
Cognitive AI represents a significant leap forward in the quest to imbue machines with human-like understanding and reasoning capabilities. At its core, AI seeks to simulate human thought processes in a computerized model, enabling machines to solve complex problems, make decisions, and learn from experiences in a way that mirrors human cognition. This advanced form of AI goes beyond executing programmed tasks, venturing into the realm of understanding context, processing natural language, recognizing patterns, and even exhibiting emotional intelligence in interactions.
1. Introduction to Cognitive AI
Cognitive Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a big step forward in making machines think and reason like humans.
It helps computers solve problems, make decisions, and learn from experiences similar to how people do.
This advanced AI goes beyond simple tasks, understanding context, processing language, recognizing patterns, and even showing some emotional intelligence in interactions.
Cognitive AI is important because it changes machines from just doing tasks to thinking and interacting like humans.
This has a huge impact on technology and society, revolutionizing industries, improving decision-making, and creating more natural ways for people to interact with computers.
Cognitive AI combines insights from neuroscience, psychology, computer science, and data analytics to create systems that can perform complex cognitive functions.
This includes understanding language, recognizing images, solving problems, and learning from data. Developing Cognitive AI involves integrating machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and data analytics to mimic human thought processes.
Advancements in computing power, data availability, and AI research have fueled the evolution of Cognitive AI.
These advancements have allowed systems to not only process information but also understand and interpret it in context.
As a result, Cognitive AI systems can engage in sophisticated interactions, make informed decisions, and provide valuable insights.
Cognitive AI is more than just technology; it’s a collaboration between human and artificial intelligence. It enhances human capabilities and can help solve complex challenges in healthcare, environmental conservation, education, and economic development.
Exploring Cognitive AI’s potential, applications, challenges, and future directions gives us a glimpse into a future where machines not only assist but also enhance human efforts.
Understanding Cognitive AI isn’t just about creating thinking machines; it’s about exploring the nature of intelligence and the future of human-machine collaboration.
2. Evolution of Cognitive AI
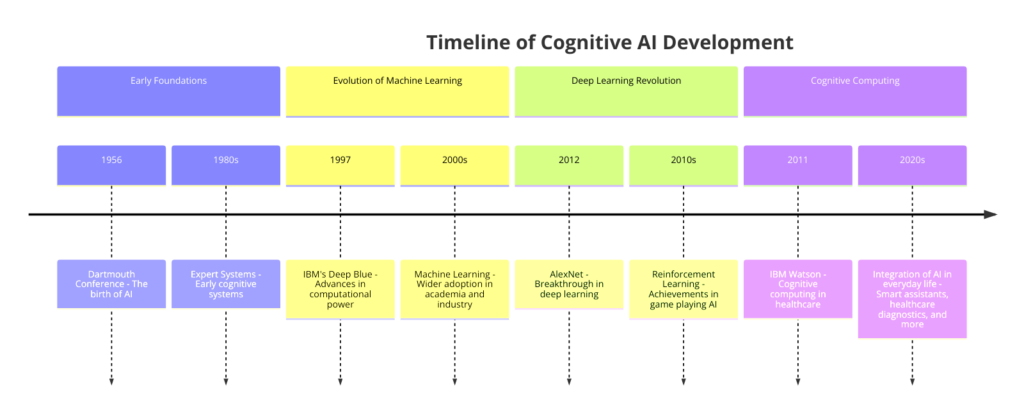
The journey of Cognitive AI reflects humanity’s ongoing quest to understand and replicate intelligence in machines. This evolution traces back to the early days of computing and spans decades of innovation and research.
Historical Background: The idea of machines mimicking human intelligence goes back to early computing pioneers like Alan Turing, who questioned whether machines could think. The 1950s and 1960s saw the birth of AI as a field, with researchers exploring symbolic AI and rule-based systems for logical reasoning. However, limitations in computing power and understanding of cognition led to “AI winters,” periods of slowed progress and skepticism.
Key Advancements: Interest in AI revived in the late 20th and early 21st centuries due to improvements in computing power, data availability, and new algorithms. The shift from rule-based systems to machine learning models, which learn from data, marked significant progress in achieving cognitive capabilities in AI.
