AI in disaster management has marked a significant turning point in disaster management. Traditionally, managing natural and human-made disasters has been a reactive process, fraught with challenges in prediction, response speed, and resource allocation. However, integrating AI technologies into disaster management strategies has transformed this landscape, enabling a more proactive, precise, and efficient approach.

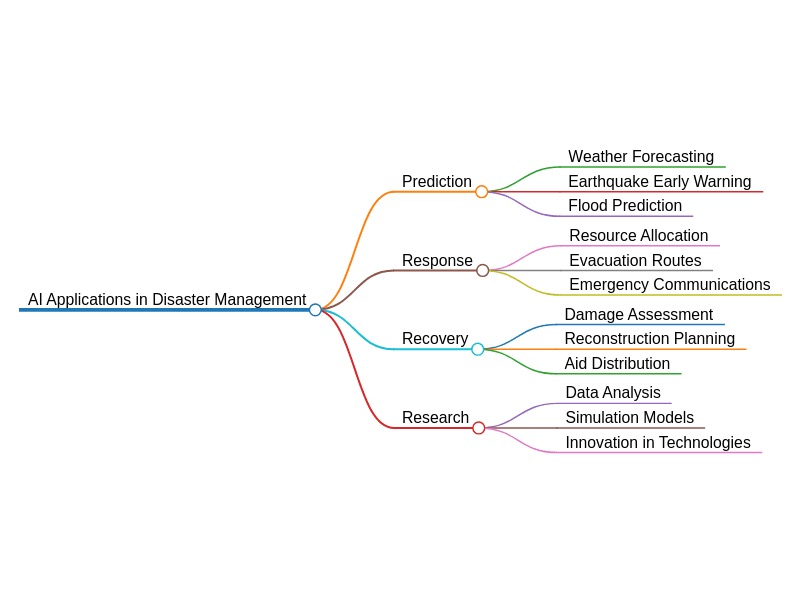
AI’s critical role in disaster management encompasses the entire cycle of disaster response, from early warning and risk assessment to emergency coordination, damage assessment, recovery planning, and providing humanitarian aid.
By leveraging AI, stakeholders can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, predict potential impacts with greater accuracy, and optimize resource allocation to effectively mitigate the effects of disasters.
The transformative impact of AI on disaster management cannot be overstated.
For instance, AI-driven early warning systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process data from various sources, including satellite imagery, weather stations, and historical disaster data.
This allows for predicting natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes, with unprecedented accuracy and timeliness.
As a result, authorities can issue warnings earlier, potentially saving lives and reducing economic losses.
Moreover, AI technologies facilitate a more coordinated response effort during disasters. By analyzing real-time data from multiple sources, AI systems can assist in making informed decisions quickly, ensuring that emergency services are deployed where needed most.
This capability is critical in managing the chaotic environments that typically follow disasters, where efficient resource distribution can significantly affect survival rates and recovery efforts.
In the aftermath of disasters, AI also plays a crucial role in damage assessment and recovery planning. By analyzing images and data collected from affected areas, AI algorithms can quickly identify the extent of damage, prioritize areas needing immediate assistance, and inform the recovery process.
This not only speeds up the response but also contributes to more effective resource use in the rebuilding phase.
Furthermore, AI’s application extends to supporting displaced populations and managing humanitarian aid.
AI-driven platforms can optimize aid distribution, ensuring resources reach those in need promptly and efficiently.
Additionally, AI can support displaced populations through information dissemination, healthcare provision, and psychological support, leveraging chatbots and virtual assistance platforms.
Despite its potential, deploying AI in disaster management is challenging.
Data accuracy, privacy concerns, the digital divide, and ethical considerations must be addressed to responsibly harness AI’s full potential.
Ensuring equitable access to AI-driven resources, maintaining transparency in AI’s decision-making processes, and safeguarding personal data are paramount concerns that need careful consideration.
In conclusion, integrating AI into disaster management represents a paradigm shift towards more resilient and effective disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
As AI technologies evolve, their potential to save lives, reduce economic losses, and support communities in the aftermath of disasters is immense.
Encouraging continuous innovation and responsible integration of AI into disaster management strategies is essential for harnessing this potential, ultimately leading to a future where the impact of disasters can be significantly mitigated.
1. AI in Early Warning and Risk Assessment
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into early warning systems and risk assessment processes significantly advances our ability to predict and mitigate the impacts of natural disasters.
These AI-driven technologies leverage vast datasets, including historical weather patterns, geological surveys, and real-time environmental monitoring, to forecast potentially catastrophic events with increasing accuracy and lead times.
