AI in Governance stands as a beacon of transformation across various sectors, with governance and regulatory frameworks being no exception. Integrating AI in these areas enhances and revolutionizes public administration functions and policies, redefining them. As we embark on this exploration, it’s crucial to understand AI’s multifaceted role in governance and its profound implications for regulatory practices.
1. The Role of AI in Governance and Regulatory Frameworks

Overview of AI in Governance and Regulatory Frameworks
With its unparalleled data processing capabilities and advanced analytical prowess, AI offers unique solutions to longstanding challenges in governance.
It aids in automating administrative processes, facilitates accurate and efficient analysis of large data sets, and provides predictive insights to guide policy and decision-making.
This technological advancement enables governments to respond more swiftly and effectively to their constituents’ needs, improving service delivery and increasing public satisfaction.
Moreover, AI’s role extends beyond mere administrative efficiency.
It plays a critical part in regulatory compliance and monitoring, where it can sift through vast amounts of data to identify potential violations or areas of concern, thereby enhancing the enforcement of laws and regulations.
This capability is particularly beneficial in sectors like finance, healthcare, and environmental protection, where compliance with regulatory standards is paramount.
The Importance of AI in Governance and Policy-making
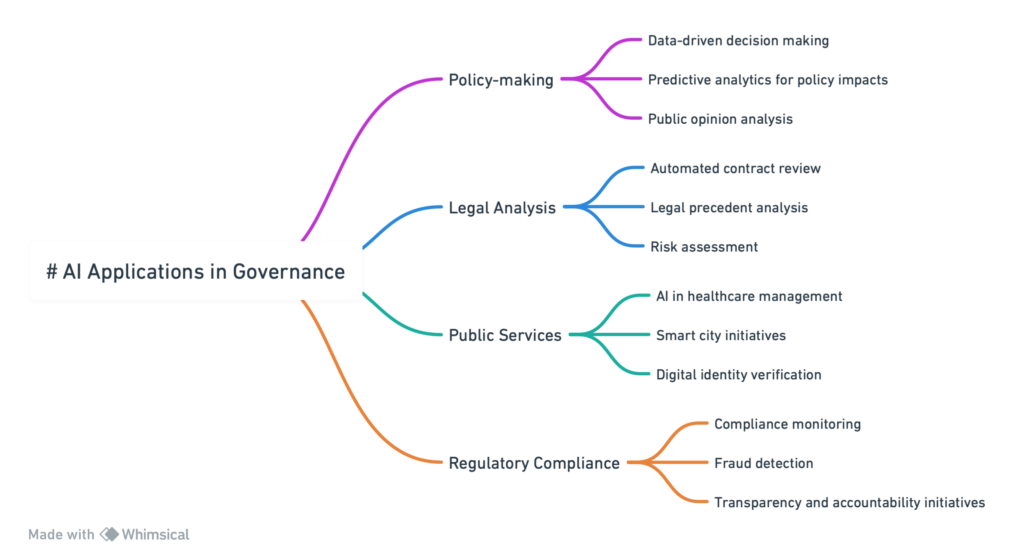
The significance of AI in Governance and policymaking cannot be overstated.
By harnessing AI, governments can achieve a level of insight and efficiency previously unattainable.
AI-driven data analysis helps uncover patterns and trends that inform policy development, ensuring that decisions are based on solid evidence and comprehensive analysis.
Furthermore, AI can simulate the potential impacts of policy options, providing policymakers with a valuable tool for evaluating the consequences of their decisions before implementation.
AI’s contributions to public administration also extend to enhancing transparency and accountability.
Through AI in Governance can offer citizens more personalized and accessible services, fostering a sense of inclusivity and participation in public affairs.
Additionally, AI applications can improve the tracking and reporting of governmental actions, allowing for greater scrutiny and public oversight.
However, integrating AI into governance is challenging.
Issues related to privacy, data security, ethical considerations, and the digital divide must be addressed to ensure that AI’s benefits are accessible to all and that its use does not inadvertently exacerbate existing inequalities or introduce new forms of bias.
The advent of AI in governance and regulatory frameworks marks a pivotal shift towards more efficient, transparent, and responsive public administration.
Its potential to transform policy-making, enhance service delivery, and ensure regulatory compliance is immense.
However, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of AI’s ethical and social implications, as well as strategic investments in technology and human capital.
As we dive deeper into AI in Governance application in public service delivery, regulatory compliance, policymaking, and beyond, it’s clear that AI is not just a tool for innovation but a cornerstone for the future of adequate and equitable governance.