Milestones in Cognitive AI:
- IBM Watson’s Victory in Jeopardy! (2011): IBM Watson’s win in the quiz show Jeopardy! showed Cognitive AI’s ability to understand natural language, process vast information, and make decisions under pressure.
- Rise of Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant demonstrated AI’s ability to understand and respond to natural language, making AI part of everyday life.
- Advancements in Neural Networks: Technologies like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image processing and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sequence analysis have been crucial in advancing Cognitive AI.
The evolution of Cognitive AI reflects a combination of technological advancements, theoretical insights, and practical applications. From early attempts at logical reasoning to today’s deep learning and neural networks, Cognitive AI’s development has been driven by understanding human intelligence and enhancing machine capabilities. Each milestone has pushed the boundaries of machine abilities and deepened our understanding of human cognition. The future of Cognitive AI holds even more potential for significant impacts on technology and society.
3. Core Technologies Behind Cognitive AI

Cognitive AI combines multiple technologies to simulate human-like thought processes in machines. These core technologies include machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), data analytics, and neural networks.
Machine Learning and Data Analytics: Machine learning allows systems to learn from data and improve over time without explicit programming for each task. Data analytics provides insights and patterns that machine learning algorithms use to make decisions. Together, they form the foundation of cognitive systems, enabling pattern recognition, outcome prediction, and insight derivation from vast data amounts.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is crucial for machines to understand and generate human language. It includes tasks like speech recognition, text analysis, sentiment analysis, and language translation. NLP enables Cognitive AI systems to process and interpret human communication, engaging in human-like dialogues. Advances in NLP have been key to developing virtual assistants and chatbots.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning: Neural networks, inspired by the human brain, are pivotal in Cognitive AI. They consist of interconnected nodes that process input data, learning to recognize patterns. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning with many neural network layers, has dramatically improved Cognitive AI capabilities. Deep learning algorithms excel at tasks like image and speech recognition, central to developing systems that perceive and interpret the world.
Simulating Human Thought Processes: The goal of Cognitive AI is to simulate human thought processes, requiring various AI technologies. Beyond machine learning, NLP, and neural networks, Cognitive AI systems incorporate reasoning, problem-solving, and even emotional intelligence. Techniques like reinforcement learning (learning through trial and error) and transfer learning (applying knowledge from one domain to another) further enhance AI cognitive capabilities.
Neural networks play a crucial role in simulating human thought by mimicking brain processes, enabling systems to learn and think similarly to humans. This has led to significant advancements in creating AI systems that process information, understand context, make judgments, and learn from experiences.
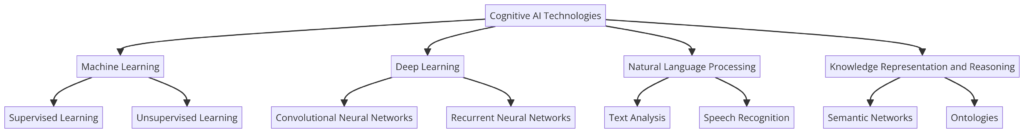
The core technologies behind Cognitive AI—machine learning, NLP, data analytics, and neural networks—represent the forefront of AI research and development. They enable systems to understand, learn, and interact with the world, once the domain of human intelligence. As these technologies evolve, so will Cognitive AI capabilities, promising a future where machines assist, augment, and potentially surpass human cognitive abilities in some tasks.