AI-Driven Early Warning Systems

AI and machine learning models are improving early warning systems for various natural disasters, including earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires.
These systems analyze data from satellite imagery, seismic activity sensors, river water levels, and atmospheric data to predict the onset of natural disasters.
For instance, AI models can now predict hurricanes and their potential paths by analyzing historical data and current weather patterns, giving communities more time to prepare or evacuate.
One innovative application of AI in early warning systems is using deep learning algorithms to detect patterns indicative of earthquakes.
By analyzing seismic data in real time, these algorithms can identify the precursors to earthquakes, potentially providing crucial minutes of warning before the tremors are felt.
Similarly, in flood prediction, AI algorithms process meteorological data and historical flood information to forecast flooding events, enabling timely evacuations and the protection of vulnerable assets.
Case Studies of AI-Driven Risk Assessment Tools
- Flood Prediction in Bangladesh: Bangladesh, which is prone to severe flooding, has benefitted from AI-driven risk assessment tools. The implementation of machine learning models, which analyze data from river sensors, rainfall records, and satellite images, has enabled more accurate flood forecasting. This initiative has significantly improved communities’ preparedness and reduced the impact of floods.
- Earthquake Risk Assessment in California: California, a region with a high risk of earthquakes, has seen the development of AI models that assess the risk of earthquake-induced damage to buildings and infrastructure. These models use data from past earthquakes, building materials, and construction practices to predict potential damage, guiding emergency services and urban planning efforts to mitigate risk effectively.
- Wildfire Prediction in Australia: In Australia, AI algorithms are being used to predict the outbreak and spread of wildfires. By analyzing factors such as temperature, humidity, vegetation type, and wind patterns, these models can forecast high-risk areas and likely paths of wildfires, aiding in fire prevention efforts and the strategic deployment of firefighting resources.
2. Effectiveness in Disaster Mitigation

The effectiveness of AI-driven early warning systems and risk assessment tools is evident in their ability to provide actionable intelligence before disasters.
These technologies have proven instrumental in saving lives, protecting property, and reducing economic losses.
The key to their effectiveness lies in continuously improving AI models through the incorporation of new data and advanced machine learning techniques, which enhances their predictive accuracy over time.
Moreover, deploying AI in risk assessment has empowered governments, NGOs, and communities with valuable insights for better planning and preparedness.
By identifying high-risk zones and potential disaster impacts, stakeholders can prioritize mitigation efforts, invest in resilient infrastructure, and develop comprehensive evacuation plans.
In conclusion, AI’s contribution to early warning and risk assessment represents a quantum leap in our capacity to foresee and mitigate natural disasters.
By adopting AI-driven technologies, the global community can enhance its resilience against the inevitable challenges posed by natural disasters, safeguarding lives and livelihoods with greater efficacy than ever before.
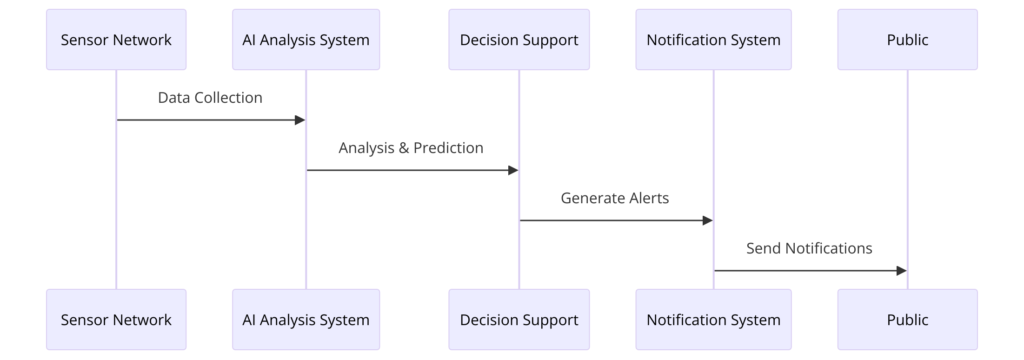
3. AI in Emergency Response Coordination
The deployment of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in emergency response coordination represents a pivotal shift towards more efficient and effective disaster management.
By leveraging AI technologies, emergency response teams can optimize their strategies, ensuring rapid, targeted, and well-coordinated actions after disasters.
Optimizing Emergency Response Strategies
AI technologies offer unparalleled capabilities in processing and analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time, which is crucial for emergency response coordination.
During disasters, the situation can change rapidly, and access to accurate, up-to-date information is vital for practical response efforts.
