhance safety, and ensure that cities are more livable and adaptive to their residents’ changing needs and expectations.
The integration of AI technologies in urban development is critical for several reasons.
Firstly, it addresses the pressing challenges of urbanization, such as overcrowded public spaces, strained infrastructure, and environmental degradation, by enabling more brilliant, more efficient city planning and management.
AI-driven solutions can predict traffic flows, optimize public transport routes, monitor air quality, and manage waste more effectively, significantly improving urban environments.
Moreover, AI fosters economic growth and competitiveness by streamlining urban operations and services, attracting businesses and investments.
Intelligent systems can also facilitate personalized services for residents, enhance access to healthcare, education, and public services, and improve the overall citizen experience.
However, the path to integrating AI into intelligent cities is laden with challenges, including ethical considerations around privacy and surveillance, the need for substantial investments in technology and infrastructure, and the digital divide that could exacerbate inequalities within urban populations.
Ensuring the responsible and inclusive deployment of AI technologies is paramount to realizing their full potential in creating equitable, sustainable, and thriving urban ecosystems.
In conclusion, the role of AI in shaping intelligent cities is indispensable and profound.
As urban areas continue to evolve, the symbiotic relationship between AI and urban development will become increasingly central to creating spaces that are not only smart in their use of technology but also in their ability to provide for the needs of all residents.
The journey towards integrating AI into the fabric of urban life is complex and multifaceted. Still, the vision it offers—a future where cities are intelligent, efficient, and inclusive—provides a compelling blueprint for the future of urban living.
2. AI in Traffic and Transportation Management

The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in traffic and transportation management within smart cities marks a pivotal shift towards more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly urban mobility solutions.
As cities grow denser and demand for transportation networks increases, the traditional methods of managing traffic and transportation systems must be revised.
AI offers a promising alternative, providing the tools to analyze complex datasets, predict traffic conditions, and optimize transportation networks in ways previously unimaginable.
Optimization of Traffic Flow
One of AI’s primary applications in transportation is optimizing traffic flow. By deploying AI algorithms and machine learning models, cities can process real-time data from traffic sensors, cameras, and GPS devices to understand traffic patterns and adjust signals accordingly.
This real-time traffic management can significantly reduce congestion, lower emission levels, and improve road safety.
For instance, adaptive traffic signal control systems use AI to analyze traffic conditions and adjust signal timings dynamically, reducing wait times at intersections and smoothing the flow of vehicles through busy urban areas.
Enhancing Public Transportation
AI also plays a crucial role in enhancing public transportation systems.
By analyzing passenger data and travel patterns, AI can help transit authorities optimize routes, schedules, and fleet management, ensuring that services are aligned with user demand.
Predictive analytics can forecast peak travel times and adjust service levels accordingly, improving public transport’s efficiency and reliability.
Furthermore, AI-enabled chatbots and virtual assistants provide passengers with real-time information and personalized travel recommendations, enhancing the user experience.
Case Studies of AI-Driven Transportation Solutions
Several cities around the globe have successfully implemented AI-driven transportation solutions, showcasing the potential of AI to transform urban mobility:
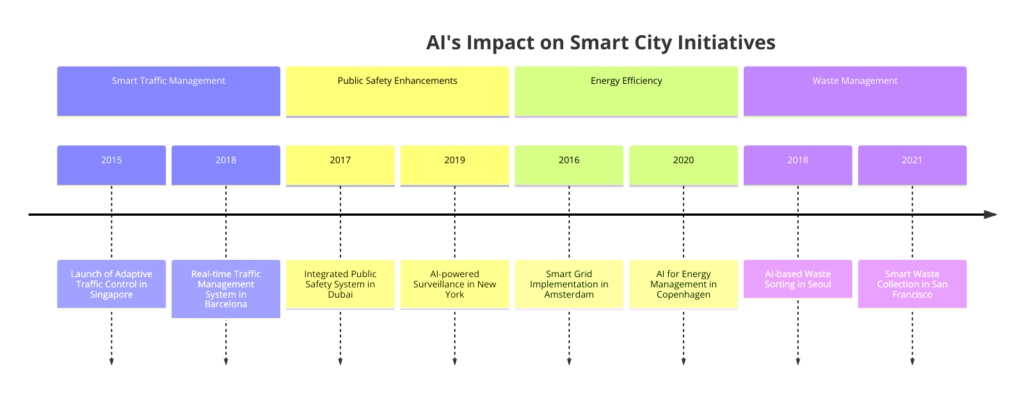
- Singapore: Known for its innovative city initiatives, Singapore has implemented an AI-driven traffic management system that uses real-time traffic data to optimize traffic light timings and manage congestion. The system has significantly improved traffic flow and reduced travel times across the city.
