Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) have transformed the field of artificial intelligence (AI), especially in how computers handle human language. Created by OpenAI, GPT models can understand and generate text that sounds like it was written by a person.
1. What Are Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT)?

Definition and Purpose
Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) are advanced AI models that can produce text similar to how people write.
They use something called the Transformer architecture, which helps them understand and create language effectively.
Instead of being trained for specific tasks, GPT models are pre-trained on a lot of text from the internet. This allows them to handle many different tasks, like answering questions or writing stories.
Overview of GPT’s Role in AI
GPT models play a big role in AI by making it easier for machines to understand and create human language.
They are used in many areas, like generating articles, translating languages, and helping with customer support.
These models have greatly advanced AI, making it better at handling language.
Significance in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
In Natural Language Processing (NLP), GPT models have set new standards.
They can understand the context, generate relevant responses, and adapt to different language styles.
This progress helps make interactions with computers more natural and effective.
2. Understanding GPT Architecture
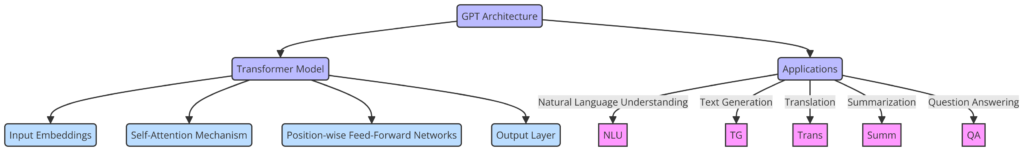
The Transformer Model
The Transformer model, introduced in the paper “Attention is All You Need,” is different from older models. It uses a self-attention mechanism that helps the model focus on different parts of a sentence to understand it better. This makes it more effective at picking up on complex language patterns compared to older models.
Core Features
- Self-Attention Mechanism: This feature lets GPT models pay attention to different parts of the text to make accurate predictions. It helps in understanding the context by looking at all the words in a sentence, making the generated text more coherent and relevant.
- Multi-Layer Architecture: GPT models have many layers, each with numerous neurons. For example, GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters spread across its layers. This setup allows the model to handle a wide range of language tasks with high precision.
- Pre-training and Fine-Tuning: GPT models go through two stages of training. First, they learn general language patterns from a huge amount of text data. Then, they are fine-tuned on smaller, specific datasets to improve their performance on particular tasks.
- Generative Capabilities: GPT models can create text based on the patterns they’ve learned during training. This means they can write paragraphs, translate languages, and even generate code.
3. Evolution of GPT Models
GPT-1 (2018)
GPT-1, introduced in 2018, was the first of its kind and showed the potential of large-scale language models. It demonstrated that a model trained on a wide range of internet text could perform various tasks effectively.
GPT-2 (2019)
Released in 2019, GPT-2 was a major upgrade with a much larger dataset and model size. It could generate more realistic and coherent text, leading to discussions about the ethical use of AI-generated content.
GPT-3 (2020)
GPT-3, launched in 2020, took a big leap with its massive size and improved capabilities. It could generate text, answer questions, and even write code, showcasing its versatility across many tasks.
GPT-4 (2023)
The latest model, GPT-4, introduced in 2023, further advanced the technology. It has better performance in understanding context and generating text and can handle text, images, and audio. GPT-4 addresses some limitations of earlier models, offering more accurate and nuanced responses.
4. Training and Development
Training Process
Training GPT models involves large amounts of data and computing power.
- Pre-training: GPT models start by learning from a huge amount of text from the internet. This phase helps the model understand general language patterns but requires a lot of computing resources.
- Fine-tuning: After pre-training, the model is adjusted using smaller, specialized datasets for specific tasks. This improves the model’s ability to handle particular applications, like writing or customer service.
Challenges
- Computational Resources and Costs: Training large models like GPT-4 requires a lot of computing power and energy, which can be expensive and have an environmental impact.
- Data Quality and Bias: It’s important to ensure the training data is diverse and unbiased to avoid unfair outcomes. This means carefully selecting data and using strategies to reduce bias.
- Overfitting and Solutions: GPT models can sometimes perform well on training data but struggle with new data. Techniques like regularization help prevent this problem, making the model more reliable in different situations.
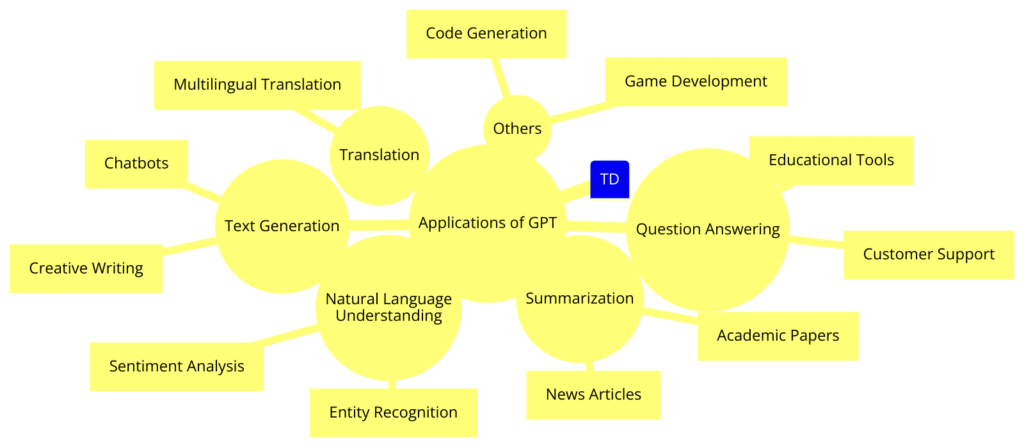
5. Applications Across Various Domains

