AI in public policy emerges as a pivotal juncture in the evolution of governance and societal advancement. This intersection represents a dynamic arena where the analytical prowess of AI meets the structured world of policy-making, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance the efficiency, responsiveness, and effectiveness of public services and policy initiatives. The incorporation of AI into the policy-making process is propelled by its ability to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns and trends, and generate predictive insights, thus enabling a more informed and strategic approach to governance.
The importance of AI in public policy cannot be overstated. It has the potential to transform traditional policy-making processes, making them more adaptive to rapidly changing socio-economic and environmental landscapes.
By leveraging AI, policymakers can access and interpret complex data in real-time, facilitating evidence-based decisions better aligned with society’s needs and expectations.
Moreover, AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and data analytics offer tools for enhancing transparency, accountability, and public engagement in policy-making.
Integrating AI into policy-making also promises societal advancement by addressing pressing challenges such as climate change, healthcare, education, and security more effectively.
For instance, AI can provide insights into climate modeling, predict healthcare trends to inform public health policies, personalize education through adaptive learning systems, and enhance public safety through predictive policing models.
These applications showcase AI’s versatility and highlight its potential to contribute to sustainable development and well-being.
However, integrating AI into public policy also raises critical questions about ethics, privacy, data governance, and the potential for algorithmic bias.
Ensuring that AI-driven policy-making is equitable, transparent, and accountable requires a thoughtful approach to designing, implementing, and overseeing AI technologies.
It necessitates a collaborative effort among technologists, policymakers, and the public to establish guidelines and frameworks that safeguard ethical principles while maximizing AI’s benefits for society.
The journey of incorporating AI into public policy is developing, with pioneering applications and pilot projects paving the way for broader adoption.
As we stand at this juncture, the potential for AI to revolutionize policy-making and governance is immense.
This promises a future where data-driven and AI-enhanced policies foster greater societal well-being, resilience, and prosperity.
This exploration begins with understanding how AI is utilized in policy analysis and development, setting the stage for a deeper dive into its transformative impact on public engagement, policy implementation, and beyond.
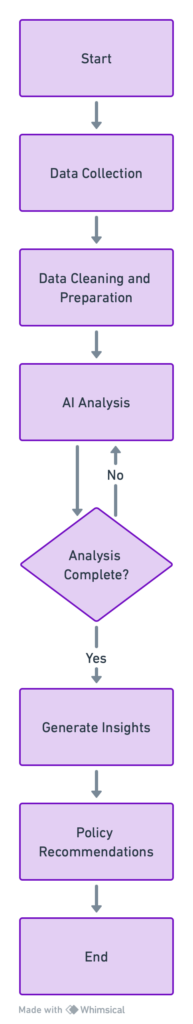
1. AI in Policy Analysis and Development

Artificial intelligence (AI) is a critical tool for transforming raw data into actionable insights for policy analysis and development in an era characterized by unprecedented data generation.
This process, pivotal in public policy, leverages AI’s computational and analytical capabilities to sift through complex, voluminous datasets, identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that might elude traditional analysis.
Using AI technologies—spanning machine learning algorithms, natural language processing (NLP), and big data analytics—facilitates a nuanced understanding of societal needs, enabling policymakers to craft informed, evidence-based policies.
Harnessing AI for Data-Driven Insights
At the core of AI’s application in policy development is its ability to process and analyze data at a scale and speed beyond human capability.
Machine learning models, for instance, can predict outcomes based on historical data, offering insights into the potential impacts of policy decisions.
Natural language processing enables the analysis of public sentiment and feedback from vast quantities of text, such as social media posts, news articles, and public comments, ensuring that policy development is responsive to the public’s voice.
Transformative Examples of AI in Policy Analysis
- Environmental Policy: AI models are instrumental in climate science, analyzing satellite imagery and environmental data to predict climate change impacts. This information guides the development of policies aimed at mitigation and adaptation strategies, contributing to sustainable development goals.
