
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) as a potent force reshaping every facet of human life brings with it a spectrum of ethical considerations that are as complex as they are critical. The intersection of AI with ethics is not merely an academic discourse but a practical necessity, as the decisions made by AI systems increasingly influence the social fabric, economy, and individual lives. The importance of ethics in AI development and deployment cannot be overstated; it underpins the trustworthiness, fairness, and societal acceptance of AI technologies.
1. Introduction to Ethical Considerations and Future Implications of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing many aspects of our lives, bringing important ethical issues we need to think about.
These ethical considerations are essential because AI decisions affect society, the economy, and individuals.
Ethics in AI is crucial for ensuring AI is trustworthy, fair, and accepted by society.
Ethical issues in AI include privacy, data protection, bias, fairness, and the impact of automation on jobs.
As AI becomes more common, it can affect people and communities, raising questions about the values these systems represent.
Developing ethical AI means designing, implementing, and using AI in ways that uphold human values and rights.
Embedding ethics into AI is important for two reasons.
First, it ensures AI benefits humanity, improving well-being and advancing social good.
Second, it helps avoid harm and unintended consequences that could make people lose trust in technology.
Ethical AI aims to align technology with human values, making it transparent and beneficial for society.
Exploring ethical considerations in AI shows how these issues are interconnected.
Privacy concerns involve how AI collects, stores, and uses personal data.
Bias and fairness focus on ensuring AI decisions don’t discriminate.
The impact on jobs highlights the need to manage workforce changes due to automation.
Security involves preventing the misuse of AI in cyberattacks and weapons.
AI governance and ethical development require collaboration among developers, companies, governments, and the global community.
Establishing policies and ethical frameworks is essential for reaping AI benefits while protecting against risks.
Discussing ethical considerations and future implications of AI is about navigating challenges and envisioning a future where AI enhances human abilities, promotes fairness, and contributes to societal progress.
Engaging all stakeholders in ethical AI development is crucial for achieving AI’s transformative potential responsibly and equitably.
2. AI and Privacy
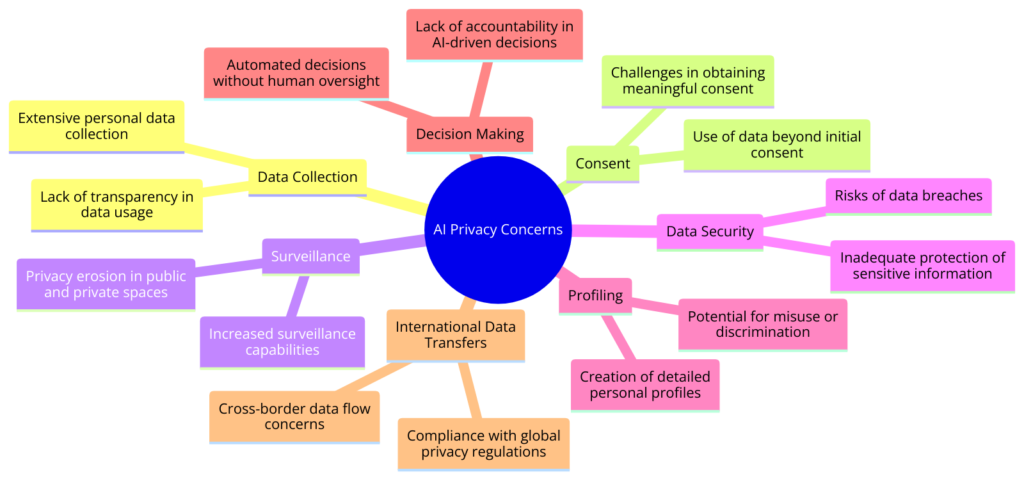
In the AI era, privacy is a major concern, touching on personal freedom and security. AI technologies greatly increase the ability to collect, analyze, and use data, raising important questions about privacy and surveillance.
Concerns About Data Collection, Usage, and Surveillance: AI systems need data to work well. From personalized recommendations to predicting outcomes, AI depends on large amounts of data. However, collecting this data can invade privacy, as personal information may be gathered without explicit consent.
AI in surveillance expands monitoring, tracking people’s movements, behaviors, and emotions. While this can enhance security, it also invades privacy, creating a society where algorithms scrutinize every action.