- Barcelona: Barcelona’s integrated urban mobility platform utilizes AI to analyze data from various transportation modes, optimize routes, and reduce congestion. As a result, the city has seen improvements in traffic flow and a reduction in pollution levels.
- Pittsburgh, USA: Pittsburgh has adopted an AI-based traffic signal control system called Surtrac, which has led to a 25% reduction in travel times and a 20% reduction in emissions. The system dynamically adjusts traffic signals based on real-time traffic conditions, demonstrating the efficacy of AI in urban traffic management.
These case studies illustrate AI’s transformative potential in redefining urban transportation, offering insights into how cities can leverage technology to address the challenges of urban mobility.
By employing AI-driven solutions, cities can improve traffic and transportation systems and enhance the overall quality of life for their residents.
Integrating AI in traffic and transportation management is revolutionizing how cities handle urban mobility, offering scalable, dynamic, and efficient solutions to age-old problems of congestion, inefficiency, and environmental impact.
As technology advances, the potential for further innovations in this field is vast, promising a future where urban transportation is not a source of frustration but a seamless, integrated part of city living.
The success stories from cities like Singapore, Barcelona, and Pittsburgh serve as beacons for other urban areas looking to tackle transportation challenges through the intelligent application of AI technologies.
3. AI in Public Safety and Security

Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) in public safety and security initiatives represents a significant advancement in the efforts of intelligent cities to protect citizens, assets, and infrastructure.
AI technologies offer unparalleled capabilities in surveillance, emergency response, crime prediction, and law enforcement, enhancing the efficacy and efficiency of public safety operations.
These innovations not only bolster the ability of cities to respond to immediate threats but also enable a proactive approach to security and safety management.
Enhancing Surveillance with AI
AI-driven surveillance systems are at the forefront of transforming urban security landscapes.
These systems utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze real-time video footage, identifying suspicious behaviors, unauthorized access, or potential security threats with remarkable accuracy.
Unlike traditional surveillance methods, AI can monitor vast areas simultaneously, reducing the reliance on human monitoring and significantly enhancing the coverage and effectiveness of security operations.
Moreover, when ethically and judiciously applied, facial recognition technology can aid in identifying wanted individuals or tracking persons of interest, contributing to safer public spaces.
AI in Emergency Response and Crime Prediction
AI also plays a crucial role in emergency response and crime prediction.
By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, AI algorithms can predict where crimes are more likely to occur, allowing law enforcement agencies to allocate resources more effectively and prevent criminal activities before they happen.
Similarly, in emergency response, AI systems can quickly analyze incoming data from various sources, including emergency calls, social media, and sensor networks, to assess situations in real-time and guide responders to the most critical areas.
This capability ensures a timely and coordinated emergency response, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
Examples of AI Applications in City-Wide Security Systems
Several cities globally have pioneered the use of AI in public safety and security, demonstrating the potential of these technologies to create safer urban environments:
- Chicago, USA: The city’s Strategic Decision Support Centers use AI and predictive analytics to identify potential crime hotspots and deploy police resources more strategically. This approach has contributed to a noticeable reduction in crime rates in areas where the technology is used.
- London, UK: London’s Metropolitan Police Service employs AI-driven facial recognition technology to identify suspects in crowded public spaces, enhancing the city’s ability to prevent and respond to criminal activities.
- Dubai, UAE: Dubai has implemented an AI-powered security system across the city, utilizing facial recognition and real-time surveillance analytics to enhance public safety. The system is part of Dubai’s brilliant city initiative, aiming to create one of the safest cities in the world.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the benefits of AI in public safety and security are evident, these technologies also raise significant ethical and privacy concerns.