2. AI in Public Service Delivery

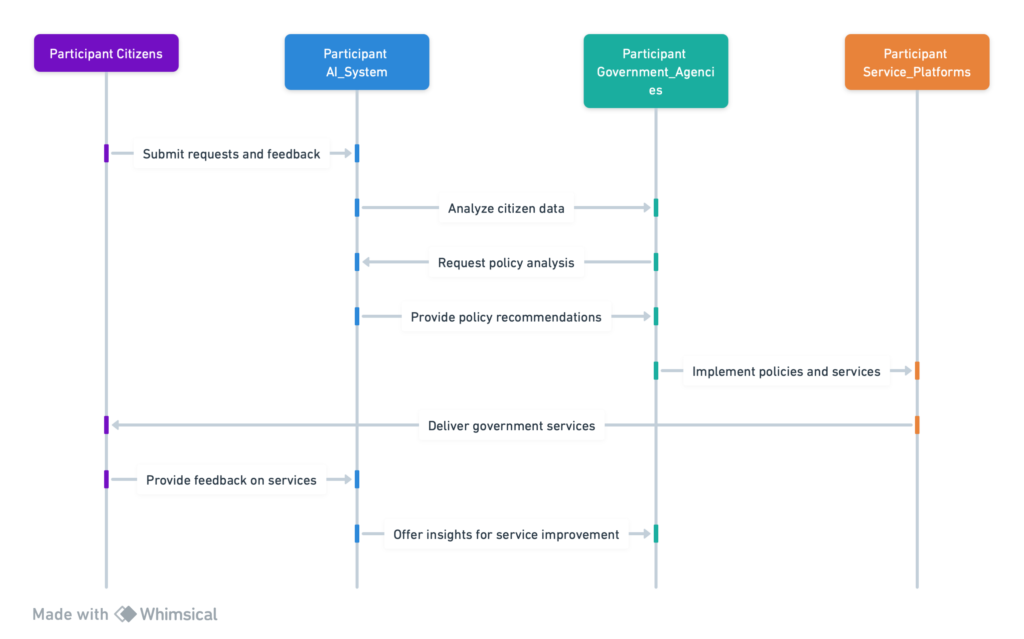
The application of AI in Governance in public service delivery signifies a monumental shift towards more efficient, effective, and citizen-centric governance.
This transformative technology redefines the interface between governments and citizens, promising a future where public services are more accessible, personalized, and responsive.
Through the lens of AI, we explore its impact on enhancing the delivery of public services, illustrated by compelling case studies that showcase the innovative use of AI in public service initiatives.
Enhancing Efficiency and Effectiveness in Public Services
AI in Governance, with their ability to process and analyze data at unprecedented speeds and scale, are instrumental in streamlining government operations.
By automating routine tasks, AI frees up valuable resources, allowing public servants to focus on complex issues requiring human judgment and empathy.
Moreover, AI-driven analytics enable governments to predict service demand, optimize resource allocation, and identify bottlenecks in service delivery, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and effectiveness.
The use of AI in Governance also enhances the customer experience.
Through natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide citizens with 24/7 access to information and services, answer inquiries, and assist with transactions in multiple languages.
This not only increases accessibility but also reduces waiting times and improves overall satisfaction with public services.
Case Studies of AI-driven Public Service Initiatives
- AI in Healthcare: In various countries, AI has been deployed to improve public health services. For instance, AI algorithms are used to analyze medical imaging, helping doctors diagnose diseases such as cancer more accurately and swiftly. Additionally, AI-driven platforms have been developed to predict outbreaks of infectious diseases, enabling governments to take proactive measures in public health management.
- Smart Cities Initiatives: Many cities worldwide use AI to enhance urban living. AI is used in traffic management systems to analyze real-time traffic data, optimize traffic flow, and reduce congestion. Similarly, AI-powered waste management systems ensure efficient trash collection, while intelligent lighting systems adjust street lighting based on pedestrian and vehicle movement, conserving energy and improving safety.
- Social Welfare Distribution: AI is revolutionizing how social welfare programs are administered, ensuring that assistance reaches those in need more efficiently. By analyzing data from various sources, AI systems can identify eligible beneficiaries, predict their needs, and streamline aid distribution, reducing fraud and ensuring a more equitable distribution of resources.
- Education: AI applications in education provide personalized learning experiences to students, adapting to their learning pace and style. AI-driven platforms offer tutoring and support outside the classroom, identify learning gaps, and provide teachers with insights to improve their instructional methods, enhancing educational outcomes.
Integrating AI in Governance delivery is not just about technological advancement; it’s about reimagining how governments interact with and serve their citizens.