Balancing Innovation with Privacy Rights: The challenge is balancing AI benefits with the right to privacy. This requires strong privacy protections for data collection, storage, and use by AI systems. Privacy-by-design principles, which consider privacy from the start, are crucial.
Transparency and consent are key to maintaining privacy. Users should know how their data is used and have control over it, including the option to opt-out or understand consent implications.
Regulatory Frameworks and Ethical Guidelines: Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU set strict data protection requirements and grant individuals rights over their data.
Beyond legal regulations, ethical guidelines must emphasize privacy, considering long-term data use implications and implementing safeguards against misuse.
Privacy concerns in AI involve technical, ethical, legal, and societal dimensions. Addressing these requires efforts from technology developers, policymakers, and the global community to establish practices and regulations that protect privacy. As AI evolves, respecting privacy will be essential to ensure technological advancements benefit society without compromising freedom and security.
3. Bias and Fairness in AI
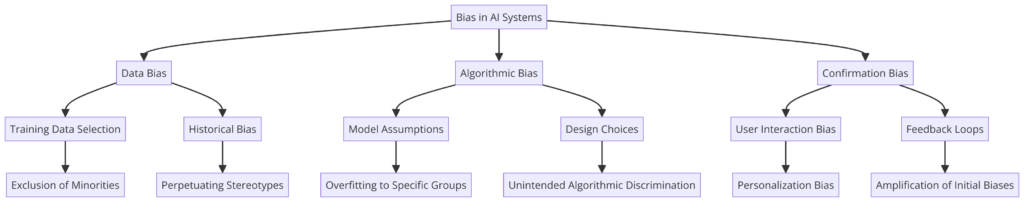
Bias and fairness in AI are major concerns as these technologies influence society. Algorithmic bias can lead to unfair outcomes, worsening existing inequalities. Ensuring fairness in AI is both a technical challenge and a moral necessity.
Addressing Algorithmic Bias and Ensuring Fairness: AI systems learn from data, and if the data is biased, AI decisions will be too. Biases can come from historical inequalities or skewed datasets. Recognizing and addressing these biases is crucial for fair AI.
Ensuring fairness means implementing measures to identify, reduce, and monitor biases throughout AI development. This includes using diverse datasets, fairness metrics, and regular audits. Fair AI also requires transparency in decision-making and the ability for affected people to challenge decisions.
Case Studies and Implications of Biased AI Systems:
- Recruitment Tools: Some AI tools for screening job applicants have shown bias against certain groups, favoring criteria that reflect past hiring biases, leading to unfair treatment.
- Criminal Justice Systems: AI used in policing and sentencing has shown biases against racial minorities, raising concerns about fairness and justice in law enforcement.
Strategies for Mitigating Bias:
- Inclusive Data and Diverse Teams: Using representative datasets and having diverse development teams can help reduce bias. Different perspectives can identify and address potential biases.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: Adhering to frameworks that prioritize fairness and nondiscrimination is essential, guiding AI design and deployment with social justice and human rights principles.
Bias and fairness in AI are critical challenges linked to broader societal issues. Tackling them requires technical solutions, ethical considerations, and regulatory oversight. Committing to fair and unbiased AI ensures these technologies positively impact society, enhancing equity and fairness. The journey to ethical AI requires continuous vigilance, evaluation, and adaptation to serve humanity’s good.
4. AI and Job Displacement
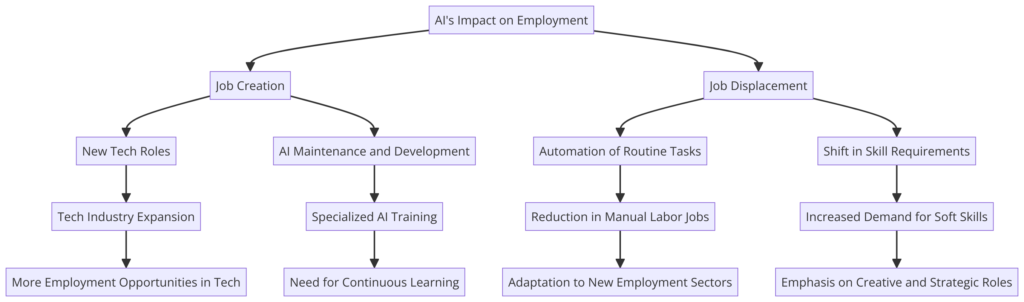
AI’s impact on the workforce and potential job losses is a significant concern. While AI brings efficiency and innovation, it also risks displacing jobs. Understanding this impact and planning for a balanced future is crucial.