Surveillance and predictive policing must be balanced with the rights of individuals to privacy and freedom from undue monitoring.
Ensuring transparency, accountability, and public oversight in deploying AI systems is crucial to addressing these challenges and maintaining public trust.
AI’s role in enhancing public safety and security within smart cities is transformative and expanding.
By leveraging AI technologies, cities can improve surveillance, emergency response, and crime prediction, contributing to safer and more secure urban environments.
However, the successful and ethical implementation of these technologies requires careful consideration of privacy, civil liberties, and community engagement.
As smart cities continue to evolve, the integration of AI in public safety operations stands as a testament to the potential of technology to protect and enhance the lives of urban residents.
4. AI in Energy and Utilities Management

Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) in energy and utility management is a game-changer for intelligent cities, driving efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in urban energy systems.
AI technologies offer innovative solutions for optimizing energy consumption, enhancing utility operations, and promoting environmental stewardship.
By leveraging AI, cities can meet the growing energy demands of urban populations and advance toward their sustainability and carbon neutrality goals.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
AI applications in energy management focus on optimizing consumption patterns across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Smart meters and AI-driven analytics platforms enable real-time energy usage monitoring and analysis, identifying inefficiencies and suggesting improvements.
AI algorithms can predict peak load times and adjust energy distribution accordingly, reducing strain on the grid and preventing outages.
Furthermore, AI-enhanced energy management systems allow for dynamic pricing, encouraging consumers to use energy during off-peak hours, flattening demand curves, and enhancing grid stability.
Promoting Renewable Energy Integration
A critical aspect of AI’s role in energy management is facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into the urban grid.
AI algorithms optimize the operation of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, by predicting weather conditions and adjusting energy production accordingly.
This capability ensures a steady and reliable supply of green energy, even under variable environmental conditions.
Additionally, AI-driven energy storage systems manage the storage and release of renewable energy, maximizing the utility of green power and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Enhancing Utility Operations
AI significantly enhances utility services’ operational efficiency.
Through predictive maintenance, AI algorithms analyze data from sensors embedded in utility infrastructure to predict potential failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespans.
Water utilities employ AI to detect leaks and manage water distribution, reducing waste and ensuring sustainable water use.
These intelligent systems improve the reliability and efficiency of utility services and contribute to substantial cost savings for providers and consumers.
Innovations in AI for Smarter Energy Use
Cities around the world are pioneering AI innovations for more intelligent energy use. For instance:
- Copenhagen, Denmark: To become carbon neutral by 2025, Copenhagen employs AI to manage its district heating system, optimizing heat production and distribution to match demand more efficiently.
- San Diego, USA: San Diego integrates AI with its public utility operations to optimize water treatment processes and energy consumption, demonstrating significant efficiency improvements and operational cost reductions.
- Tokyo, Japan: Tokyo uses AI to manage its electric grid, incorporating large-scale battery storage systems and renewable energy sources, which has enhanced grid stability and increased the use of clean energy.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI offers transformative energy and utility management potential, challenges such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and the digital divide must be addressed.
Ensuring equitable access to the benefits of AI-driven energy innovations is essential for fostering inclusive and sustainable urban development.
The role of AI in transforming energy and utility management is pivotal for the sustainability and resilience of smart cities.
By optimizing energy consumption, promoting the integration of renewable energy, and enhancing utility operations, AI technologies pave the way for more sustainable, efficient, and reliable urban energy systems.
As cities continue to innovate and implement AI solutions, the vision of sustainable and intelligent urban living becomes increasingly achievable, demonstrating the critical role of technology in shaping the future of urban energy management.
5. AI in Waste Management and Environmental Protection

Adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) in waste management and environmental protection revolutionizes how smart cities approach sustainability and ecological stewardship.
This transformative technology offers the tools to enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and foster greener urban environments.
Through AI-driven solutions, cities can tackle the challenges of waste management and environmental protection with unprecedented precision and effectiveness, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
AI-driven Solutions for Waste Collection and Recycling
AI significantly improves waste management processes by optimizing waste collection routes, schedules, and recycling processes. Intelligent waste collection systems use AI algorithms to analyze data from waste bins equipped with sensors, determining their fill levels and predicting the optimal collection times.