4. Applications of Cognitive AI
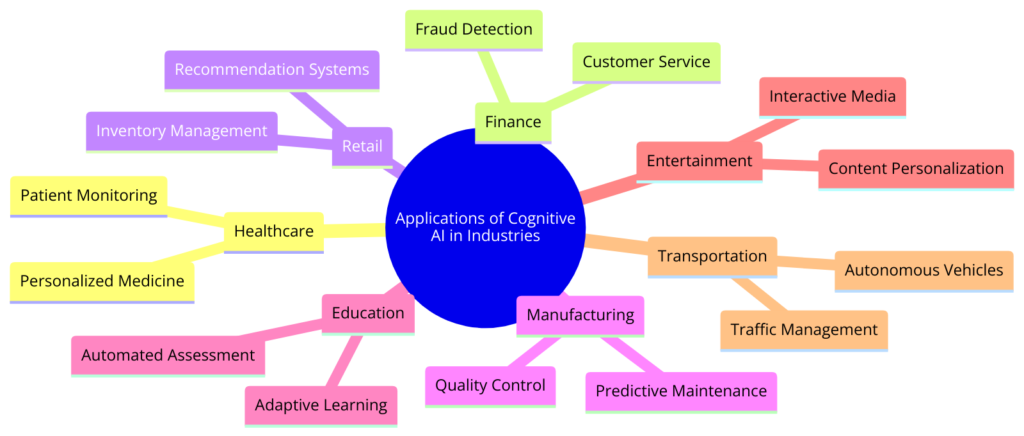
Cognitive AI is transforming various industries by improving operations, decision-making, and customer experiences. By leveraging cognitive technologies, businesses can use vast data to gain insights and automate complex tasks.
Healthcare: Cognitive AI aids in diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. AI systems analyze medical images, genetic information, and clinical data for early diagnosis and personalized medicine. Virtual health assistants provide 24/7 support, offering patients guidance and reminders.
Finance and Banking: Cognitive AI is used for fraud detection, risk management, and customer service. AI analyzes transaction patterns and customer behavior to identify fraud and assess credit risks accurately. Cognitive chatbots and virtual assistants offer personalized financial advice and support.
Education: Cognitive AI provides personalized learning experiences by assessing students’ strengths and weaknesses, adapting content and teaching methods. This personalized approach addresses learning gaps and enhances engagement. AI also automates administrative tasks, allowing educators to focus on teaching.
Retail and E-Commerce: Cognitive AI enhances customer engagement and streamlines operations in retail. Personalized shopping recommendations, inventory management, and supply chain optimization drive efficiency and satisfaction. Virtual shopping assistants offer real-time help and advice.
Manufacturing: Cognitive AI improves productivity, quality control, and maintenance in manufacturing. AI systems monitor equipment and predict failures, reducing downtime and costs. AI-driven quality inspection systems identify defects better than human inspectors.
Transportation and Logistics: Cognitive AI optimizes routing, fleet management, and logistics, leading to cost savings and efficiency. AI analyzes traffic data and weather to optimize routes, reducing fuel consumption and improving delivery times.
Case Studies:
- IBM Watson Health: Uses Cognitive AI to analyze medical data, assisting doctors in diagnosing diseases and recommending personalized treatments.
- AlphaGo by DeepMind: Demonstrated Cognitive AI’s potential by mastering the game of Go, outperforming world champions through learning and strategic reasoning.
Challenges in Deployment: Deploying Cognitive AI comes with challenges, including ensuring data privacy, managing biases in AI algorithms, and integrating cognitive systems into existing workflows without disruption.
Conclusion: Cognitive AI’s applications demonstrate its versatility and potential to drive innovation. By simulating human thought processes, Cognitive AI offers intelligent, adaptive solutions. As technology advances, Cognitive AI’s application scope will expand, opening new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and improved decision-making across industries.
5. Challenges in Cognitive AI

While Cognitive AI has great potential, it faces many challenges, from technical issues to ethical and societal concerns.
Technical Hurdles:
- Complexity of Human Cognition: Simulating complex human thought processes like understanding context, emotional intelligence, and creative thinking is tough.
- Data Quality and Availability: Cognitive AI needs vast, high-quality data to learn and make accurate decisions. Obtaining such data, especially in sensitive areas like healthcare, is challenging.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating Cognitive AI into current infrastructures and workflows can be complex and costly.
Ethical Considerations:
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can learn and perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair outcomes. Minimizing bias is crucial.
- Privacy: Cognitive AI often processes sensitive information. Balancing AI benefits with privacy protection is important.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency in AI decision-making and accountability for those decisions is essential.
Societal Impacts:
- Employment and Economic Disruption: AI automation raises concerns about job displacement and economic disruption. Addressing workforce development and social safety nets is important.
- Dependency and De-skilling: Relying too much on AI could lead to people losing certain skills. Balancing AI convenience with maintaining human skills is a challenge.
Future Directions: Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, including AI advancements, ethical considerations, policy-making, and human factors. Innovations in explainable AI (making AI decision processes transparent) and ethical AI guidelines are steps in the right direction.