AI systems can integrate data from various sources, including satellite imagery, social media, emergency call logs, and sensor networks, to provide a comprehensive picture of the disaster’s impact.
Machine learning algorithms can predict the evolution of ongoing disasters, such as the spread of wildfires or the progression of a flood, allowing responders to anticipate changes and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Furthermore, AI can assist in resource allocation by determining the most critical needs and prioritizing deploying resources such as medical supplies, food, water, and rescue teams to the most needed areas.
AI Applications in Coordinating Rescue and Relief Operations
- Drone Surveillance and Search Operations: AI-powered drones have become invaluable search and rescue operations tools. These drones, equipped with cameras and sensors, can quickly cover vast areas, identifying stranded or injured individuals in remote or inaccessible regions. AI algorithms analyze the drone-captured imagery in real time, enabling the rapid deployment of rescue teams to specific locations.
- AI-Driven Communication Platforms: Communication between different response teams and affected communities can be challenging in the chaos that often follows disasters. AI-driven communication platforms can streamline information sharing, ensuring all parties can access timely and accurate data. Natural language processing (NLP) technologies enable the analysis of incoming reports from various sources, automatically categorizing and routing information to the relevant responders.
- Resource Distribution and Logistics: AI is crucial in optimizing resource distribution logistics. By analyzing data on road conditions, affected populations, and available resources, AI algorithms can plan the most efficient routes for delivering aid. This ensures that help reaches those in need as quickly as possible, reducing the risk of secondary crises, such as disease outbreaks due to lack of clean water or medical supplies.
Examples of AI Applications in Emergency Response
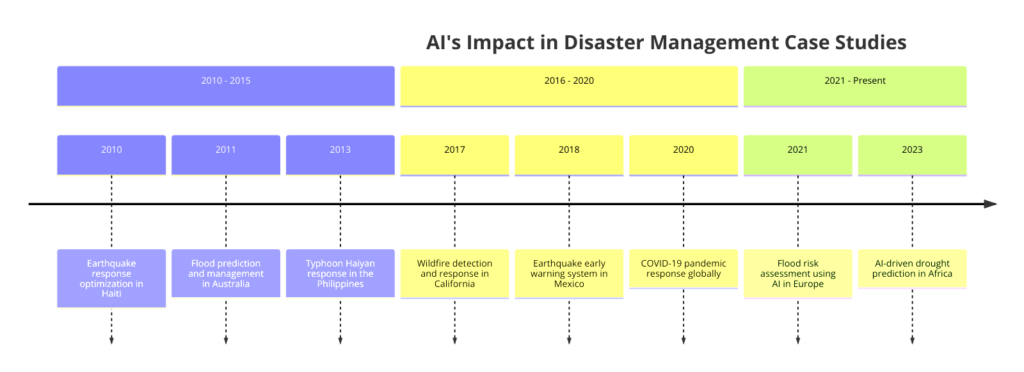
- Earthquake Response in Mexico: Following a significant earthquake, AI technologies were used to quickly analyze social media and emergency call data to identify the hardest-hit areas. This information enabled a more focused deployment of rescue teams and resources, significantly improving the response efforts.
- Flood Relief Coordination in India: In response to severe flooding, AI-driven tools were deployed to manage the logistics of aid distribution. By predicting flood progression and analyzing affected regions, AI algorithms helped to ensure that supplies like food, water, and medicines were efficiently distributed to displaced populations.
- Wildfire Management in the United States: During recent wildfires, AI was utilized to predict fire spread, enabling preemptive evacuations and the strategic positioning of firefighting resources. Drones, guided by AI, provided real-time surveillance, aiding containment efforts and minimizing damage.
The utilization of AI in emergency response coordination has dramatically enhanced the capacity of response teams to act swiftly and effectively in the face of disasters.
By harnessing the power of AI, emergency response strategies can be continuously improved, ensuring that when disasters strike, the most vulnerable are reached with the help they need promptly and efficiently.
As AI technologies evolve, their potential to save lives and mitigate the impact of disasters grows, marking a new era in disaster management where technology and human ingenuity converge to foster resilience and hope amidst adversity.
4. AI in Damage Assessment and Recovery Planning

The aftermath of disasters presents a complex challenge, requiring rapid assessment of damage to prioritize response efforts and plan recovery strategies.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative tool, offering capabilities to analyze post-disaster damage and efficiently plan recovery and rebuilding processes.
Role of AI in Analyzing Post-Disaster Damage
A quick and accurate damage assessment is crucial for effective response and recovery planning in the immediate aftermath of a disaster.