The Impact of AI on the Workforce: AI and automation transform industries by performing tasks faster, more accurately, and cheaper than humans. This boosts productivity and economic growth but raises concerns about job displacement, especially for repetitive tasks.
AI’s impact isn’t all negative; it creates new opportunities in AI development, oversight, maintenance, and roles requiring creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking.
Potential Job Losses: Sectors at high risk include manufacturing, transportation, and administrative roles, where tasks can be easily automated. AI also affects healthcare, finance, and creative industries, transforming these fields.
The concern isn’t just job loss but the quality and accessibility of new jobs created by AI advancements. Ensuring meaningful employment opportunities in these new roles is a societal challenge.
Strategies for Job Transition and Reskilling:
- Lifelong Learning and Reskilling: Emphasizing lifelong learning and reskilling helps workers transition to new roles. Governments, educational institutions, and employers must collaborate on programs that equip individuals with skills for emerging jobs.
- Job Transition Support: Support mechanisms like unemployment benefits, career counseling, and job placement services are vital for helping individuals navigate job transitions. Policies encouraging job creation in AI-affected sectors can mitigate employment impacts.
- Creating a Flexible Workforce: Cultivating adaptability and flexibility reduces job automation vulnerability. This involves technical and digital literacy and soft skills like problem-solving and communication.
AI and job displacement highlight a critical crossroads for work’s future. While AI presents challenges in job loss, it offers opportunities for new employment and human capability enhancement. Addressing this transition requires concerted efforts to ensure the workforce is prepared for changes. Focusing on reskilling, lifelong learning, and job transition support can harness AI benefits while minimizing employment disruption.
5. AI and Security

AI in cybersecurity and defense offers innovative ways to protect assets but also brings unique challenges, especially in autonomous weapons and AI-powered cyberattacks. Balancing AI advancements with global security is essential.
Concerns Regarding AI in Cybersecurity and Autonomous Weapons:
- Cybersecurity: AI’s ability to analyze vast data sets quickly makes it a powerful tool against cyber threats. However, it can also enhance cyberattacks, automating vulnerability discoveries and adapting to countermeasures in real-time.
- Autonomous Weapons: AI-powered autonomous weapons raise ethical and security concerns. Machines making life-and-death decisions without human intervention pose moral dilemmas and conflict escalation risks.
Balancing AI Advancements with Global Security:
- Ethical Frameworks and International Regulations: Establishing ethical frameworks and regulations for AI in security and defense is crucial. These should ensure AI is used ethically and according to international law.
- Human Oversight: Keeping human oversight in AI-driven security systems, including weapons, is essential for ethical and informed decision-making, reducing risks of full autonomy.
- Collaboration and Transparency: Collaboration among nations, industries, and academia is vital for developing AI security standards and best practices. Transparency in AI research and applications fosters trust and collective problem-solving.
AI’s role in cybersecurity and autonomous weapons is a double-edged sword, offering benefits and challenges. AI in security needs cautious integration, ethical consideration, and international cooperation. Balancing innovation with global security requires ethical guidelines, human oversight, and transparency, ensuring AI enhances security while serving the greater good and respecting international law and human rights.