- Health Policy: In the health sector, AI algorithms analyze patterns in healthcare data, identifying risk factors for diseases, predicting outbreaks, and informing public health policies. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI was pivotal in analyzing infection rates and mobility data to guide lockdown policies and resource allocation.
- Economic Policy: AI’s predictive analytics power economic forecasting models, helping policymakers anticipate economic trends, assess the impact of fiscal policies, and make informed decisions on monetary policy, taxation, and public spending.
Impact on Public Policy Formulation
The impact of AI-driven policy analysis is profound and far-reaching.
By providing a deeper, data-driven understanding of complex issues, AI enables the formulation of more targeted, effective policies.
It enhances the agility of the policy-making process, allowing for real-time adjustments based on new data and insights.
Moreover, AI-driven analyses democratize policy development by incorporating a broader range of data sources, including public feedback, ensuring that policies reflect society’s diverse needs and perspectives.
Navigating Challenges
Despite its potential, integrating AI into policy analysis is challenging.
Concerns about data privacy, security, and the ethical use of AI are paramount.
Additionally, the risk of algorithmic bias and transparency in AI algorithms necessitate rigorous standards and oversight to ensure that AI-driven policy analysis upholds principles of equity and fairness.
AI represents a transformative force in policy analysis and development, offering tools that can significantly enhance public policy’s efficacy, responsiveness, and inclusiveness.
As we continue to explore and expand AI’s applications in this field, it is crucial to address the ethical, security, and privacy challenges accompanying its use.
By doing so, we can harness AI’s full potential to inform and improve policy-making processes, ultimately contributing to more informed, effective, and equitable public policies.
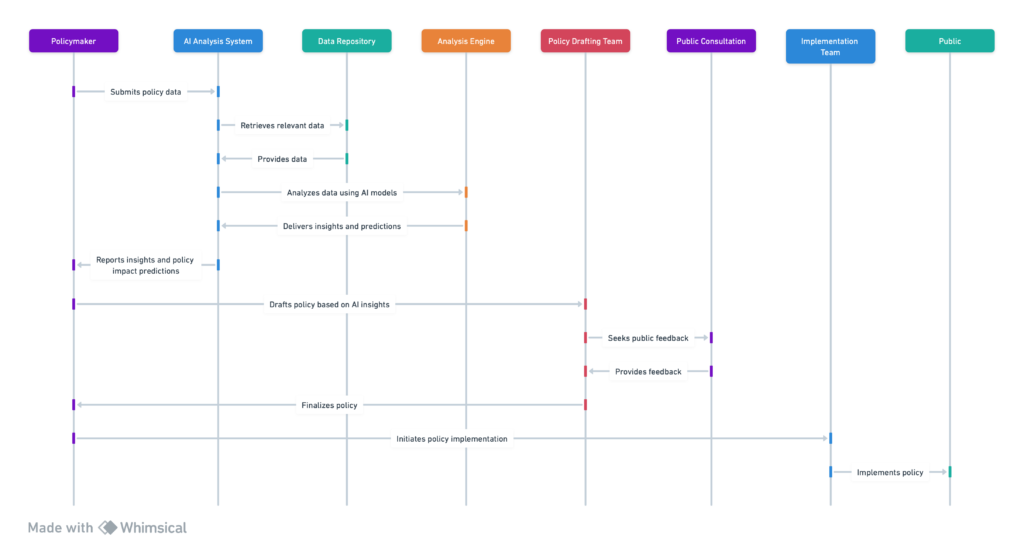
2. AI in Public Engagement and Consultation

Public engagement and consultation are fundamental to the democratic process, ensuring that policy-making is inclusive and reflects the public’s needs and opinions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing this aspect of governance by introducing innovative methods to facilitate and amplify public participation.
Utilizing AI technologies like natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, and machine learning, governments, and public institutions can now engage with citizens more effectively, analyze public sentiment at scale, and incorporate a broader range of perspectives into the policy-making process.
Enhancing Public Participation with AI
AI technologies transform public engagement by making it more accessible, inclusive, and efficient.
Platforms powered by AI can handle large volumes of interactions simultaneously, breaking down barriers to participation that many citizens face.