AI technologies, particularly those involving image recognition and processing, play a pivotal role in this process.
By analyzing satellite imagery, aerial drone footage, and other visual data, AI algorithms can quickly identify areas of destruction, quantify damage, and categorize affected structures and infrastructure.
These AI systems can process vast amounts of data much faster than human analysts, providing emergency responders and recovery planners with timely information.
This rapid assessment allows for a more directed response, ensuring that resources such as medical aid, shelter, and repair crews are allocated efficiently and to the most needy areas.
Innovations in AI for Efficient Disaster Recovery Planning
AI’s contribution to disaster recovery planning extends beyond initial damage assessment.
By leveraging predictive analytics and machine learning models, AI can forecast a disaster’s long-term impacts on a community, including economic disruptions, potential for secondary disasters, and long-term housing needs.
This foresight enables planners to devise responsive and proactive recovery strategies that address immediate needs while laying the groundwork for sustainable rebuilding and resilience against future disasters.
- Infrastructure and Urban Planning: AI models can analyze damage data alongside urban planning databases to recommend the most effective reconstruction strategies, incorporating resilience against future disasters. This includes advising on rebuilding infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utilities, to enhance their durability and reduce vulnerability to future events.
- Resource Optimization: AI-driven tools can optimize resource allocation throughout the recovery process. By modeling different recovery scenarios, these tools can help decision-makers prioritize investments in reconstruction efforts, ensuring that limited resources are used efficiently to support the most critical recovery activities.
- Community Support and Resilience Building: AI applications extend to supporting affected communities through recovery and beyond. This includes AI-driven platforms for managing and distributing aid and tools for engaging communities in the recovery process, ensuring that rebuilding efforts align with the residents’ needs and priorities.
Examples of AI in Damage Assessment and Recovery
- Earthquake Recovery in Nepal: Following a devastating earthquake, AI-powered analysis of satellite images assessed structural damage across remote areas. This rapid assessment was crucial in directing aid and reconstruction efforts, significantly speeding up the recovery process.
- Hurricane Damage in the Caribbean: In the wake of a powerful hurricane, AI algorithms analyzed drone-captured imagery to map the extent of damage to critical infrastructure. This information guided the strategic deployment of repair teams to restore essential services, such as electricity and water, in a prioritized manner.
- Flood Recovery Planning in Europe: AI models were employed to evaluate the impact on residential areas and predict future flooding risks after severe flooding. This informed the development of recovery plans that included measures to increase flood resilience, such as redlining water management systems and reinforcing levees.
AI’s role in damage assessment and recovery planning illustrates its potential to respond to disasters more effectively and anticipate and mitigate future risks.
The application of AI technologies in the aftermath of disasters can significantly accelerate the recovery process, ensuring that affected communities can rebuild stronger and more resiliently.
As AI continues to evolve, its integration into disaster management strategies promises a future where the impact of disasters can be substantially reduced, fostering more resilient societies capable of withstanding the challenges of an increasingly unpredictable world.
5. AI in Humanitarian Aid and Support

The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in humanitarian aid and support represents a critical evolution in how assistance is provided to communities affected by disasters.
AI technologies offer innovative solutions to manage and distribute aid more effectively, ensuring that resources reach those most in need.
Additionally, AI-driven platforms support displaced populations, addressing their immediate needs and contributing to their long-term well-being.
Managing and Distributing Humanitarian Aid
Efficient management and distribution of humanitarian aid are paramount in the aftermath of a disaster. AI can significantly enhance these processes through predictive analytics, logistics optimization, and needs assessment algorithms.
By analyzing data from various sources, including social media, satellite imagery, and on-the-ground sensors, AI models can predict which areas will need the most support and what kind of aid is required, from medical supplies to food and water.
Logistics optimization algorithms are crucial in ensuring that aid is distributed efficiently.
These algorithms analyze factors such as road conditions, weather forecasts, and the availability of transportation resources to determine the best routes for delivering aid.
This speeds up the delivery process and minimizes waste by ensuring that resources are allocated where they are needed most.
AI-Driven Platforms for Supporting Displaced Populations
Disasters often result in significant displacement, with communities losing their homes and livelihoods. AI-driven platforms can offer crucial support to these displaced populations in several ways:
- Tracking and Reunification: AI-powered systems can help track displaced individuals and reunite families separated during disasters. By processing data from registration centers, social media, and other sources, these systems can identify and match records of missing persons, facilitating faster reunification efforts.