These case studies exemplify the potential of AI to make public services more accessible, efficient, and tailored to the population’s needs.
However, the successful implementation of AI in public services requires careful planning, ethical considerations, and ongoing evaluation to ensure that the benefits are equitably distributed and that the technology serves the public good.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in public service delivery promises to expand, offering new opportunities to enhance the quality and accessibility of government services, making a tangible difference in the lives of citizens worldwide.
3. AI in Regulatory Compliance and Monitoring

The deployment of AI in Governance in regulatory compliance and monitoring represents a pivotal advancement in ensuring adherence to laws and standards across various industries.
By harnessing the power of AI, regulatory bodies and businesses can automate the complex and labor-intensive processes of monitoring compliance, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of regulatory enforcement.
AI’s Role in Monitoring Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
AI technologies, through their ability to process vast quantities of data rapidly and identify patterns, are uniquely positioned to revolutionize regulatory compliance.
Machine learning algorithms can sift through millions of documents, transactions, and activities to detect anomalies or deviations from regulatory norms, flagging potential non-compliance for human review.
This capability speeds up the compliance monitoring process and significantly reduces the risk of oversight and human error.
In addition to monitoring, AI systems can predict areas of potential non-compliance before they become problematic.
By analyzing trends and patterns in data, AI can alert organizations to the risks of future violations, allowing for preemptive corrective measures.
This predictive aspect of AI ensures higher compliance levels and fosters a more proactive approach to regulatory adherence.
Examples of AI in Financial and Environmental Regulations
- Financial Regulations: AI is critical in combating fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes in the financial sector. For example, AI systems analyze real-time transaction data, identifying suspicious activities that may indicate money laundering or fraud. These systems can learn from historical data to continually improve their detection capabilities, making them invaluable tools for financial institutions seeking to comply with stringent regulatory requirements.
- Environmental Regulations: AI is also making strides in enforcing environmental regulations. AI-powered drones and satellite imagery monitor deforestation, illegal mining, and pollution levels in real-time, providing environmental regulators with accurate and up-to-date information on potential violations. Furthermore, AI algorithms can analyze data from various sources to predict environmental impacts, aiding in developing and enforcing regulations to protect natural resources and mitigate climate change.
The application of AI in regulatory compliance and monitoring is a testament to the technology’s potential to transform traditional approaches to governance and oversight.
By automating the detection of non-compliance and enhancing the predictive capabilities of regulatory bodies, AI improves the efficiency and accuracy of regulatory enforcement and contributes to a more transparent and accountable regulatory environment.
As AI in Governance evolve, their integration into regulatory practices is expected to deepen, offering new opportunities for innovation in compliance monitoring.
However, the successful adoption of AI in this domain requires careful consideration of ethical and privacy concerns and the development of robust frameworks to ensure the responsible use of AI in regulatory processes.
4. AI in Policy-making and Decision Support

AI in Governance into policy-making and decision-support systems marks a significant leap forward in how governments and public administrations approach governance and public service delivery.
By leveraging AI’s data processing and analytical capabilities, decision-makers can access insights and foresight that were previously unattainable, enabling more informed, evidence-based policy decisions.
Utilizing AI for Data-driven Policy-making and Governance Decisions
AI technologies facilitate the analysis of large datasets, allowing policymakers to understand complex patterns, trends, and relationships within the data.
This deep analysis supports evidence-based policy-making, where decisions are guided by empirical data rather than intuition or precedent.
Machine learning models, for example, can predict the outcomes of various policy options on social, economic, and environmental levels, providing a solid foundation for making informed governance decisions.
In addition to supporting decision-making, AI tools can enhance public engagement in the policy-making process.
Analyzing sentiment on social media and other digital platforms, AI algorithms can gauge public opinion on policy issues, enabling governments to align their strategies more closely with their constituents’ needs and preferences.
Innovations in AI for Urban Planning and Public Policy
- Urban Planning: AI revolutionizes urban planning through predictive modeling and simulation techniques. These tools allow urban planners to visualize the impact of different development projects on traffic flow, housing, and public services, among other factors. AI-driven analytics also support sustainable urban development by optimizing resource allocation, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing environmental impact.
- Public Safety and Security: AI applications in public safety, such as predictive policing, help allocate law enforcement resources more efficiently, targeting areas at higher risk of crime based on historical data and trend analysis. Similarly, AI-driven disaster management systems can predict natural disasters more accurately, enabling preemptive evacuations and resource deployment to mitigate the impact on affected communities.