For example, chatbots and virtual assistants, equipped with NLP capabilities, can provide information on policy proposals, collect feedback, and answer queries in real time, offering a more interactive and engaging consultation process.
Case Studies: AI-Powered Platforms in Action
- E-Participation Platforms: Countries like Estonia have leveraged AI to enhance e-participation platforms, enabling citizens to propose new legislation, comment on existing proposals, and participate in decision-making processes online. These platforms use AI to analyze public submissions, identify common themes, and gauge public sentiment, ensuring policymakers are informed of the public’s views.
- Social Media Analysis for Public Sentiment: Various governments and organizations use AI to monitor and analyze social media platforms, gathering insights into public opinion on policy issues. By employing sentiment analysis, these entities can identify trends in public sentiment, emerging concerns, and overall support or opposition to policy initiatives, allowing for more responsive governance.
The Impact of AI on Public Consultation
Integrating AI into public engagement processes has significantly impacted policy-making, making it more dynamic and responsive to public input.
AI’s ability to process and analyze large datasets enables a more thorough consideration of public feedback, ensuring that a wide array of voices is heard.
This enriches the policy-making process with diverse perspectives and enhances the legitimacy and acceptance of policy decisions among the public.
Overcoming Challenges
While AI offers promising opportunities for enhancing public engagement, it also presents challenges that must be addressed. Issues such as the digital divide, privacy concerns, and the potential for manipulating public opinion through AI-driven platforms necessitate careful consideration.
Ensuring transparency in how AI algorithms process and analyze public feedback is crucial for maintaining trust in public consultation.
AI has the potential to transform public engagement and consultation in policy-making profoundly.
By leveraging AI technologies, governments and public institutions can ensure more inclusive, efficient, and responsive public participation.
As we move forward, it is imperative to carefully navigate the challenges associated with AI’s integration into public engagement, ensuring that these technologies enhance democratic processes and foster a more engaged and informed citizenry.
3. AI in Policy Implementation and Monitoring

The implementation and monitoring phase is crucial in the policy-making cycle, as it determines policies’ real-world effectiveness and informs necessary adjustments.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is significantly advancing this phase by providing tools for real-time data analysis, predictive analytics, and performance tracking.
These AI-driven innovations enhance policy implementation efficiency and ensure that policies are adaptive and responsive to changing circumstances and needs.
Utilizing AI for Effective Policy Monitoring
AI technologies offer a suite of capabilities that transform traditional methods of policy monitoring.
Using machine learning algorithms and big data analytics, AI systems can process vast amounts of information from diverse sources, including social media, sensors, and government databases, to provide insights into policy performance.
This real-time monitoring capability allows for the rapid identification of issues and challenges, enabling timely interventions and adjustments.
Innovations in AI for Policy Implementation
- Intelligent Infrastructure: AI applications in innovative city initiatives exemplify how technology can support policy implementation in urban planning and infrastructure development. Sensors and AI-powered analytics monitor traffic flow, energy consumption, and public safety, providing data-driven insights to optimize city management and improve urban living conditions.
- Healthcare Policy Monitoring: In the healthcare sector, AI tools analyze patient data, treatment outcomes, and healthcare service delivery to assess the impact of health policies. This includes tracking the effectiveness of public health initiatives, such as vaccination programs, by analyzing health outcomes and identifying areas for improvement.
- Environmental Policy Enforcement: AI technologies are vital in monitoring environmental regulations and policies. Satellite imagery and AI analysis track deforestation, pollution levels, and compliance with environmental protection policies, enabling more effective enforcement and conservation efforts.
The Impact of AI on Policy Evaluation
Integrating AI into policy monitoring and evaluation processes has a profound impact, allowing policymakers to make data-driven decisions.
The insights from AI-driven analysis offer a detailed understanding of policy outcomes, facilitating evidence-based adjustments that enhance policy effectiveness.
Furthermore, predictive analytics can forecast future trends and potential challenges, allowing for proactive policy adjustments.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Accountability
While AI offers transformative potential for policy implementation and monitoring, it also raises challenges related to data privacy, security, and the ethical use of technology.