- Virtual Healthcare Services: AI can provide displaced populations access to virtual healthcare services, including mental health support. Through chatbots and telemedicine platforms, individuals can receive medical consultations, psychological counseling, and health-related information, addressing the gap in physical healthcare infrastructure.
- Education and Employment Opportunities: AI platforms can support displaced populations by offering online education and job-matching services. These platforms use AI to match individuals’ skills and experiences with available educational resources and employment opportunities, helping them rebuild their lives.
Examples of AI Applications in Humanitarian Aid and Support
- Aid Distribution in Conflict Zones: In conflict-affected regions, AI-driven drones have been used to map safe routes for delivering aid. Additionally, AI algorithms analyze risk factors to ensure that aid convoys avoid danger zones, enabling the safe delivery of supplies to besieged communities.
- Support for Refugees: AI platforms have been deployed in refugee camps to provide educational services and psychological support. By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning, these platforms offer personalized learning experiences and mental health counseling, significantly improving refugees’ well-being.
- Natural Disaster Response: AI-powered platforms have been utilized to manage aid distribution following natural disasters. By analyzing data on affected populations and available resources, these platforms optimize the allocation and delivery of supplies, ensuring that assistance reaches those in need promptly.
Integrating AI in humanitarian aid and support can transform disaster response efforts, making them more efficient, effective, and responsive to the needs of affected populations.
By leveraging AI for logistics optimization, needs assessment, and the provision of support services, humanitarian organizations can significantly improve the quality and speed of their response.
As AI technologies continue to advance, their application in humanitarian contexts promises to enhance the resilience of communities against future disasters, ensuring that aid and support are delivered where they are needed most in a manner that upholds dignity and promotes the recovery of those affected.
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI Deployment for Disaster Management

Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into disaster management brings significant benefits, from improving early warning systems to enhancing response coordination and aiding recovery efforts.
However, deploying AI in this critical domain also presents challenges and ethical considerations that must be carefully navigated to ensure the technology’s responsible and effective use.
Challenges in Deploying AI for Disaster Management
- Data Accuracy and Reliability: One of the foundational challenges in utilizing AI for disaster management is ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data used to train AI models. Only accurate, complete, and biased data can lead to incorrect predictions, potentially exacerbating the situation by misguiding response efforts.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of AI in disaster management often involves collecting, analyzing, and sharing individuals’ data, raising significant privacy concerns. Ensuring that sensitive information is protected and that data collection and processing practices comply with privacy laws and ethical standards is crucial.
- Digital Divide: The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals and communities with access to modern information and communication technology and those without. This divide can limit the effectiveness of AI-driven disaster management initiatives, as those most in need of assistance may be the least likely to benefit from these advancements due to lack of access to technology.
Ethical Considerations in AI Use for Disaster Response
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency in how AI systems make decisions and establishing clear lines of accountability for those decisions are essential ethical considerations. Stakeholders should understand how AI models are developed, the data they use, and the rationale behind their predictions and recommendations.
- Equity and Fairness: AI-driven disaster management efforts must be designed to ensure equity and fairness. This means ensuring that AI technologies do not inadvertently prioritize certain groups over others or exacerbate existing inequalities in disaster response and recovery efforts.
- Informed Consent: Where personal data is involved, obtaining informed consent from individuals whose data is collected and used is an ethical imperative. This is particularly challenging in disaster contexts, where obtaining consent may be difficult due to the urgency and scale of the situation.
Navigating Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Addressing these challenges and ethical considerations requires a multifaceted approach:
- Robust Data Governance: Establishing strong data governance frameworks can help ensure data accuracy and protect privacy. This includes implementing data quality checks, ensuring data anonymization where possible, and adhering to international data protection regulations.
- Inclusive Design and Deployment: AI systems should be designed and deployed to bridge the digital divide. This could involve developing low-tech solutions that can be accessed without the latest technology or ensuring that AI-driven services are available in multiple languages and accessible formats.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with communities, disaster response organizations, policymakers, and ethicists in the development and deployment of AI solutions can help identify potential ethical issues and ensure that systems are designed with fairness and inclusivity in mind.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: AI systems should be continuously monitored and evaluated to ensure they perform as intended and not causing unintended harm. This includes revising models as new data becomes available and being prepared to adjust or withdraw AI solutions if they are found to exacerbate vulnerabilities.
The deployment of AI in disaster management offers transformative potential to save lives, reduce suffering, and accelerate recovery.
However, realizing this potential requires careful attention to the challenges and ethical considerations associated with using AI.