Cognitive AI’s challenges are diverse, spanning technical, ethical, and societal domains. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for Cognitive AI to enhance decision-making, automate complex tasks, and improve understanding. Collaboration among technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and society is key to shaping Cognitive AI’s future, ensuring it aligns with ethical standards and contributes positively to societal progress.
6. The Future of Cognitive AI

The future of Cognitive AI promises advancements that could redefine human-machine interaction and intelligence. Key trends and directions indicate a path toward more sophisticated, ethical, and impactful cognitive systems.
Technological Advancements:
- Enhanced Natural Language Understanding: Future Cognitive AI will understand human language better, capturing nuances and cultural contexts. This will enable more natural and effective communication, opening possibilities for AI-assisted education, therapy, and diplomacy.
- General AI and Adaptive Learning: Cognitive AI will evolve towards General AI, showing broader cognitive abilities and learning new tasks with minimal human help. Adaptive learning algorithms will refine AI knowledge and skills over time, mimicking human learning.
- Integrated Multimodal Systems: Future Cognitive AI will integrate speech, text, images, and sensory data for a holistic understanding of the environment, enhancing AI’s ability to interpret complex scenarios and interact dynamically.
Ethical and Societal Considerations:
- Ethical AI Development: As Cognitive AI becomes more autonomous, embedding ethical considerations, fairness, and accountability in AI algorithms will be crucial.
- Privacy and Security: Ensuring data privacy and security will remain important. Advances in encryption, secure computing, and privacy-preserving techniques will protect sensitive information.
- Workforce Transformation: Cognitive AI will transform the workforce, requiring education and training programs to prepare for human-AI collaboration. Strategies to mitigate job displacement and augment human capabilities with AI will be important.
Predictions for the Future:
- Cognitive AI in Decision-Making: Cognitive AI will play a bigger role in complex decisions, from corporate strategy to public policy. AI will aid decision-makers with comprehensive data analysis and predictive insights.
- Personalized AI Assistants: Future AI assistants will understand individual preferences and needs, offering tailored support, advice, and companionship, blending technology with personal interaction.
The future of Cognitive AI holds immense promise, marked by advancements bridging human and machine intelligence. Realizing this potential requires technological innovation and a commitment to ethics, societal engagement, and thoughtful AI integration. Collaboration among researchers, ethicists, policymakers, and society will shape a world where Cognitive AI enhances human capabilities, fosters well-being, and respects individual rights.
7. Conclusion

Exploring Cognitive AI shows its potential to mimic and extend human cognitive capabilities in machines. This journey through Cognitive AI’s definition, evolution, core technologies, applications, challenges, and future prospects highlights its transformative potential and the many considerations it involves.
Cognitive AI combines machine learning, natural language processing, data analytics, and neural networks to replicate human thought processes. Its development marks a significant leap in creating machines that understand, reason, and interact with the world like humans. Cognitive AI’s applications in healthcare, finance, education, and other fields show its potential to revolutionize industries and improve quality of life.
However, Cognitive AI’s journey comes with challenges, including technical hurdles, ethical dilemmas, and societal impacts. Addressing these challenges is crucial for harnessing Cognitive AI’s benefits while minimizing negative effects. Ethical development, emphasizing fairness, transparency, and accountability, alongside privacy and security protection, is essential. Societal implications, like employment and the digital divide, need thoughtful consideration and action.
Looking ahead, Cognitive AI’s future holds promising advancements, such as General AI, multimodal systems, and enhanced language understanding. Ethical AI development, privacy and security improvements, and workforce transformation will shape Cognitive AI’s trajectory, ensuring it aligns with societal values and contributes positively to human progress.
Cognitive AI’s potential is immense, offering a glimpse into a future where intelligent machines augment human capabilities, foster innovation, and address complex societal challenges. The path forward requires a collective effort from technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and society. By embracing opportunities and navigating challenges, Cognitive AI can enhance human life and usher in a new era of intelligence and understanding.
FAQ & Answers
What is Cognitive AI?
Cognitive AI refers to AI systems that mimic human brain functions, learning from experiences and making reasoned decisions.