Ensuring the accuracy and fairness of AI algorithms is critical to maintaining public trust in the policy evaluation process.
Transparency in AI methodologies and accountability for AI-driven decisions are essential to address these challenges effectively.
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping the policy implementation and monitoring landscape, offering unparalleled capabilities for analyzing policy effectiveness and facilitating adaptive governance.
As AI technologies continue to evolve, their integration into policy evaluation processes promises to enhance the responsiveness and efficiency of public policies.
However, navigating the ethical and practical challenges associated with AI’s use in governance will be crucial in realizing its full potential in supporting dynamic and effective policy-making.
4. AI in Predictive Policymaking
Predictive policymaking represents a paradigm shift in formulating public policies, moving from a reactive to a proactive stance.
By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI), policymakers can use predictive analytics to forecast future societal trends, potential crises, and the impacts of various policy options.
This capability is crucial for developing strategies that are both effective and resilient, enabling societies to more adeptly navigate the complexities of the modern world.
The Role of AI in Forecasting Societal Trends
AI-driven predictive analytics employs machine learning algorithms and big data to analyze historical and current data, identifying patterns that can predict future events or trends.
This approach is applied across various domains, including public health, economic development, environmental sustainability, and public safety, and it offers insights that guide strategic policy decisions.
Applications of Predictive Policymaking
- Public Health: AI models predict disease outbreaks, allowing governments to allocate resources efficiently and develop health policies that preemptively address public health crises.
- Economic Forecasting: AI tools analyze market trends, employment data, and financial indicators to forecast economic conditions, informing fiscal policies and social welfare programs.
- Environmental Management: Predictive models assess the impact of climate change, predict ecological degradation, and inform policies on conservation, sustainable development, and disaster preparedness.
- Urban Planning: AI algorithms forecast urban growth patterns, helping policymakers plan infrastructure projects, housing policies, and transportation systems that accommodate future needs.
The Impact of Predictive Policymaking
AI enables predictive policymaking, which allows governments to anticipate changes and challenges, leading to more timely and effective policy interventions. This approach enhances the agility of public policies, enabling them to adapt to evolving societal needs and expectations. Moreover, predictive analytics can help allocate public resources more efficiently, targeting interventions where they are most needed and likely to have the most significant impact.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While predictive policymaking offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges.
These include ensuring predictions’ accuracy, addressing potential biases in AI algorithms, and managing privacy concerns related to large datasets.
Ethical considerations, such as how predictive insights are used and the potential for surveillance, must be carefully managed to maintain public trust and protect individual rights.
AI in predictive policymaking promises to transform public policy development, offering a proactive approach that anticipates future challenges and opportunities.
By leveraging AI-driven insights, policymakers can craft strategies that are not only responsive but also anticipatory, enhancing societal resilience and well-being.
However, realizing the full potential of predictive policymaking requires addressing its ethical and practical challenges and ensuring that AI technologies are used responsibly and equitably in the service of the public good.
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Policymaking

As AI technologies increasingly infiltrate the public policy domain, they bring challenges and ethical considerations that necessitate careful attention.
AI’s promise of enhancing governance and public service delivery is accompanied by concerns over data bias, transparency, accountability, privacy, and equity.
Addressing these issues is paramount to ensuring that AI-driven policymaking upholds democratic values and promotes societal well-being without compromising individual rights or exacerbating inequalities.
Data Bias and Algorithmic Fairness
One of the most pressing challenges in AI-driven policy-making is the risk of data bias, which can lead to skewed outcomes and discriminatory policies.
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on; historical data often reflects existing prejudices, which can be perpetuated or even amplified by AI algorithms.
Ensuring algorithmic fairness requires rigorous auditing of AI systems, diverse data sets that reflect the plurality of society, and continuous monitoring to identify and correct biases.
Transparency and Accountability
The “black box” nature of many AI systems poses significant challenges to transparency and accountability in policy-making.
The complexity of AI algorithms can make it difficult for policymakers and the public to understand how decisions are made, undermining trust in AI-driven initiatives.