6. Future of AI Governance
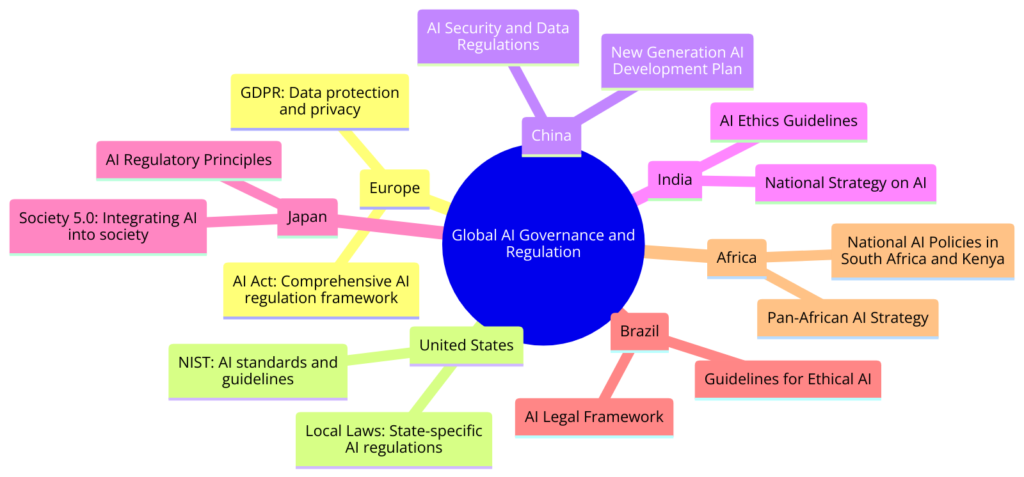
As AI technologies evolve and spread, comprehensive governance frameworks become crucial. Future AI governance involves policies, regulations, and ethical guidelines to ensure responsible AI use, maximizing benefits and mitigating risks.
Discussing the Need for Policies and Regulations: AI advances challenge existing legal and regulatory frameworks. Issues like privacy, data protection, bias, and accountability highlight the need for updated policies addressing AI-specific challenges.
AI governance must consider technology’s global nature, advocating for international cooperation to establish standards beyond national borders. This global approach addresses concerns affecting humanity, such as ethical AI in surveillance and weapons.
Global Efforts and Challenges in Governing AI: Organizations like the United Nations, European Union, and OECD propose frameworks for AI governance. The EU’s GDPR and proposed Artificial Intelligence Act are legislative efforts to regulate AI.
Achieving international consensus on AI governance is challenging due to differing cultural values, economic interests, and political systems. Technological innovation often outpaces policy development.
The Role of Multi-Stakeholder Engagement: Effective AI governance requires engagement from governments, private sector, academia, and civil society. This multi-stakeholder approach ensures diverse perspectives in policy development, making governance frameworks comprehensive and adaptable.
Public-private partnerships can foster innovation while ensuring ethical AI development. Engaging the public in AI governance discussions promotes transparency and builds trust.
Future AI governance is a complex, evolving field needing proactive, informed, and collaborative approaches. As AI shapes society’s future, robust governance frameworks are essential for responsible, ethical AI use. Balancing innovation with ethics, data protection, and individual rights is key to navigating AI’s challenges and opportunities. Global cooperation and multi-stakeholder engagement strive for AI governance that fosters innovation while upholding ethics and fairness.
7. Ethical AI Development

Ethical AI development is essential for responsibly using AI technologies. It includes principles, frameworks, and practices ensuring AI is fair, transparent, accountable, and aligned with human values and rights. Developers, corporations, and governments play key roles in navigating AI’s ethical landscape.
Principles and Frameworks for Ethical AI: Ethical principles guide AI development, including fairness, accountability, transparency, privacy, and non-discrimination. Frameworks built on these principles offer a blueprint for ethical AI design and deployment.
Organizations propose ethical AI guidelines, like the European Commission’s Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI, which include human agency, technical robustness, and privacy.
Role of Developers, Corporations, and Governments:
- Developers: Integrate ethics into AI design and development, conducting bias assessments, ensuring data privacy, and creating transparent AI systems.
- Corporations: Establish governance structures prioritizing AI ethics, invest in ethical AI research, foster ethical organizational culture, and engage stakeholders.
- Governments: Create regulations encouraging ethical AI development while protecting citizens’ rights, address AI-specific concerns, and promote international collaboration for global ethical standards.
Challenges in Ethical AI Development: Navigating AI ethics involves challenges like eliminating bias, ensuring transparency in complex algorithms, and balancing innovation with ethics. The global nature of AI raises questions about universal ethical principles and regulation applicability across different cultures.
Ethical AI development requires active engagement from all AI stakeholders. Adhering to ethical principles and frameworks helps create AI systems that are innovative, effective, fair, transparent, and aligned with human dignity and rights. Committing to ethical AI is crucial for realizing AI’s potential as a positive societal force. The future of AI’s societal impact depends on navigating these ethical considerations responsibly, ensuring AI enhances rather than undermines society.