This ensures timely waste removal and reduces the operational costs and environmental impact associated with waste collection by minimizing unnecessary vehicle movements.
In recycling, AI-powered sorting systems enhance the efficiency and accuracy of separating recyclable materials.
These systems use machine vision and deep learning algorithms to identify, sort, and separate different types of materials at high speeds, significantly improving the recycling rate and quality of materials recovered.
This technology addresses one of the critical challenges in recycling operations – the contamination of recyclable streams – thereby promoting more sustainable waste management practices.
Monitoring Environmental Health with AI
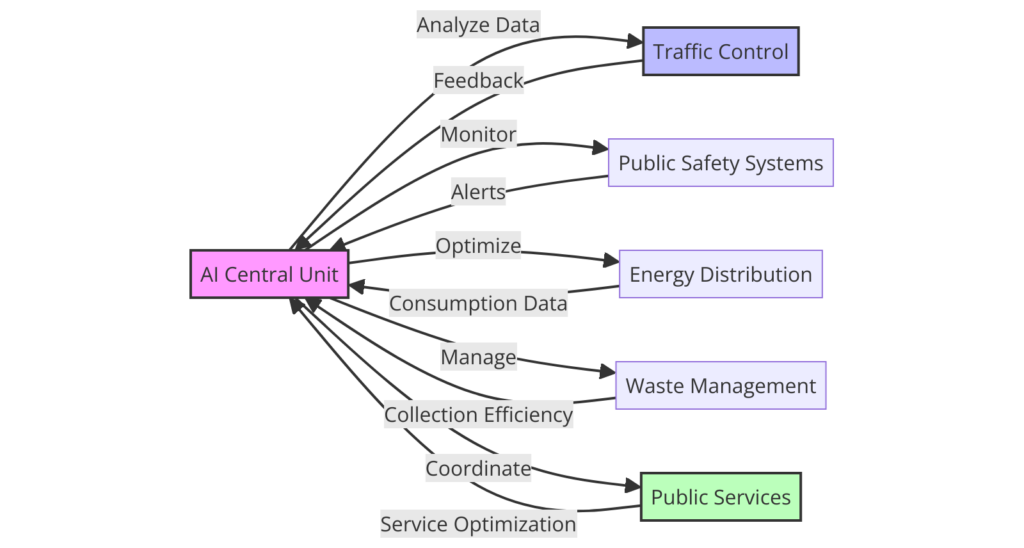
AI plays a crucial role in monitoring and protecting urban environmental health.
AI systems can detect and predict ecological hazards such as air and water pollution by analyzing data from sensors, satellites, and other monitoring devices, enabling timely interventions to mitigate their impact.
For example, AI algorithms analyze air quality data in real-time, identifying pollution sources and forecasting pollution levels, which informs policy decisions and public health advisories.
AI also contributes to biodiversity conservation efforts within urban settings. By analyzing data from camera traps, acoustic sensors, and satellite images, AI can track wildlife populations, monitor habitat changes, and identify threats to biodiversity.
This information is vital for city planners and conservationists in creating and maintaining green spaces and wildlife corridors, enhancing urban biodiversity while providing residents with valuable green spaces.
AI’s Impact on Promoting Green Practices
The integration of AI in urban environmental initiatives encourages the adoption of green practices among citizens and industries.
AI-optimized smart energy systems, which reduce emissions and efficiency, set a precedent for sustainable energy use.
Similarly, AI-driven platforms can engage citizens in sustainability efforts, offering personalized recommendations for reducing their environmental footprint, such as optimizing energy use, improving waste segregation, and promoting sustainable transportation options.
Examples of AI Applications in Urban Settings
Cities worldwide are leveraging AI to enhance their waste management and environmental protection efforts:
- Seoul, South Korea: The company implemented AI in its waste management system to optimize collection routes and schedules, significantly reducing operational costs and improving recycling rates.
- San Francisco, USA: Uses AI-powered sorting systems in recycling facilities to increase the accuracy and efficiency of material recovery, setting a benchmark for sustainable waste management practices.