By adopting a responsible and inclusive approach to AI deployment, disaster management professionals can harness the power of AI to enhance disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts while ensuring that the technology serves the needs and respects the rights of all affected individuals.
7. The Future of AI in Disaster Management

The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into disaster management is poised for transformative growth.
Emerging trends and advancements suggest a future where AI not only augments current practices but revolutionizes how societies prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters.
Predictions for AI Evolution in Disaster Management
- Enhanced Predictive Analytics: AI’s capacity for predictive analytics is expected to grow significantly, leveraging more sophisticated models and more prominent, diverse datasets. This will improve the accuracy and timeliness of disaster predictions, from forecasting extreme weather events with more excellent lead times to predicting the outbreak and spread of wildfires with unprecedented precision.
- Autonomous Response Systems: Future developments may see fully autonomous AI-driven systems deployed for immediate disaster response. These systems could include autonomous drones for search and rescue missions, robotic units for delivering aid in hazardous conditions, and automated infrastructure shutdowns to prevent further damage.
- Integrated AI Platforms: The future of disaster management will likely feature integrated AI platforms that combine data from various sources, including satellite imagery, social media, IoT devices, and more. These platforms will offer real-time, holistic views of disaster impacts, enabling coordinated response efforts across agencies and organizations.
Emerging Trends and Advancements
- Quantum Computing: Integrating quantum computing into AI could drastically reduce the time needed for data processing and analysis, allowing for near-instantaneous decision-making in disaster scenarios. This could significantly enhance early warning systems and dynamic resource allocation during emergency responses.
- Blockchain for Data Integrity: Blockchain technology could ensure the integrity and security of data used in AI-driven disaster management. By creating immutable records of data and transactions, blockchain can enhance trust in AI predictions and decisions and facilitate more effective coordination among stakeholders.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for Training and Response: AR technology, combined with AI, could revolutionize disaster response training by simulating complex emergency scenarios. Additionally, AR can support responders in the field by overlaying vital information, such as safe routes and hazard locations, onto their real-world view.
Challenges and Considerations for the Future
As AI technologies advance, addressing data privacy challenges, ethical AI use, and ensuring equitable access remains crucial.
The future of AI in disaster management must be guided by principles of transparency, accountability, and inclusivity, ensuring that technological advancements benefit all segments of society, particularly those most vulnerable to disasters.
Moreover, integrating advanced AI technologies requires robust infrastructure and significant investment in research and development.
Collaborative efforts among governments, the private sector, academia, and non-profit organizations will be essential to harnessing AI’s full potential in disaster management.
The future of AI in disaster management holds promising prospects for enhancing the efficacy and efficiency of disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
By embracing emerging trends and advancements in AI, alongside addressing associated challenges and ethical considerations, the field can move towards a future where the impact of disasters is significantly mitigated.
Continuous innovation and responsible integration of AI technologies will be vital to realizing this vision, fostering a safer, more resilient world in the face of natural and human-made disasters.
8. Conclusion: AI’s Vital Role in Advancing Disaster Management Practices
The exploration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) within disaster management reveals a landscape rich with potential and marked by transformative advancements.
AI’s integration across the spectrum of disaster preparedness, response, recovery, and humanitarian support underscores its indispensable role in shaping future disaster management strategies.
This concluding section encapsulates the significant contributions of AI to disaster management, reiterating the importance of continuous innovation and responsible integration to harness its full potential.
AI technologies have proven to be a game-changer in enhancing the ability of communities and nations to respond to natural and human-made disasters more effectively.
From predictive analytics that enable early warning systems to sophisticated algorithms that optimize emergency response and recovery efforts, AI has demonstrated its capacity to save lives, reduce economic losses, and support affected populations in their most vulnerable moments.
The application of AI in early warning and risk assessment has transformed how disasters are predicted and prepared for, offering unprecedented accuracy and lead times.
In emergency response coordination, AI-driven platforms and tools have facilitated more efficient and targeted deployment of resources, ensuring that aid reaches those in need swiftly and effectively.
Moreover, in the aftermath of disasters, AI’s role in damage assessment and recovery planning has been invaluable, providing critical insights that guide rebuilding efforts and contribute to the resilience of communities.
The utilization of AI in managing humanitarian aid and supporting displaced populations further illustrates its capacity to address complex challenges with innovative solutions.
Through optimized logistics, virtual healthcare, and support services, AI technologies have brought new dimensions to the delivery of humanitarian aid, emphasizing the importance of technology in fostering humanitarian principles.
However, deploying AI in disaster management has challenges and ethical considerations.