8. Conclusion

Exploring ethical considerations and future implications of AI highlights a crucial moment in technology’s evolution and societal integration. AI ethics discussions are intertwined with AI’s practical use and societal impact. As AI advances, responsible development and deployment become more important, addressing ethical challenges alongside innovation.
AI’s impact on privacy, bias, fairness, jobs, security, governance, and ethical development creates a complex narrative. Each area presents unique challenges requiring thoughtful consideration, innovative solutions, and collaborative action. Balancing AI benefits with potential risks and ethical dilemmas demands prioritizing human values, rights, and well-being.
The future outlook on AI is promising yet cautionary. AI can solve complex problems, improve life quality, and unlock new knowledge. However, unchecked AI development can worsen societal inequalities, infringe on rights, and challenge ethics. Navigating this requires proactive AI governance, policies, and regulations fostering innovation while preventing misuse.
Ethical AI development emphasizes the responsibility of developers, corporations, and governments to design and use AI respecting ethics and promoting the common good. Ethical AI principles and frameworks guide integrating ethics into AI lifecycle stages.
Navigating AI’s ethical considerations and future implications reveals a complex but manageable path. Embracing ethical AI development, fostering global collaboration, and engaging in continuous dialogue help harness AI’s transformative power responsibly and equitably. The future of AI, shaped by today’s collective actions and decisions, promises a world where technology advances human capabilities and enriches the human experience.
FAQ & Answers
1. What are the main ethical concerns associated with AI?
Key concerns include privacy, bias and fairness, job displacement, and security issues.
How can bias in AI be addressed?
Through diverse data sets, transparency in algorithms, and continuous monitoring for biases.
Scenario-Based Questions
“Ethical Dilemmas in AI” – Scenario-based questions to understand ethical complexities.
Autonomous Vehicles: A self-driving car encounters a situation where it has to make a split-second decision to either swerve and potentially harm pedestrians or stay on course and harm the passengers. How should the car be programmed to make such decisions, and who should be responsible for setting these ethical guidelines?
Scenario 1: Autonomous Vehicles

You are a member of a team developing the decision-making algorithms for a fleet of autonomous vehicles. During testing, the AI encounters a situation where it must decide between two potentially harmful outcomes: swerving to avoid hitting a group of pedestrians and potentially endangering the passengers, or staying on course and risking harm to the pedestrians.
As a member of the team, you are tasked with determining the ethical guidelines for how the AI should make decisions in such scenarios. How do you approach this dilemma, and what factors do you consider in determining the appropriate course of action for the AI?
Considerations:
- Utilitarianism vs. Deontology: Do you prioritize minimizing harm overall (utilitarianism) or adhering to a set of moral principles (deontology)?
- Value of Human Life: How do you weigh the lives of the pedestrians against the lives of the passengers?
- Legal and Liability Issues: Who would be legally responsible if the AI makes a decision resulting in harm?
- Public Perception and Trust: How do you ensure that the AI’s decision-making process is transparent and understandable to the public?
- Technological Constraints: What limitations or capabilities does the AI system have that might influence its decision-making process?
- Cultural and Societal Values: How do cultural differences and societal norms influence the ethical guidelines for the AI?
These considerations highlight the complexity of developing ethical guidelines for autonomous vehicles and the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration among ethicists, engineers, policymakers, and other stakeholders to address these challenges.
AI in Healthcare: A hospital adopts an AI system to diagnose patients. The AI recommends a course of treatment that differs from the human doctor’s opinion. Should the doctor trust the AI’s recommendation, even if it goes against their own judgment? How can bias in AI algorithms be identified and mitigated in such critical settings?
Scenario 2: AI in Healthcare

You work for a healthcare organization that is considering implementing an AI system to assist doctors in diagnosing patients. During the testing phase, the AI frequently recommends treatment plans that differ from those suggested by human doctors. Some doctors are hesitant to trust the AI’s recommendations, fearing that they may be inaccurate or not fully understand the rationale behind them.
As a member of the team responsible for integrating AI into healthcare, you are tasked with addressing these concerns and ensuring that the AI system is effectively utilized by healthcare professionals. How do you navigate the ethical considerations involved in integrating AI into healthcare settings?
Considerations:
- Patient Safety: How do you ensure that the AI’s recommendations prioritize patient safety and well-being?
- Doctor-Patient Relationship: How do you maintain trust between doctors and patients when AI is involved in the decision-making process?