- Singapore: This country employs AI for environmental monitoring, using data analytics to track air quality and water pollution levels, aiding in the swift implementation of corrective measures to protect public health and the environment.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers substantial benefits for waste management and environmental protection, it also presents challenges related to data privacy, ethical technology use, and ensuring that AI-driven solutions do not disproportionately benefit wealthier communities.
Addressing these challenges requires a balanced approach that prioritizes transparency, inclusivity, and the ethical deployment of AI technologies.
AI’s role in waste management and environmental protection is a testament to the technology’s potential to drive sustainable urban development.
AI technologies are pivotal in guiding smart cities towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future by enhancing waste collection and recycling processes, monitoring ecological health, and promoting green practices.
As urban areas continue to grow, the innovative application of AI in sustainability efforts will be crucial in ensuring the health and well-being of urban environments and their inhabitants.
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI for Smart Cities
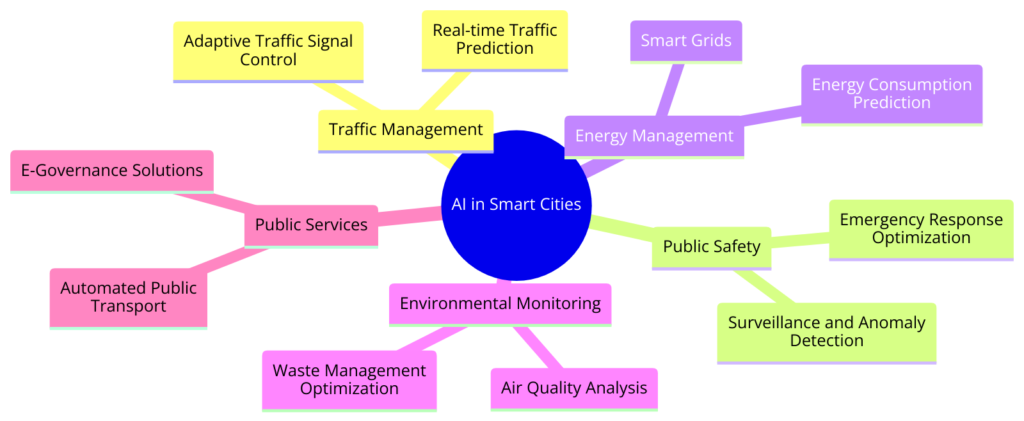
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) in smart cities heralds a new era of efficiency, convenience, and sustainability in urban management.
However, this transformation has its challenges and ethical considerations.
As cities become more innovative, deploying AI technologies raises significant concerns about privacy, data security, the digital divide, and ethical governance.
Addressing these concerns is critical to ensuring that the benefits of smart cities are realized equitably and sustainably.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns
One of the most pressing issues associated with AI in smart cities is the potential for invasive surveillance and privacy breaches.
While AI-powered surveillance systems can enhance public safety, they can also lead to a society where citizens are constantly monitored, raising concerns about individual freedom and autonomy.
Striking a balance between leveraging AI for public safety and protecting citizens’ privacy rights is a complex challenge that requires transparent policies, robust data protection measures, and strict regulations on the use of surveillance technologies.
Data Security and Protection
The vast amounts of data collected and analyzed by AI systems in smart cities are a treasure trove for insights and efficiency improvements but pose significant security risks.
Cyberattacks targeting urban infrastructure can have catastrophic consequences, from disrupting public services to compromising sensitive personal information.
Ensuring the security of AI systems and the data they process is paramount, necessitating advanced cybersecurity measures, regular audits, and a framework for rapid response to data breaches.
The Digital Divide and Inequality
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals with access to modern information and communication technology and those without.
In the context of smart cities, the benefits of AI-driven innovations could disproportionately favor those with digital access and literacy, exacerbating existing inequalities.
Ensuring that innovative city initiatives are inclusive and equitable requires targeted policies to bridge the digital divide, such as investing in digital literacy programs and providing affordable access to technology.
Ethical AI Deployment and Algorithmic Bias
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on and the objectives they are designed to achieve.
There’s a significant risk of algorithmic bias, where AI systems perpetuate or exacerbate societal biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes in areas such as policing, job recruitment, and social services.
Developing ethical guidelines for AI deployment, ensuring diversity in training datasets, and implementing transparent, accountable AI systems are crucial steps in mitigating algorithmic bias.