Data accuracy, privacy concerns, the digital divide, and the need for transparency and accountability in AI decision-making processes highlight the complexities of integrating advanced technologies into highly sensitive and impactful areas.
Addressing these challenges through robust data governance, inclusive design, stakeholder engagement, and continuous monitoring is essential to ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of AI in disaster management holds promising prospects for further innovations and advancements.
The potential integration of emerging technologies like quantum computing, blockchain, and augmented reality offers exciting opportunities to enhance the efficacy and efficiency of disaster management practices.
Yet, harnessing AI’s full potential in this field requires a commitment to ethical principles, collaborative efforts, and sustained investment in research and development.
In conclusion, AI is a pivotal force in advancing disaster management practices, offering tools and insights that can significantly mitigate disaster impacts.
Encouraging continuous innovation and responsible integration of AI technologies is crucial for developing more resilient societies capable of withstanding the challenges posed by natural and human-made disasters.
As we move forward, the collective effort of the global community in embracing and advancing AI in disaster management will be instrumental in protecting lives, preserving livelihoods, and promoting the well-being of affected populations worldwide.
FAQ & Answers
1. How is AI used in disaster management?
AI is utilized for early warning systems, emergency response coordination, damage assessment, recovery planning, and humanitarian aid distribution, significantly improving the efficiency and effectiveness of disaster management efforts.
2. What are the challenges of using AI in disaster management?
Challenges include ensuring data accuracy and privacy, overcoming technological barriers, and addressing ethical concerns related to AI deployment in emergency situations.
Quizzes
Quiz 1: “AI in Disaster Scenarios” – Match AI technologies to their applications in disaster management scenarios.
For a quiz on “AI in Disaster Scenarios,” we’ll examine different AI technologies and match them with their appropriate applications in disaster management. This will help demonstrate how AI can play a crucial role in enhancing response strategies, improving resilience, and increasing efficiency in times of crises.
AI Technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Computer Vision
- Deep Learning (DL)
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Predictive Analytics
- Drones and Robotics
Disaster Management Applications:
A) Damage Assessment: Rapid evaluation of affected areas to identify damages and prioritize response efforts.
B) Crisis Mapping: Creating detailed maps to visualize the extent of disaster impacts and aid in planning rescue missions.
C) Search and Rescue Operations: Enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of search and rescue missions.
D) Real-Time Communication: Facilitating effective communication between different agencies and affected populations.
E) Early Warning Systems: Providing timely alerts to populations about impending disasters.
F) Resource Allocation: Optimizing the distribution of limited resources to areas where they are needed most.
G) Survivor Detection: Locating people in disaster-struck areas using advanced imaging technologies.
Matches:
- Machine Learning (ML): E) Early Warning Systems – ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets from various sources to predict disasters before they occur, providing critical early warnings.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): D) Real-Time Communication – NLP can be used to interpret and translate communications across different languages in real-time, facilitating clearer and faster interactions during emergencies.
- Computer Vision: A) Damage Assessment – Computer vision technologies enable rapid and accurate analysis of visual data to assess damage following disasters.
- Deep Learning (DL): G) Survivor Detection – Deep learning models, particularly those trained on image recognition, are crucial for identifying survivors in complex disaster environments.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): B) Crisis Mapping – GIS integrates with AI to produce dynamic maps that reflect real-time conditions, helping in strategic planning and execution of disaster response.
- Predictive Analytics: F) Resource Allocation – Predictive analytics uses data to forecast needs and optimize the distribution of resources like food, water, and medical supplies during disasters.
- Drones and Robotics: C) Search and Rescue Operations – Drones and robotic systems, often enhanced with AI, are employed to navigate disaster-hit areas, providing live feedback and assisting in rescue operations.
These matches show how AI technologies are employed across different facets of disaster management, from prediction and planning to actual response efforts. They highlight the potential of AI to significantly improve disaster resilience and response capabilities, reducing the impact on human life and property.
Quiz 2: “Innovations in Disaster Management” – A quiz on recent AI innovations in the field of disaster management.
For a quiz on recent AI innovations in the field of disaster management, I’ll formulate questions that highlight new technological advancements and applications of artificial intelligence that have significantly enhanced the capabilities in managing and responding to disasters.
Question 1: AI for Early Warning Systems
What innovation has AI brought to early warning systems for natural disasters? A) AI has enabled the use of social media data to enhance prediction accuracy. B) AI can predict disasters with 100% accuracy, eliminating all risk. C) AI replaces all traditional sensors and monitoring equipment. D) AI has introduced virtual reality simulations to replace real-time alerts.