- Environmental Policy: In ecological policy, AI tools monitor climate change indicators, model the effects of environmental policies, and predict the outcomes of conservation efforts. This information is crucial for developing policies that effectively address ecological challenges, promote sustainability, and protect natural resources.
- Healthcare Policy: AI is instrumental in shaping healthcare policies by analyzing health trends, disease spread patterns, and the effectiveness of public health interventions. AI-driven models can forecast future healthcare needs, helping policymakers allocate resources efficiently and develop strategies to improve public health outcomes.
AI in Governance role in policy-making and decision support showcases its potential to transform traditional governance models into more dynamic, responsive, and efficient systems.
By harnessing AI’s predictive analytics and data-driven insights, policymakers can address the complex challenges of modern society more effectively.
Innovations in AI offer promising avenues for enhancing urban planning, public safety, environmental sustainability, and healthcare, among other areas.
However, successfully integrating AI into policy-making processes requires a commitment to ethical standards, data privacy, and public engagement.
As AI continues to evolve, its contribution to informed governance and policy decisions is set to increase, paving the way for more adaptive and resilient public administration practices.
5. AI in Legal and Judicial Systems

Infusing AI in Governance into the legal and judicial systems presents a transformative shift towards more efficient, accessible, and equitable justice delivery mechanisms.
The legal profession and judiciary can streamline operations, enhance case management, and improve decision-making processes by leveraging AI’s data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics capabilities.
AI Applications in Legal Research and Case Analysis
AI technologies have significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of legal research. Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms can sift through vast legal databases to find relevant case law, statutes, and legal precedents in a fraction of the time it would take a human researcher.
This capability speeds up the legal research process and ensures a more comprehensive review of pertinent legal materials, aiding lawyers in building more substantial cases.
Furthermore, AI tools are used for predictive legal analysis, where machine learning models evaluate the outcomes of similar cases to predict the potential success of legal arguments in court.
This application of AI assists legal professionals in strategizing more effectively, guiding the selection of cases to pursue, and informing settlement decisions.
AI in Court Proceedings
AI in Governance impact extends to the courtroom, where it supports judges and legal practitioners in managing caseloads and streamlining court procedures.
AI-driven document analysis tools help organize and summarize case files, making it easier for judges to navigate complex information and for lawyers to prepare their cases.
Moreover, some jurisdictions are experimenting with AI-powered tools to assist in evaluating evidence and making procedural decisions.
However, the latter is approached with caution to ensure fairness and transparency.
AI technologies also reduce the backlog of cases in many judicial systems by automating routine tasks and enabling virtual court proceedings.
This expedites case resolution and makes justice more accessible, especially in remote areas with limited physical court infrastructure.
The Potential of AI for Enhancing Justice Delivery
The adoption of AI in Governance legal and judicial systems holds promise for enhancing justice delivery in several ways.
Firstly, it can improve legal access by providing low-cost or free legal assistance through AI-powered platforms, making legal advice more accessible to underserved populations.
Secondly, AI can contribute to more consistent and unbiased legal decisions by providing judges and lawyers with comprehensive data analysis and precedent-based recommendations.
However, using AI in legal and judicial contexts is challenging.
Concerns about algorithmic bias, transparency in AI decision-making processes, and the need for legal professionals to understand and interpret AI outputs critically are paramount.
Ensuring the ethical use of AI in legal practices requires ongoing scrutiny, regulatory oversight, and the development of standards and guidelines that prioritize fairness and justice.
AI’s integration into the legal and judicial systems heralds a new era of justice delivery characterized by efficiency, accessibility, and potentially greater fairness.
From legal research and case analysis to courtroom proceedings and beyond, AI applications are reshaping the legal profession and judiciary landscape.
As these technologies evolve, so will their impact on legal practices, offering opportunities and challenges in pursuing justice.
Ensuring that AI’s use in legal contexts upholds the principles of transparency, fairness, and accessibility will be crucial in realizing its full potential to enhance justice delivery for all.
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-driven Governance

As AI in Governance continues to permeate various aspects of governance and public administration, it brings to light many challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed to harness its potential responsibly.
Applying AI in governance offers transformative possibilities for efficiency, decision-making, and service delivery.
However, these advancements also raise significant concerns regarding transparency, accountability, public trust, and the ethical use of technology.
Addressing Issues of Transparency, Accountability, and Public Trust
One of the paramount challenges in AI-driven governance is ensuring transparency and accountability, particularly given the often opaque nature of AI algorithms.
The “black box” problem, where humans do not easily understand the decision-making processes of AI systems, poses a significant hurdle to public accountability.
With clear insights into how AI makes decisions, it becomes easier to ensure these systems are fair, unbiased, and serving the public interest.