Governance and Public Trust
The successful implementation of AI in intelligent cities requires technological innovation, effective governance, and the public’s trust.
Establishing governance frameworks that prioritize ethical considerations, public engagement, and accountability is essential.
Public confidence can be fostered through transparent decision-making processes and stakeholder engagement, as well as by demonstrating the tangible benefits of AI technologies in improving urban living conditions.
As smart cities evolve, AI deployment’s challenges and ethical considerations become increasingly complex.
Addressing these issues requires a multidisciplinary approach involving policymakers, technologists, ethicists, and citizens to ensure that intelligent cities remain places where technology serves the public good, enhancing the quality of life without compromising individual rights or social equity.
Through careful consideration and proactive governance, the potential of AI to transform urban environments can be realized in a manner that is both ethical and beneficial for all residents.
7. The Future of AI in Smart Cities
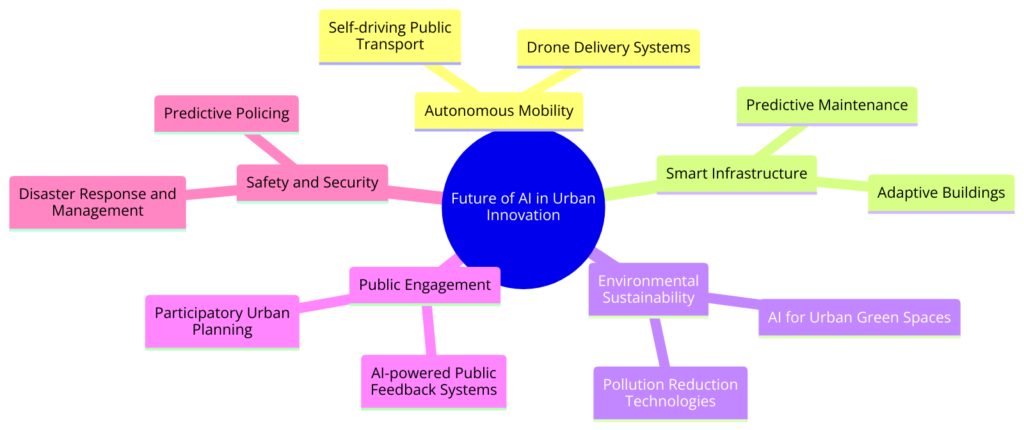
As we delve into the future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in smart cities, it’s clear that the potential for innovation and transformation is boundless.
AI is set to redefine urban living with advancements that promise to make cities more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to the needs of their residents.
The convergence of AI with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G networks, and blockchain, will further amplify its impact, driving the development of intelligent cities towards new horizons of connectivity and intelligence.
Predictions for AI-Driven Urban Evolution
The evolution of AI-powered intelligent cities is expected to usher in a new era of urban operation and experience.
Predictive analytics and machine learning models will enable cities to anticipate and mitigate challenges before they escalate, from traffic congestion and pollution to energy shortages and emergency responses.
This proactive approach to urban management will enhance the efficiency of city services and significantly improve the quality of life for urban dwellers.
AI will also play a crucial role in achieving sustainability goals.
Through optimized resource management and data-driven decision-making, smart cities will reduce their environmental footprint, embracing green energy, sustainable transportation, and waste reduction practices.
AI’s ability to analyze and optimize complex systems will be pivotal in creating urban environments that are not only technologically advanced but also harmonious with the natural world.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Several emerging trends and innovations highlight the future direction of AI in smart cities:
- Autonomous Mobility: The integration of AI in transportation will advance beyond traffic management and public transit optimization to include autonomous vehicles and drones. These self-driving modes of transport will revolutionize urban mobility, reducing congestion, improving safety, and providing innovative freight and personal transport solutions.
- Smart Infrastructure: AI will enable the development of intelligent buildings and infrastructure that are energy-efficient, resilient, and capable of self-maintenance. Through continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance, urban infrastructure will become more durable and less prone to failures, contributing to the overall sustainability of smart cities.
- Digital Twins: AI-powered digital twins—virtual replicas of physical city assets and processes—will become widespread. These models will allow city planners and administrators to simulate and analyze the impact of various policies and changes in a virtual environment before implementing them in the real world, optimizing urban development projects and policy interventions.