- Explainability and Transparency: How do you ensure that the AI’s recommendations are transparent and understandable to healthcare professionals?
- Accountability and Liability: Who is responsible if the AI’s recommendations lead to adverse outcomes? How do you establish accountability and address liability issues?
- Bias and Fairness: How do you mitigate bias in the AI algorithms to ensure fair treatment across diverse patient populations?
- Professional Autonomy: How do you balance the autonomy of healthcare professionals with the guidance provided by AI systems?
- Regulatory Compliance: What regulatory frameworks need to be considered to ensure that the use of AI in healthcare complies with ethical standards and legal requirements?
Addressing these considerations requires collaboration between healthcare professionals, AI experts, ethicists, regulators, and other stakeholders to develop ethical guidelines and best practices for integrating AI into healthcare in a responsible and ethical manner.
Job Automation: A company implements AI-powered automation that results in the displacement of many workers. What ethical responsibilities does the company have towards those workers who have lost their jobs? Should there be regulations in place to ensure that AI deployment doesn’t disproportionately harm certain groups in society?
Scenario 3: Job Automation

You are a consultant advising a company that is considering implementing AI-powered automation in its operations, which could result in the displacement of a significant number of workers. The company is concerned about the ethical implications of this decision and wants to ensure that it minimizes harm to affected employees and maintains its ethical responsibilities to its workforce and society at large.
As a consultant, you are tasked with developing strategies to address the ethical considerations associated with job automation. How do you approach this dilemma, and what steps do you recommend to mitigate the potential negative impacts of AI-powered automation on employees?
Considerations:
- Job Displacement: How do you minimize the negative impact of automation on employees who may lose their jobs?
- Retraining and Upskilling: How can the company support affected employees through retraining and upskilling programs to transition to new roles or industries?
- Economic Justice: How do you ensure that the benefits of automation are equitably distributed among all stakeholders, including workers?
- Ethical Hiring Practices: How can the company ensure that its hiring practices are fair and inclusive, particularly in light of potential biases introduced by AI in recruitment processes?
- Social Responsibility: What role does the company have in addressing broader societal challenges, such as income inequality and unemployment, that may be exacerbated by automation?
- Stakeholder Engagement: How do you engage with employees, unions, and other stakeholders to ensure that their concerns are heard and addressed throughout the automation process?
- Long-Term Impact: How do you consider the long-term implications of automation on the workforce, economy, and society, and develop strategies to mitigate potential risks?
Addressing these considerations requires a comprehensive approach that considers not only the technological aspects of automation but also its social, economic, and ethical implications. By proactively addressing these issues, the company can demonstrate its commitment to ethical business practices and responsible use of AI technologies.
Social Media Algorithms: Social media platforms use AI algorithms to curate content for users. These algorithms often prioritize content that generates more engagement, leading to echo chambers and the spread of misinformation. How can platforms balance the ethical considerations of free speech with the need to prevent harm caused by the dissemination of false information?
Scenario 4: Social Media Algorithms

You are a policy advisor working for a government agency tasked with regulating social media platforms. There is growing concern about the role of AI algorithms in curating content and the potential negative impacts on society, such as the spread of misinformation, polarization, and the amplification of harmful content.
As a policy advisor, you are responsible for developing recommendations to address these concerns and ensure that social media platforms prioritize ethical considerations in their algorithmic content curation processes. How do you approach this challenge, and what policy recommendations do you propose to mitigate the negative effects of AI algorithms on social media?
Considerations:
- Transparency and Accountability: How do you ensure that social media platforms are transparent about how their algorithms work and accountable for the content they promote?
- Content Moderation: What measures can be implemented to improve the moderation of harmful or misleading content, including the development of AI-powered content moderation tools?
- User Empowerment: How can users be empowered to better understand and control their online experiences, such as through customizable content filters or access to algorithmic preferences?
- Diversity and Inclusion: How can algorithms be designed to promote diverse perspectives and mitigate the formation of echo chambers and filter bubbles?
- Regulatory Oversight: What regulatory frameworks need to be established or strengthened to ensure that social media platforms operate in accordance with ethical standards and protect users’ rights?
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: How can governments, civil society organizations, and industry stakeholders collaborate to address the complex challenges posed by AI algorithms in social media?