Addressing this challenge requires the development of explainable AI models that allow for the scrutiny of decision-making processes and the establishment of accountability mechanisms for AI-driven outcomes.
Privacy Concerns
AI in public policy also raises substantial privacy concerns, particularly when personal data is collected, analyzed, and utilized to inform policy decisions.
Ensuring the protection of individual privacy while leveraging AI for the public good necessitates robust data governance frameworks, strict data protection regulations, and secure data processing practices that safeguard personal information against misuse or breach.
Equity and Social Justice
AI-driven policymaking must also address issues of equity and social justice, ensuring that the benefits of AI technologies are accessible to all segments of society, including marginalized and vulnerable groups.
This involves designing AI systems that address rather than exacerbate social inequalities and promoting inclusive policies that consider AI’s disparate impacts across different populations.
Ethical Frameworks for Responsible AI Use
To navigate these challenges, comprehensive ethical frameworks for AI use in public policy must be developed and implemented.
Such frameworks should encompass principles of fairness, accountability, transparency, and privacy and guide the responsible deployment of AI technologies in governance.
Moreover, engaging diverse stakeholders in developing these frameworks can help ensure they reflect various perspectives and values.
Integrating AI into public policy-making offers transformative potential and introduces complex ethical and practical challenges.
Addressing these challenges through robust ethical frameworks, transparent and accountable AI practices, and a commitment to equity and social justice is crucial for harnessing AI’s capabilities responsibly.
As AI evolves, ongoing dialogue, ethical scrutiny, and adaptive regulation will ensure that AI-driven policymaking serves the public interest and enhances societal well-being.
6. The Future of AI in Public Policy

As we look toward the future, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in public policy is poised for significant evolution.
Emerging trends and advancements in AI technologies promise to transform governance and policy-making further, enhancing the ability to address complex societal challenges with greater precision and foresight.
This future landscape will likely be characterized by more sophisticated AI applications, deeper integration of AI across all levels of governance, and an increased focus on ethical and responsible AI use.
Advancements in AI Technologies
Future advancements in AI, including improvements in machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, will offer new tools for data-driven policy analysis, public engagement, and policy implementation monitoring.
These technologies will enable a more nuanced understanding of societal needs and more accurate forecasting of policy outcomes, facilitating more responsive and adaptive policymaking.
Deepening Integration of AI in Governance
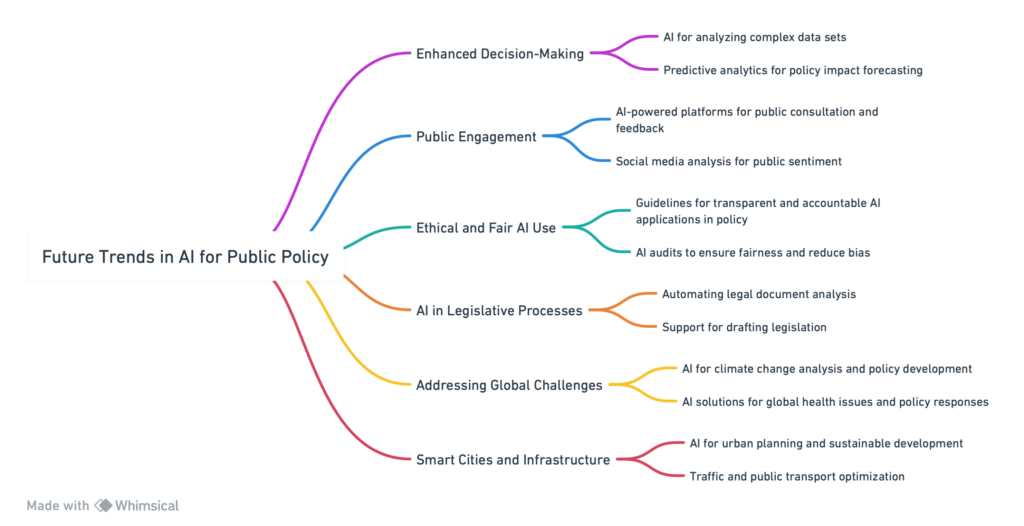
AI’s integration into governance is expected to deepen.