How does Cognitive AI differ from traditional AI?
Unlike traditional AI, Cognitive AI involves understanding, reasoning, and learning, thereby providing more nuanced and complex decision-making capabilities.
QUIZ
Quiz 1: “Identify the Cognitive AI Application”
Below are descriptions of Cognitive AI solutions followed by a list of industry applications.
Your task is to match each Cognitive AI solution to its most relevant industry application. Cognitive AI Solutions:
Predictive Maintenance: Uses machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures before they happen, based on historical data and real-time monitoring.
Customer Service Chatbots: Implements natural language processing to understand and respond to customer queries in real-time, providing 24/7 customer support.
Fraud Detection Systems: Employs machine learning and anomaly detection techniques to identify unusual patterns and potential fraudulent activities in financial transactions.
Healthcare Diagnostics: Utilizes AI to analyze medical images, such as X-rays or MRIs, to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately and swiftly.
Supply Chain Optimization: Integrates AI to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and improve logistics, ensuring efficient supply chain management.
Industry Applications:
A. Healthcare: Enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and improving patient care through advanced analytics and imaging technology.
B. Retail: Optimizing inventory management, personalizing customer experiences, and improving operational efficiencies through data analysis and predictive modeling.
C. Manufacturing: Increasing equipment uptime, reducing maintenance costs, and improving production efficiency through predictive maintenance and quality control.
D. Finance: Enhancing security, reducing fraud, and improving customer experience through advanced analytics, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice.
E. Customer Support: Improving response times, reducing operational costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction through automated responses and personalized interaction.
Match the Cognitive AI Solution to Its Industry Application:
Predictive Maintenance – ?
Customer Service Chatbots – ?
Fraud Detection Systems – ?
Healthcare Diagnostics – ?
Supply Chain Optimization – ?
Can you match each Cognitive AI solution to its corresponding industry application?
Here are the matches for each Cognitive AI solution to its most relevant industry application:
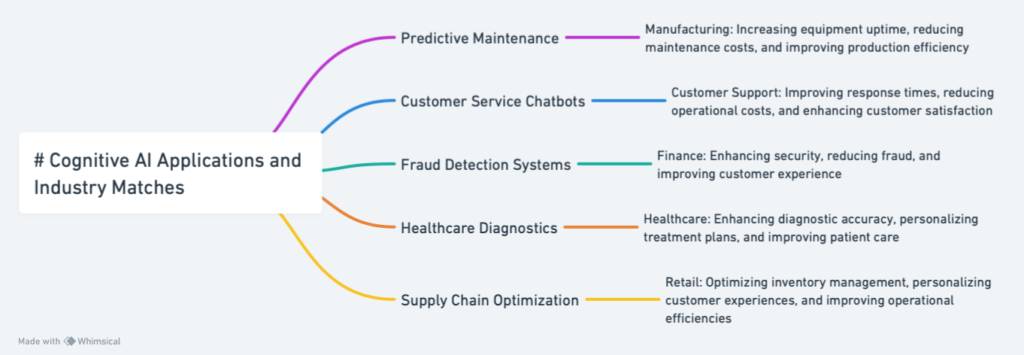
- Predictive Maintenance – C. Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance is directly applicable to the Manufacturing industry, where it can significantly increase equipment uptime, reduce maintenance costs, and improve production efficiency by predicting equipment failures before they happen.
- Customer Service Chatbots – E. Customer Support: Customer Service Chatbots are well-suited for the Customer Support industry, improving response times, reducing operational costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction through automated responses and personalized interaction.
- Fraud Detection Systems – D. Finance: Fraud Detection Systems find their most relevant application in the Finance industry, enhancing security, reducing fraud, and improving customer experience through the identification of unusual patterns and potential fraudulent activities in financial transactions.
- Healthcare Diagnostics – A. Healthcare: Healthcare Diagnostics using AI is most relevant to the Healthcare industry, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and improving patient care through advanced analytics and imaging technology.
- Supply Chain Optimization – B. Retail: Supply Chain Optimization using AI is particularly relevant to the Retail industry, optimizing inventory management, personalizing customer experiences, and improving operational efficiencies through data analysis and predictive modeling.