- Research and Innovation: What role can research and innovation play in developing new approaches to algorithmic content curation that prioritize ethical considerations and societal well-being?
Addressing these considerations requires a multi-stakeholder approach involving collaboration between governments, social media platforms, researchers, and civil society organizations. By implementing comprehensive policy measures, it is possible to mitigate the negative impacts of AI algorithms on social media and promote a more ethical and responsible online environment.
Surveillance AI: Law enforcement agencies use facial recognition technology for surveillance purposes. This technology has the potential to infringe upon individuals’ privacy rights and disproportionately target certain demographics. What safeguards should be put in place to ensure that the use of AI in surveillance respects individuals’ rights and freedoms?
Scenario 5: Surveillance AI

You are a member of a legislative committee tasked with drafting regulations for the use of facial recognition technology by law enforcement agencies. There is growing concern about the potential for abuse of this technology, including privacy violations, unjust surveillance, and discriminatory practices.
As a member of the committee, you are responsible for developing regulations that balance the need for effective law enforcement with the protection of individuals’ rights and freedoms. How do you approach this task, and what regulatory measures do you propose to address the ethical considerations associated with the use of surveillance AI?
Considerations:
- Privacy Protection: How do you ensure that individuals’ privacy rights are respected when deploying facial recognition technology for surveillance purposes?
- Transparency and Accountability: What mechanisms can be put in place to ensure transparency about when and how facial recognition technology is used, as well as accountability for any misuse or abuse?
- Bias and Discrimination: How do you mitigate the risk of bias and discrimination in facial recognition algorithms, particularly against marginalized communities?
- Consent and Opt-Out Mechanisms: Should individuals have the right to opt out of being subject to facial recognition surveillance, and if so, how can this be implemented effectively?
- Oversight and Regulation: What regulatory framework should be established to govern the use of facial recognition technology by law enforcement agencies, including requirements for data storage, access, and retention?
- Public Engagement and Consultation: How can the public be engaged in the development of regulations governing facial recognition technology to ensure that diverse perspectives and concerns are considered?
- Alternatives and Limitations: What alternatives to facial recognition technology exist for achieving law enforcement objectives, and under what circumstances should facial recognition be used or restricted?
Addressing these considerations requires a careful balancing of competing interests, including public safety, individual rights, and societal values. By developing robust regulatory measures, it is possible to harness the potential benefits of surveillance AI while mitigating its ethical risks and ensuring accountability and transparency in its use.
- AI in Criminal Justice: AI systems are increasingly being used to assist judges in making sentencing decisions. However, these systems may perpetuate biases present in historical data, leading to unfair outcomes, especially for marginalized communities. How can the criminal justice system ensure that AI tools are used in a fair and transparent manner?
Scenario 6: AI in Criminal Justice

You are a member of a task force convened to examine the use of AI systems in assisting judges with sentencing decisions. There is concern that these systems may perpetuate biases present in historical data, leading to unfair outcomes, particularly for marginalized communities.
As a member of the task force, you are responsible for developing guidelines to ensure that AI tools are used in a fair and transparent manner within the criminal justice system. How do you approach this challenge, and what measures do you propose to address the ethical considerations associated with the use of AI in sentencing?
Considerations:
- Bias Mitigation: How do you ensure that AI algorithms used in sentencing decisions are free from bias and discrimination, particularly against historically marginalized groups?
- Transparency and Explainability: What steps can be taken to ensure that AI-driven sentencing decisions are transparent and understandable to judges, defendants, and other stakeholders?
- Accountability and Oversight: What mechanisms should be in place to hold both the developers of AI systems and the criminal justice agencies using them accountable for any errors, biases, or unfair outcomes?
- Data Quality and Integrity: How can the quality and integrity of the data used to train AI algorithms be ensured, and how do you address any biases or inaccuracies in the data?
- Human Oversight and Discretion: Should AI systems be used as decision-making tools or as aids to assist human judges in their decision-making process? How do you strike the right balance between automation and human judgment?
- Rehabilitation and Fairness: How can AI systems be designed to prioritize rehabilitation and fairness in sentencing decisions, rather than punitive measures that perpetuate cycles of incarceration?
- Community Engagement: How can communities affected by AI-driven sentencing decisions be engaged in the development and implementation of guidelines to ensure that their concerns and perspectives are considered?