Moreover, using AI in Governance raises questions about public trust.
For AI to effectively integrate into governance, citizens must trust that AI systems are reliable, decisions are made fairly, and personal data is handled securely and ethically.
Establishing this trust requires robust mechanisms for transparency, oversight, and engagement with the public on how AI is used in governance.
Ethical Considerations in AI-driven Governance
Ethical considerations are at the core of responsibly integrating AI into governance.
These include privacy concerns, as AI systems often rely on large datasets that may contain sensitive personal information.
Ensuring the ethical use of data, with respect for privacy and consent, is crucial in maintaining public trust.
Bias and discrimination present another ethical challenge.
AI systems can perpetuate or even amplify existing biases if trained on biased data sets or if their algorithms inadvertently discriminate against certain groups.
Addressing these issues requires ongoing efforts to develop fair, equitable, and inclusive AI.
As AI takes over specific administrative tasks, the risk of automation-related job displacement in the public sector also warrants ethical consideration.
Developing strategies to manage this transition, such as retraining programs and policies to support affected workers, is essential for integrating AI into governance.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Ethical AI Use
To overcome these challenges and ensure the ethical use of AI in governance, several strategies can be employed:
- Developing Clear Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing regulations that set standards for transparency, accountability, and ethical AI use in governance is critical. These frameworks should also include provisions for regular auditing and assessment of AI systems to ensure compliance with ethical standards.
- Promoting Public Engagement: Engaging with citizens about using AI in governance can help build trust and ensure that deploying AI technologies aligns with public values and expectations. This engagement can include public consultations, transparency reports, and educational initiatives.
- Investing in Ethical AI Research: It is vital to support research into ethical AI development, including methods for enhancing algorithmic transparency and fairness. This research can inform the creation of AI systems that are not only effective but also respect human rights and democratic values.
- Implementing Bias Mitigation Strategies: Actively working to identify and mitigate biases in AI systems through diverse training data, bias detection algorithms, and inclusive design practices is essential for fair and equitable AI applications in governance.
Integrating AI into governance and public administration presents a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges.
While the potential of AI in Governance is immense, realizing this potential in an ethical, transparent, and accountable way is paramount.
Addressing the ethical considerations and challenges associated with AI-driven governance requires a concerted effort from policymakers, technologists, and the public.
By developing robust frameworks for ethical AI use, engaging with citizens, and investing in research, we can navigate these challenges and ensure that AI serves the public good, enhancing the efficiency and equity of governance for all.
7. The Future of AI in Governance and Regulations
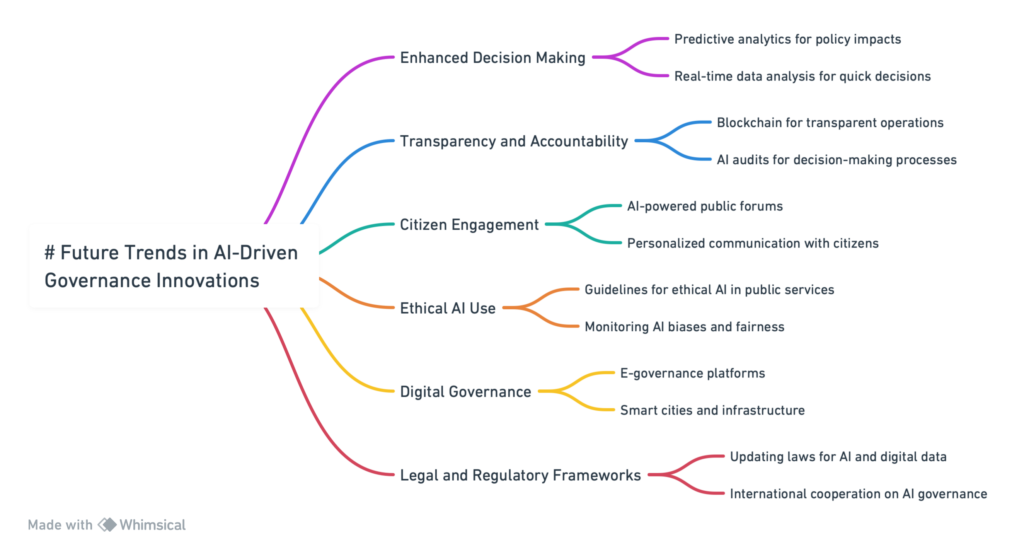
The future of AI in Governance and regulatory frameworks is poised at the brink of transformative change.
As AI technologies evolve and mature, their role in public administration, policy-making, and regulatory compliance will expand significantly.