Question 2: AI-Enhanced Drones for Disaster Response
How are AI-enhanced drones used in disaster response? A) To deliver internet service to disaster areas. B) To replace all ground-based emergency responders. C) To provide real-time data and imagery, supporting search and rescue operations. D) To control weather patterns and prevent disasters.
Question 3: Machine Learning in Flood Forecasting
What role does machine learning play in flood forecasting? A) It completely eliminates the occurrence of floods. B) It uses historical data and real-time inputs to predict flood events and their potential impacts. C) It is used to build physical barriers against floods automatically. D) Machine learning is involved in redirecting water flows physically.
Question 4: Computer Vision in Damage Assessment
What is a key application of computer vision in post-disaster scenarios? A) To replace all human assessments and decisions in damage evaluation. B) To automate the visual assessment of damage, quickly identifying affected areas and quantifying damage levels. C) To create holographic images of disasters for media. D) To project visual simulations of possible future disasters.
Question 5: Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Emergency Communication
How is NLP utilized in emergency communication systems? A) NLP translates emergency broadcasts into all languages instantly. B) NLP is used to generate fictional disaster scenarios for training. C) It enables the automatic detection and dissemination of emergency notifications across various platforms. D) NLP replaces all forms of traditional communication in emergencies.
Question 6: Predictive Analytics for Resource Allocation
How does predictive analytics improve resource allocation during disasters? A) It predicts the exact timing and location of future disasters. B) It ensures an infinite supply of resources. C) It uses data-driven insights to optimize the distribution of resources based on predicted needs and impacts. D) Predictive analytics are used to create resource allocation simulations only.
Question 7: AI Applications in Crisis Mapping
What recent innovation has AI introduced in crisis mapping? A) AI has replaced maps with GPS-only navigation systems. B) AI integrates real-time data from multiple sources to update maps dynamically, aiding in effective response planning. C) AI creates virtual landscapes that replace real environments. D) AI has eliminated the need for maps in disaster management.
These questions explore how AI technologies are currently enhancing various aspects of disaster management, from predictive capabilities and resource allocation to real-time operational support. They emphasize the critical role of AI in improving responses to and preparations for disasters.
Here are the answers to the quiz on recent AI innovations in the field of disaster management:
Question 1: AI for Early Warning Systems
Correct Answer: A) AI has enabled the use of social media data to enhance prediction accuracy. AI innovations in early warning systems include leveraging social media and other non-traditional data sources to improve the accuracy and timeliness of predictions for natural disasters.
Question 2: AI-Enhanced Drones for Disaster Response
Correct Answer: C) To provide real-time data and imagery, supporting search and rescue operations. AI-enhanced drones are crucial in disaster response for providing immediate aerial views, assessing damage, and locating survivors, thereby supporting effective and efficient search and rescue efforts.
Question 3: Machine Learning in Flood Forecasting
Correct Answer: B) It uses historical data and real-time inputs to predict flood events and their potential impacts. Machine learning improves flood forecasting by analyzing patterns in historical data and real-time environmental inputs, helping to predict flood events and their potential severity with greater accuracy.
Question 4: Computer Vision in Damage Assessment
Correct Answer: B) To automate the visual assessment of damage, quickly identifying affected areas and quantifying damage levels. Computer vision technologies enable the automated analysis of images and videos to assess damage quickly and accurately, which is essential for rapid response and recovery efforts.
Question 5: Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Emergency Communication
Correct Answer: C) It enables the automatic detection and dissemination of emergency notifications across various platforms. NLP is utilized in emergency communication systems to automatically interpret, translate, and distribute emergency information across different languages and platforms, enhancing the reach and effectiveness of alerts.
Question 6: Predictive Analytics for Resource Allocation
Correct Answer: C) It uses data-driven insights to optimize the distribution of resources based on predicted needs and impacts. Predictive analytics aids in disaster management by analyzing various data sources to forecast needs and optimize the allocation of resources like food, water, and medical supplies to areas where they are most needed.
Question 7: AI Applications in Crisis Mapping
Correct Answer: B) AI integrates real-time data from multiple sources to update maps dynamically, aiding in effective response planning. Recent innovations in AI for crisis mapping involve integrating data from various sources, including satellites, drones, and on-the-ground sensors, to create dynamic maps that reflect real-time conditions, significantly aiding in disaster response and planning.
These answers highlight the transformative impact of AI on disaster management, showcasing how advancements in technology can significantly improve preparedness, response, and recovery efforts in the face of natural and human-made disasters.