Addressing these considerations requires collaboration between experts in AI ethics, criminal justice, civil rights, and community advocacy. By developing comprehensive guidelines and oversight mechanisms, it is possible to ensure that AI is used responsibly and ethically within the criminal justice system, promoting fairness, transparency, and accountability in sentencing decisions
- AI and Privacy: Smart home devices equipped with AI capabilities collect vast amounts of data about users’ behaviors and preferences. How can companies ensure that this data is used responsibly and ethically, without compromising users’ privacy rights or exposing them to security risks?
Scenario 7: AI and Privacy

You are a privacy advocate working for a consumer rights organization concerned about the increasing prevalence of AI-powered smart home devices. These devices collect vast amounts of data about users’ behaviors and preferences, raising significant privacy concerns.
As a privacy advocate, you are tasked with developing recommendations to ensure that the use of AI in smart home devices respects users’ privacy rights and minimizes the risk of data misuse or unauthorized access. How do you approach this challenge, and what measures do you propose to address the ethical considerations associated with AI and privacy in the context of smart home devices?
Considerations:
- Data Minimization: How can smart home device manufacturers minimize the collection and retention of user data to only what is necessary for the device’s functionality?
- Privacy by Design: What steps can be taken to integrate privacy protections into the design and development of AI-powered smart home devices from the outset?
- User Consent and Control: How can users be provided with meaningful choices and controls over the collection, use, and sharing of their data by smart home devices?
- Data Security: What measures should be implemented to ensure the security of user data collected by smart home devices, including encryption, access controls, and regular security updates?
- Transparency and Accountability: How can smart home device manufacturers be transparent about their data practices and accountable for any misuse or breaches of user data?
- Regulatory Frameworks: What regulatory frameworks should be established or strengthened to govern the use of AI in smart home devices and protect users’ privacy rights?
- Education and Awareness: How can consumers be educated about the privacy risks associated with AI-powered smart home devices and empowered to make informed choices about their use?
Addressing these considerations requires collaboration between policymakers, industry stakeholders, privacy advocates, and consumers to develop robust privacy protections that balance the benefits of AI-enabled smart home devices with the need to safeguard users’ privacy rights. By implementing these measures, it is possible to ensure that AI is used ethically and responsibly in the context of smart home devices, respecting users’ privacy and promoting trust in AI technologies.
These scenarios highlight the diverse range of ethical considerations that arise from the increasing integration of AI technologies into various aspects of society. Addressing these dilemmas requires careful consideration of ethical principles, stakeholder perspectives, and the potential long-term impacts of AI deployment.
QUIZ
“AI Governance” – Test knowledge on global AI policies and regulations
- What is AI governance? a) Regulation of AI technologies b) Ethical guidelines for AI development and deployment c) Management of AI-related risks and benefits d) All of the above
- Which country introduced the first national AI strategy? a) United States b) China c) United Kingdom d) Canada
- What is the European Union’s regulation for AI called? a) AI Ethics Guidelines b) AI for Europe Act c) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) d) Artificial Intelligence Act
- Which of the following is NOT a principle outlined in the OECD’s AI Principles? a) Transparency b) Accountability c) Fairness d) Profitability
- Which organization published the Montreal Declaration for Responsible AI? a) United Nations b) World Economic Forum c) UNESCO d) None of the above
- Which country passed the world’s first law explicitly regulating autonomous weapons systems? a) United States b) Russia c) China d) Germany
- What does the acronym “AIIB” stand for in the context of AI governance? a) Artificial Intelligence Industry Bureau b) Artificial Intelligence International Board c) Artificial Intelligence Impact Assessment d) Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Which of the following is NOT a potential component of AI governance frameworks? a) Data protection and privacy b) Ethical guidelines c) Intellectual property rights d) Unlimited development and deployment
- What does the acronym “ICAIL” stand for in the context of AI governance? a) International Conference on AI Legislation b) International Conference on AI and Law c) International Consortium for AI Legislation d) None of the above
- Which international organization established the AI for Good Global Summit? a) United Nations b) World Bank c) World Health Organization d) International Monetary Fund
Answers:
- d) All of the above
- b) China
- d) Artificial Intelligence Act
- d) Profitability
- c) UNESCO
- d) Germany
- d) Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- d) Unlimited development and deployment
- b) International Conference on AI and Law
- a) United Nations