AI systems will play a crucial role in various aspects of public administration, from service delivery to regulatory compliance and public safety.
To fully leverage AI’s capabilities, technological advancements and organizational changes within public institutions will be necessary.
Ethical AI and Responsible Governance
The emphasis on ethical AI and responsible governance will grow as AI becomes more embedded in public policy-making.
This will involve the development of robust ethical frameworks, transparency standards, and accountability mechanisms to ensure that AI technologies are used to uphold public trust and protect individual rights.
Addressing AI’s ethical implications will be critical in shaping public acceptance and confidence in AI-driven governance.
Collaborative and Participatory Approaches
The future of AI in public policy will likely see more collaborative and participatory approaches to policy development.
This includes more significant engagement with citizens, stakeholders, and multidisciplinary experts in designing and implementing AI solutions.
Such collaboration can enhance AI-driven policies’ inclusivity, equity, and effectiveness.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While the future of AI in public policy is full of potential, it also presents challenges, including addressing the digital divide, ensuring data privacy and security, and managing the societal impacts of automation.
Navigating these challenges will require concerted efforts from policymakers, technologists, and society to ensure that AI technologies contribute positively to public governance and societal well-being.
The future of AI in public policy is both promising and challenging.
As AI technologies evolve, they can revolutionize policy-making and governance, making them more efficient, inclusive, and responsive to societal needs.
However, realizing this potential will depend on our ability to harness AI’s capabilities responsibly, ensuring that advancements in AI are aligned with ethical principles and public values.
The journey ahead will require ongoing dialogue, collaboration, and innovation, but the prospects for AI to contribute to better governance and improved societal outcomes are undoubtedly significant.
7. Conclusion: Envisioning a Future Enhanced by AI in Public Policy

As we conclude our journey through the intersection of AI and public policy, it’s evident that the integration of artificial intelligence holds profound potential to revolutionize how we govern and interact with societal issues.
Through detailed exploration across various domains—analysis and development, public engagement, implementation and monitoring, predictive policymaking, and ethical considerations—we’ve uncovered AI’s immense possibilities and significant challenges.
Recapping the Potential of AI
AI’s capacity to process and analyze vast amounts of data offers unprecedented opportunities for informed decision-making.
It enables policies that are more responsive, efficient, and tailored to society’s dynamic needs.
From enhancing public engagement and participation to providing real-time insights for policy adjustments, AI technologies promise a future where governance is more accessible and impactful.
Emphasizing Responsible Integration
However, the journey toward integrating AI into public policy is fraught with challenges that must be addressed. Issues of data bias, transparency, privacy, and equity remind us of the need for a principled approach to AI deployment.
As we move forward, developing ethical frameworks and robust governance structures will be paramount to ensure that AI serves the public good, respects individual rights, and promotes societal well-being.
Encouraging Ongoing Dialogue
The future of AI in public policy is not solely dependent on technological advancements but also on the continued dialogue among policymakers, technologists, ethicists, and the public.
This conversation is essential for understanding AI’s evolving landscape, addressing concerns, and identifying opportunities for its application in governance.
Collaboration across disciplines and sectors will be crucial in harnessing AI’s potential while mitigating its risks.
The Call for Innovation and Adaptation
As AI technologies continue to evolve, so must our approaches to policy-making and governance.
This calls for ongoing innovation, not just in technology but also in our legal, ethical, and societal frameworks.
Adapting to the changes brought about by AI will require a willingness to experiment, learn, and refine our methods, ensuring that policies remain relevant and effective in the face of rapid technological change.
Looking Forward
Integrating AI into public policy represents a frontier of opportunity for enhancing governance and societal outcomes.
As we stand on the precipice of this new era, AI’s potential to contribute to better, more informed decision-making and more engaged, inclusive governance is transparent.
However, realizing this potential will demand diligence, ethical consideration, and a commitment to public engagement and transparency.