This expansion promises to bring about profound shifts in how governments operate, make decisions, and interact with citizens.
Predictions for AI’s Evolving Role in Public Administration
- Advanced Decision Support Systems: AI is expected to become increasingly sophisticated in providing decision support for policymakers. Leveraging vast datasets and complex algorithms, AI will offer deeper insights and more accurate predictions about the outcomes of policy decisions, enabling more informed and strategic governance.
- Automated Regulatory Compliance: Automating regulatory monitoring and compliance through AI will likely become more widespread. AI systems will be capable of continuously scanning data to ensure adherence to regulations, significantly reducing the burden on businesses and increasing the efficiency of regulatory enforcement.
- Enhanced Public Engagement: AI will be crucial in transforming public engagement mechanisms. Through natural language processing and machine learning, governments will be able to understand better and respond to the needs and concerns of citizens, fostering a more participative and responsive democratic process.
- Personalized Public Services: The future will see a more customized approach to public service delivery, where AI tailors services to citizens’ individual needs and preferences. This personalization will improve service accessibility and satisfaction, making government services more user-centric.
Emerging Trends and Potential Future Developments
- Integration with Blockchain and IoT: Integrating AI with other cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in governance. For example, blockchain could secure AI-driven transactions and decisions, while IoT devices could provide real-time data for AI analysis in urban planning and environmental monitoring.
- Ethical and Explainable AI: As the implications of AI’s decisions become more critical, there will be a growing emphasis on developing ethical and explainable AI systems. These systems will be designed to make decisions that are not only effective but also transparent and understandable to humans, ensuring accountability and ethical integrity.
- AI in Crisis Management and Resilience Planning: AI’s role in managing public crises, such as pandemics and natural disasters, will expand. By analyzing data from multiple sources, AI can help predict crises, optimize response strategies, and manage resources efficiently, enhancing public safety and resilience.
- Global AI Governance Frameworks: The increasing use of AI in governance will necessitate the development of global frameworks and standards for AI ethics, transparency, and interoperability. Such frameworks will facilitate international cooperation and ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and beneficially across borders.
Exciting opportunities and significant challenges mark the future of AI in governance and regulations.
As AI technologies become more integrated into the fabric of public administration, they promise to make management more efficient, transparent, and responsive to the needs of citizens.
However, realizing this potential will require careful attention to ethical considerations, developing robust regulatory frameworks, and ongoing dialogue among stakeholders to ensure that AI’s benefits are maximized while its risks are mitigated.
By embracing innovation and prioritizing the public good, governments can leverage AI to foster a more equitable, effective, and forward-looking approach to governance and regulatory compliance.
8. Conclusion: AI’s Transformative Potential in Governance and Regulatory Sectors
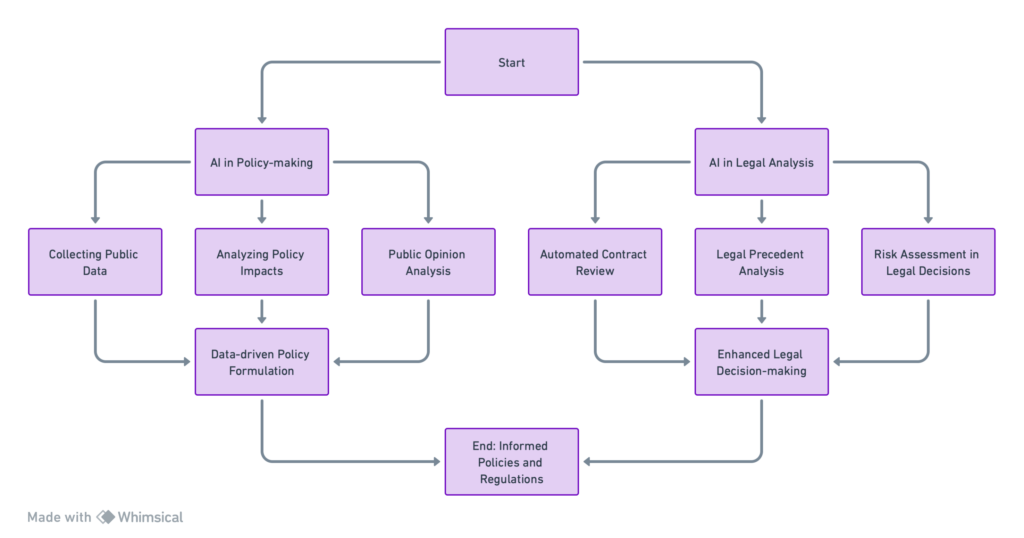
The exploration of AI in Governance and regulatory frameworks has unveiled its vast potential to revolutionize public administration, policy-making, and regulatory compliance.