- AI Governance and Ethics: Developing robust governance frameworks and ethical guidelines will be critical as AI becomes more integral to urban operations. These will ensure that AI technologies are deployed responsibly, focusing on equity, privacy protection, and inclusivity, fostering trust and acceptance among urban populations.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of AI in smart cities is challenging. To realize the full potential of AI-driven urban development, data privacy, cybersecurity, and the need for significant investment in digital infrastructure must be addressed.
Moreover, the social and ethical implications of widespread AI deployment, including job displacement and surveillance concerns, will require careful management and policy responses.
However, AI presents immense opportunities for transforming urban environments. By harnessing its power, cities can become more adaptable, resilient, and capable of meeting their inhabitants’ diverse needs.
The journey towards AI-powered urban futures is one of collaboration, innovation, and shared vision, promising to redefine the essence of city living for generations to come.
The future of AI in smart cities is a canvas of immense potential, painted with the brushstrokes of innovation, sustainability, and enhanced urban life.
As technology progresses, the vision of intelligent, connected, and sustainable urban environments becomes increasingly attainable.
The challenges ahead are significant, but so are the opportunities to create cities that are not only smart in their use of technology but also in their commitment to fostering inclusive, sustainable, and enriching lives for all their residents.
8. Conclusion: The Transformative Role of AI in Developing Smart Cities
The journey through the realms of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the development of intelligent cities unveils a narrative of profound transformation and potential.
With its capacity to process vast amounts of data, learn from patterns, and make informed decisions, AI stands as a cornerstone in the evolution of urban environments into smart cities.
This journey reflects technological advancement and a shift towards more sustainable, efficient, and human-centric urban living.
AI technologies have demonstrated their transformative potential across various domains of urban development, from traffic and transportation management to public safety, energy, waste management, and environmental protection.
These applications highlight AI’s role in enhancing the efficiency of city operations, improving residents’ quality of life, and addressing some of urbanization’s most pressing challenges, including congestion, pollution, and resource management.
Moreover, the exploration of challenges and ethical considerations surrounding the deployment of AI in smart cities has underscored the importance of responsible and inclusive technology governance.
Issues such as privacy, data security, the digital divide, and algorithmic bias require ongoing attention and action from policymakers, technologists, and the public to ensure that the benefits of smart cities are accessible to all and that the integration of AI technologies aligns with societal values and ethical principles.
Looking to the future, AI’s potential in smart cities is boundless.
Emerging trends and innovations promise to revolutionize urban living further, making cities more responsive, sustainable, and resilient.
Integrating AI with other cutting-edge technologies will continue to drive advancements in urban management and service delivery, offering new solutions to old problems and opening up possibilities for enhancing urban life in ways yet to be imagined.
In conclusion, the transformative role of AI in developing smart cities is a testament to the power of technology to reshape our urban landscapes and improve the human experience.
As we move forward, it is imperative to harness this potential responsibly, ensuring that the evolution of smart cities remains focused on creating inclusive, sustainable, and livable environments for all.
The journey of integrating AI into the fabric of urban development is complex and fraught with challenges.
Still, the vision it offers—a future where cities are intelligent, efficient, and tailored to the needs of their inhabitants—is a compelling motivation to continue pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Encouraging the responsible and sustainable integration of AI in urban planning and development is not just a technological imperative but a moral one, promising a brighter future for cities and their residents around the globe.
FAQ & Answers
1. How is AI used in smart cities?
AI is used to enhance urban living through traffic management, public safety, energy and waste management, contributing to more sustainable and efficient cities.
2. What are the challenges of implementing AI in smart cities?
Challenges include ensuring citizen privacy, securing data, and overcoming technological and infrastructure inequalities.
Quizzes
Quiz 1: “AI in Urban Solutions” – Match AI technologies to their smart city applications.
For this quiz, you’ll need to match AI technologies to specific applications within smart city contexts. Here are the AI technologies and their potential urban applications:
AI Technologies:
A. Predictive Analytics
B. Facial Recognition
C. Autonomous Vehicles
D. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
E. IoT (Internet of Things) IntegrationSmart City Applications:
- Enhancing public transportation systems for efficiency and safety.Monitoring energy consumption and optimizing usage across city infrastructures.Improving emergency response times through better resource allocation.Enhancing citizen engagement through digital platforms.Increasing public safety and security in crowded areas.