The journey ahead is both exciting and daunting, but with careful navigation, integrating AI into public policy can revolutionize governance for the betterment of society.
Let us move forward optimistically and cautiously, embracing AI’s opportunities while vigilantly addressing its challenges.
Together, we can ensure that the future of public policy is AI-enhanced but also human-centered, equitable, and just.
FAQ & Answers
1. How is AI used in public policy?
AI is employed for data-driven policy analysis, enhancing public engagement, monitoring policy implementation, and predictive policymaking, offering insights for informed decision-making and effective governance.
2. What are the challenges of implementing AI in public policy?
Challenges include addressing data biases, ensuring transparency and accountability, and managing ethical considerations related to privacy and equity.
Quizzes
Quiz 1: “AI in Public Policy” – Match AI technologies to their applications in policy-making processes.
This will help illustrate how artificial intelligence can assist in enhancing decision-making, improving transparency, and increasing efficiency in public administration.
AI Technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Predictive Analytics
- Data Visualization Tools
- Computer Vision
- Sentiment Analysis
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Public Policy Applications:
A) Policy Development: Assisting in the creation of policies by analyzing data to predict the outcomes of proposed regulations. B) Public Sentiment Analysis: Gauging public opinion on various issues from social media and other online platforms. C) Regulatory Compliance Monitoring: Ensuring policies and regulations are followed through automated analysis of data from various sources. D) Urban Planning: Using spatial data to enhance the planning and development of urban areas. E) Disaster Response: Optimizing routes and strategies for emergency response based on real-time data. F) Legislative Analysis: Automating the analysis of legal documents and bills to assist legislators in understanding potential impacts. G) Public Resource Allocation: Optimizing the distribution of public resources such as budgeting for health, education, and infrastructure.
Matches:
- Machine Learning (ML): A) Policy Development – ML algorithms can analyze complex datasets to forecast the effects of potential policies, aiding in more informed decision-making.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): F) Legislative Analysis – NLP can be employed to parse and understand complex legislative documents, simplifying the analysis process for policymakers.
- Predictive Analytics: G) Public Resource Allocation – Predictive analytics can be used to analyze past data and predict future needs, helping to allocate resources more effectively.
- Data Visualization Tools: C) Regulatory Compliance Monitoring – Visualization tools can help in monitoring compliance by providing clear and understandable representations of data, which are crucial for tracking adherence to policies and regulations.
- Computer Vision: E) Disaster Response – Computer vision can process and analyze images from drones or satellites to map disaster-impacted areas and plan effective responses.
- Sentiment Analysis: B) Public Sentiment Analysis – Sentiment analysis tools analyze public opinions expressed on social media to gauge feelings about policy issues, which can inform policy adjustments.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): D) Urban Planning – GIS uses spatial data to support the planning and development of urban infrastructure, integrating various types of data including demographic and environmental data.
These matches demonstrate the versatile applications of AI technologies in public policy, showing how they can significantly enhance the policymaking process from development to implementation and monitoring. This integration helps in making more data-driven and effective public decisions.
Quiz 2: “Policy Innovations” – A quiz on recent AI innovations in public policy and governance.
For a quiz on recent AI innovations in public policy and governance, I’ll prepare questions that focus on the transformative applications and advancements of artificial intelligence in enhancing public administration, policy-making, and service delivery. These questions will highlight how AI is being utilized to improve efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness in government operations.
Question 1: AI in Urban Planning
How is AI being used to innovate urban planning?
A) AI predicts future city populations with absolute certainty.
B) AI models traffic patterns and simulates various urban development scenarios to optimize city planning.
C) AI replaces human urban planners entirely.
D) AI is used to enforce city laws automatically without human intervention.
Question 2: Predictive Analytics in Public Health
What role does predictive analytics play in public health policy?
A) It has replaced doctors and healthcare workers.
B) It forecasts public health trends and outbreaks, helping in proactive policy formation.
C) It is used to predict the personal health issues of individuals.
D) It designs all health policies without human input.
Question 3: AI for Environmental Policy
What innovation has AI brought to environmental policy-making?