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in governance, marked by technological innovation and digital transformation, AI emerges as a pivotal force in reshaping how governments operate and interact with citizens.
This concluding section recaps the transformative impact of AI across various facets of governance and emphasizes the importance of responsible and ethical AI integration in public administration.
AI’s integration into public service delivery has demonstrated its ability to enhance efficiency, effectiveness, and accessibility, offering personalized services that meet the evolving needs of citizens.
In regulatory compliance and monitoring, AI has proven indispensable in ensuring adherence to laws and regulations, automating non-compliance detection, and fostering a more transparent and accountable regulatory environment.
Moreover, AI’s role in policy-making and decision support has shown that data-driven insights can lead to more informed and strategic governance decisions, facilitating evidence-based policy development responsive to societal needs.
In the legal and judicial systems, AI applications have streamlined processes, improved access to justice, and promised more equitable and efficient justice delivery mechanisms.
However, the journey toward AI in Governance has its challenges.
Issues of transparency, accountability, public trust, and ethical considerations remain at the forefront of discussions on AI’s role in public administration.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from policymakers, technologists, and the public to develop frameworks that ensure the responsible use of AI, prioritizing ethical standards, data privacy, and inclusivity.
As we look to the future, AI in Governance and regulations is boundless.
Emerging trends, such as the integration of AI with blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT), predict a governance landscape that is more transparent, secure, and efficient.
Yet, realizing this potential hinges on our ability to navigate AI’s ethical and societal implications, fostering an environment where technology serves the public good and enhances the quality of governance for all.
In conclusion, AI holds a transformative promise for the governance and regulatory sectors, offering opportunities to improve public services, enhance policy-making, and streamline regulatory compliance.
Encouraging AI’s responsible and ethical integration in public administration is crucial in harnessing its full potential while safeguarding democratic values and ensuring equitable benefits for society.
As we embrace the advancements of AI in Governance, it is imperative to remain vigilant in addressing the challenges it poses, guiding the evolution of public administration toward a more efficient, transparent, and inclusive future.
FAQ & Answers
1. How is AI in Governance and regulations used?
AI is used to enhance public service delivery, ensure regulatory compliance, support policy-making, and streamline legal and judicial processes.
2. What are the challenges of implementing AI in governance?
Challenges include maintaining transparency, ensuring public accountability, ethical considerations, and managing the balance between AI and human decision-making.
Quizzes
Quiz 1: “AI in Public Administration” – Identify AI applications in governance scenarios.
Let’s examine how AI technologies are being applied within the public administration and governance. Your task is to identify the specific AI application or technology used in each scenario presented below:
- Predictive Policing: A city’s police department utilizes an AI system that analyzes historical crime data and patterns to predict future crime hotspots. This system helps in allocating resources more effectively and in planning preventive measures in areas with a higher predicted crime rate.
- Smart Traffic Management: An AI-driven system in a metropolitan area analyzes real-time traffic data from cameras, sensors, and GPS devices to optimize traffic flow. It adjusts traffic signals dynamically, reduces congestion, and improves overall city mobility.
- Automated Public Service Delivery: A government agency deploys an AI-powered platform that automates the processing of routine public service requests, such as issuing permits, renewing licenses, and providing welfare benefits. This system improves service efficiency and reduces wait times for citizens.
- Environmental Monitoring and Protection: An AI application analyzes satellite imagery and environmental data to monitor changes in land use, deforestation rates, and the health of natural resources. This technology helps in enforcing environmental protection laws and planning conservation efforts.
- Public Health Surveillance: An AI system uses data from healthcare providers, pharmacies, and social media to detect early signs of disease outbreaks. This early warning system allows health authorities to respond more swiftly to public health threats and manage resources more effectively.
- E-Government Services Personalization: A government website employs AI to personalize the user experience based on their browsing history and interactions. It recommends relevant services, provides timely reminders for document renewals, and offers customized information, making the government’s digital services more user-friendly.
Identify the AI applications or technologies used in each of these public administration scenarios.
Here are the AI applications or technologies being used in the public administration scenarios:
- Predictive Policing: The technology is AI-powered Predictive Analytics. It’s used to analyze crime data and identify patterns that help predict where and when future crimes might occur, allowing for more strategic allocation of police resources and preventive measures.
- Smart Traffic Management: This scenario employs AI-driven Traffic Optimization Systems. By analyzing real-time data from various sources, these systems dynamically manage traffic flow, adjust traffic signals, and reduce congestion, enhancing urban mobility.