Match each AI technology (A-E) with its corresponding smart city application (1-5).
Here are the matches between the AI technologies and their smart city applications:
A. Predictive Analytics – 3. Improving emergency response times through better resource allocation.
Predictive analytics can analyze historical data and real-time information to forecast where emergencies are likely to occur, enabling quicker and more effective deployment of emergency services.
B. Facial Recognition – 5. Increasing public safety and security in crowded areas.
Facial recognition technology can be used in surveillance systems to identify persons of interest in real-time, enhancing safety and security in public spaces.
C. Autonomous Vehicles – 1. Enhancing public transportation systems for efficiency and safety.
Autonomous vehicles, including buses and taxis, can improve the efficiency and safety of public transportation systems by reducing human error and optimizing routes.
D. Natural Language Processing (NLP) – 4. Enhancing citizen engagement through digital platforms.
NLP enables digital platforms, such as city service chatbots and information kiosks, to understand and respond to citizen inquiries in natural language, improving access to city services.
E. IoT (Internet of Things) Integration – 2. Monitoring energy consumption and optimizing usage across city infrastructures.
IoT devices can collect data on energy usage across various city infrastructures, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization to reduce energy waste and enhance sustainability.
These matches illustrate how AI technologies are applied to address specific challenges in smart cities, from improving emergency services and public transportation to enhancing energy efficiency and citizen engagement.
Quiz 2: “Smart Cities Around the World” – A quiz on global cities leading in AI-driven smart city innovations.
Let’s explore some global cities recognized for their leadership in AI-driven smart city innovations. For each city description, try to guess the city based on its AI initiatives and smart city projects:
- City A: This Asian city is a pioneer in smart city technology, known for its “Safe City” project that utilizes AI for public safety, efficient traffic management systems, and has one of the world’s most advanced public transportation systems, integrating real-time data analysis to enhance commuter experiences.
- City B: Located in the United States, this city is at the forefront of integrating autonomous vehicles into its transportation network. It’s also known for its robust open data initiative, allowing developers to create solutions that address urban challenges such as traffic congestion and public safety.
- City C: A European city renowned for its “smart lighting” street lamps that adjust based on pedestrian and vehicle traffic, significantly reducing energy consumption. It also employs AI-driven tools for environmental monitoring, targeting improvements in air and water quality.
- City D: This Middle Eastern city is aiming to become the smartest in the world, with initiatives like AI-powered health services, blockchain for government transactions, and ambitious plans for autonomous transportation, including flying taxis.
- City E: In Southeast Asia, this city-state is a leader in smart urban solutions, with a focus on AI for predictive healthcare, smart eldercare solutions, and an extensive network of sensors and cameras to monitor everything from cleanliness to traffic conditions.
Identify the cities based on the descriptions of their AI-driven smart city innovations.
Based on the descriptions of their AI-driven smart city innovations, here are the cities:
- City A: This is likely Singapore. Singapore is well-known for its advanced use of technology in urban management, including public safety, traffic management, and public transportation, making it a model for smart cities globally.
- City B: This city could be San Francisco. As a hub of technology and innovation in the United States, San Francisco has been at the forefront of adopting autonomous vehicles and leveraging open data to solve urban issues.
- City C: This sounds like Amsterdam in the Netherlands. Amsterdam has been a leader in smart city initiatives, including smart lighting to reduce energy use and innovative projects to improve environmental sustainability.
- City D: This is likely Dubai in the United Arab Emirates. Dubai has set ambitious goals to lead in smart city technology, with projects ranging from blockchain for secure government transactions to plans for autonomous flying taxis.
- City E: This describes Singapore again, known for its comprehensive use of sensors and AI in various domains, including healthcare and urban management. Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative exemplifies its commitment to becoming a global leader in smart urban solutions.
These cities are recognized for leveraging AI and other technologies to improve urban living, showcasing the potential of smart city innovations to address challenges ranging from transportation and public safety to environmental sustainability and healthcare.