A) AI systems have completely eliminated pollution.
B) AI analyzes large datasets to predict environmental impacts and inform policy adjustments.
C) AI plants and harvests crops without human direction.
D) AI monitors individual carbon footprints in real-time.
Question 4: Machine Learning in Resource Allocation
How does machine learning contribute to public resource allocation?
A) It allocates resources based solely on historical spending.
B) It uses complex algorithms to optimize budget distribution based on predicted future needs and outcomes.
C) It eliminates the need for human financial managers.
D) It randomly distributes public resources to test economic theories.
Question 5: NLP in Legislative Processes
How is NLP utilized within legislative processes?
A) To automatically draft and enact laws without human oversight.
B) To analyze public feedback and expert testimony, helping lawmakers understand the broader implications of legislation.
C) NLP is used to create speeches for politicians.
D) It solely converts legislative documents into audio files for public distribution.
Question 6: Computer Vision in Compliance Monitoring
What is a key application of computer vision in regulatory compliance monitoring?
A) To visually identify individuals violating laws.
B) To automatically generate compliance reports without any data input.
C) To monitor infrastructural projects and ensure they adhere to environmental and safety standards.
D) It replaces all forms of human supervision in projects.
Question 7: Sentiment Analysis in Policy Feedback
What role does sentiment analysis play in gathering policy feedback?
A) It predicts whether policies will succeed or fail.
B) It provides insights into public sentiment, which can guide policy adjustments and communication strategies.
C) It enforces public sentiment on social media.
D) Sentiment analysis is used to penalize negative feedback automatically.
These questions showcase the cutting-edge developments in AI technology across public policy and governance, emphasizing how AI is streamlining processes and providing deeper insights for better decision-making.
Here are the answers to the quiz on recent AI innovations in public policy and governance:
Question 1: AI in Urban Planning
Correct Answer: B) AI models traffic patterns and simulates various urban development scenarios to optimize city planning. AI is extensively used in urban planning to model and simulate traffic patterns, which helps in designing better urban infrastructure and making informed decisions about development projects.
Question 2: Predictive Analytics in Public Health
Correct Answer: B) It forecasts public health trends and outbreaks, helping in proactive policy formation. Predictive analytics plays a crucial role in public health by using historical data and machine learning to forecast health trends and potential outbreaks, allowing governments to formulate policies proactively.
Question 3: AI for Environmental Policy
Correct Answer: B) AI analyzes large datasets to predict environmental impacts and inform policy adjustments. AI contributes to environmental policy-making by analyzing extensive environmental data, which helps predict impacts of certain actions and informs necessary policy adjustments to mitigate adverse effects.
Question 4: Machine Learning in Resource Allocation
Correct Answer: B) It uses complex algorithms to optimize budget distribution based on predicted future needs and outcomes. Machine learning aids in public resource allocation by using algorithms to analyze past data, predict future requirements, and optimize the distribution of resources like budgets, ensuring efficient and effective use.
Question 5: NLP in Legislative Processes
Correct Answer: B) To analyze public feedback and expert testimony, helping lawmakers understand the broader implications of legislation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is utilized within legislative processes to digest large volumes of public feedback and expert testimonies, which helps lawmakers grasp the broader implications and potential impacts of proposed laws.
Question 6: Computer Vision in Compliance Monitoring
Correct Answer: C) To monitor infrastructural projects and ensure they adhere to environmental and safety standards. Computer vision is applied in compliance monitoring to oversee infrastructural projects using visual data analysis, ensuring that these projects comply with environmental regulations and safety standards.
Question 7: Sentiment Analysis in Policy Feedback
Correct Answer: B) It provides insights into public sentiment, which can guide policy adjustments and communication strategies. Sentiment analysis is pivotal in evaluating public feedback on policies. It analyzes the emotional tone of public responses on social media and other platforms to provide insights that can help in refining policies and shaping effective communication strategies.
These answers underscore the profound impact of AI across various facets of public policy and governance, enhancing efficiency, predictive capabilities, and public engagement in policy-making processes.