- Automated Public Service Delivery: The application is AI-based Process Automation for government services. This platform automates routine tasks and processes in public service delivery, such as issuing permits and renewing licenses, improving efficiency and reducing wait times for citizens.
- Environmental Monitoring and Protection: This technology involves AI and Satellite Image Analysis for environmental monitoring. AI algorithms analyze satellite imagery and environmental data to track changes in ecosystems, detect deforestation, and monitor the health of natural resources, supporting conservation and environmental protection efforts.
- Public Health Surveillance: The system uses AI in Public Health Data Analysis. By gathering and analyzing data from various sources, the AI system detects early signs of disease outbreaks, providing health authorities with early warnings to enable quicker and more effective responses to public health threats.
- E-Government Services Personalization: This scenario utilizes AI for Personalization of Digital Government Services. An AI-powered government website personalizes user experiences by recommending relevant services, providing reminders, and customizing information based on users’ browsing history and interactions, making digital services more accessible and user-friendly.
Each of these AI applications demonstrates the potential to enhance efficiency, responsiveness, and decision-making in public administration, contributing to smarter governance and improved public services.
Quiz 2: “AI and Policy-making” – A quiz on AI’s role in data-driven policy decisions.
For this quiz, we’ll explore how AI is used to support data-driven policy-making. Try to identify the specific role or application of AI in the following scenarios related to policy decisions:
- Urban Planning and Development: AI analyzes data from various sources, including population density, traffic patterns, and housing data, to assist urban planners in making informed decisions about where to build new infrastructure, such as roads, parks, and residential areas, to best meet the needs of the community.
- Educational Policy Formulation: By processing data on student performance, attendance rates, and resource allocation across different schools, AI helps identify gaps and opportunities in the education system. This information aids policymakers in developing targeted interventions to improve educational outcomes and equity.
- Healthcare Resource Allocation: AI models predict future healthcare demands based on demographic trends, disease prevalence, and healthcare usage patterns. These predictions enable health authorities to allocate resources more efficiently, plan for future healthcare facilities, and ensure accessibility to medical services for all population segments.
- Environmental Regulation and Compliance: Using AI to analyze environmental data, including pollution levels, water quality, and industrial emissions, governments can identify areas of non-compliance with environmental regulations. This supports the development of more effective policies and enforcement strategies to protect natural resources.
- Social Welfare Programs Optimization: AI analyzes data from social welfare programs to identify patterns of need and the effectiveness of various interventions. This analysis helps in optimizing the allocation of resources to social programs, ensuring that support reaches those most in need and enhances the overall impact of social welfare policies.
- Public Safety and Emergency Response: AI-driven simulations and data analysis predict the impact of natural disasters and public safety incidents, aiding in the development of response strategies and emergency preparedness plans. This helps minimize risks to public safety and ensures a coordinated response to emergencies.
Identify how AI contributes to data-driven policy-making in each of these scenarios.
Here’s how AI contributes to data-driven policy-making in each scenario:
- Urban Planning and Development: AI’s role is in Data Analysis for Urban Planning. It synthesizes complex datasets to help planners understand urban dynamics and make evidence-based decisions on infrastructure development, optimizing city growth and enhancing the quality of life for residents.
- Educational Policy Formulation: AI assists in Analyzing Educational Data to identify disparities and areas needing improvement. By evaluating student performance and resource distribution, AI informs policies aimed at closing educational gaps and enhancing learning outcomes across different demographics.
- Healthcare Resource Allocation: Through Predictive Modeling in Healthcare Planning, AI forecasts future health service demands, enabling policymakers to strategically allocate resources, plan new facilities, and ensure equitable healthcare access, thus improving public health preparedness and response.
- Environmental Regulation and Compliance: AI aids in Environmental Monitoring and Policy Enforcement by analyzing data on pollution and natural resource usage. This supports the creation of more effective environmental policies and regulations, ensuring compliance and protecting the environment.
- Social Welfare Programs Optimization: The application of AI in Social Program Analysis optimizes resource distribution by identifying the most effective interventions and areas of highest need. This ensures that social welfare programs are more impactful and resources are allocated where they can make the most difference.
- Public Safety and Emergency Response: AI’s role in Emergency Preparedness and Response Planning involves using simulations and data analytics to predict and plan for natural disasters and public safety incidents. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks, save lives, and ensure a rapid, coordinated emergency response.
In each scenario, AI acts as a powerful tool for analyzing vast amounts of data, providing insights that inform policy decisions, and enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of public services and interventions.