Content Creation
GPT models are used to automate writing tasks, from drafting blog posts to creating stories. They help content creators, marketers, and writers by producing high-quality text quickly.
Language Translation
GPT models can translate text between languages more accurately than older methods. They help make communication easier across different languages.
Customer Service
In customer service, GPT models power chatbots and virtual assistants that interact with users and handle queries efficiently. This makes customer support more effective and responsive.
Educational Tools
GPT models help in education by creating personalized learning experiences. They generate practice questions, provide explanations, and assist in grading, making learning more tailored to individual needs.
Code Generation
For software developers, GPT models suggest code snippets and complete coding tasks, speeding up programming and reducing errors.
6. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Automated Journalism
News organizations like The Associated Press use AI to write routine news reports, freeing up journalists to focus on more complex stories.
Language Learning
Platforms like Duolingo use GPT models to offer practice and feedback in language learning, making it more engaging and effective.
Personalized Marketing
Companies use GPT models to create personalized marketing content, like emails and product descriptions, improving customer engagement and marketing effectiveness.
7. Ethical Considerations and Challenges

Bias and Fairness
GPT models can reflect and even amplify biases from their training data. This is a concern in areas like hiring and content moderation. Efforts are being made to identify and reduce these biases to ensure fairness.
Misinformation and Manipulation
GPT models could be misused to create false information or manipulate opinions. Developing tools to detect AI-generated content and establishing guidelines for responsible use are important to address these risks.
Privacy Concerns
Since GPT models are trained on large datasets, including personal information, protecting privacy is crucial. Measures need to be in place to secure sensitive data and maintain trust.
8. The Future of GPT and AI

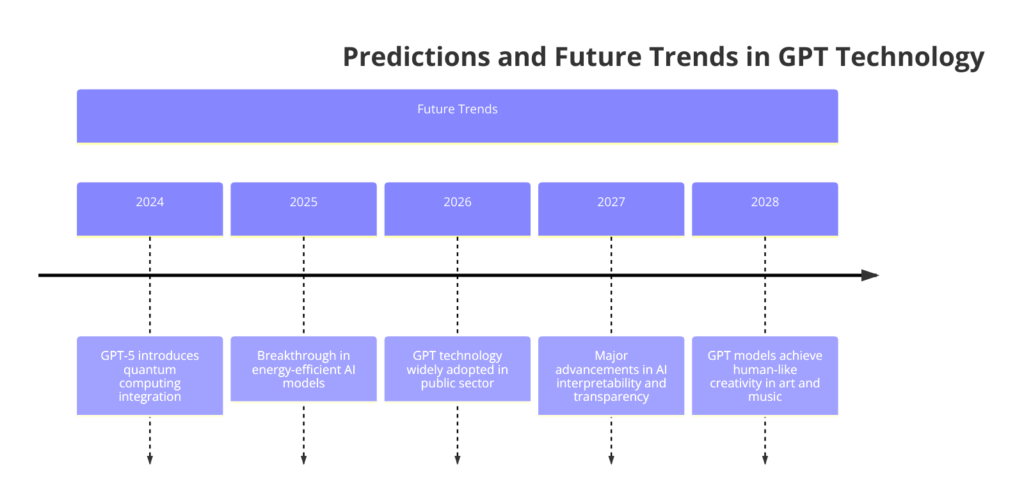
Predictions for GPT Evolution
- Increasing Model Size and Complexity: Future GPT models will be even larger and more complex, improving their ability to understand and generate text.
- Enhanced Multimodal Capabilities: Upcoming models will handle text, images, audio, and video, allowing for richer and more interactive applications.
- Improved Contextual and Emotional Intelligence: Future GPT models will better understand context and emotions, making interactions more natural.
- Ethical and Responsible AI Development: There will be a stronger focus on ethical considerations, including bias detection and privacy preservation, ensuring AI developments are beneficial and responsible.
Potential Impacts
- Education: GPT models will make learning more personalized and accessible through adaptive tools and content creation.
- Healthcare: They could help with medical research, clinical decisions, and patient interactions.
- Entertainment and Creative Industries: GPT models will offer new tools for creative work, inspiring fresh ideas and artistic expression.
- Customer Service: Advanced AI interactions will improve customer support, making it more efficient and human-like.
FAQ & Answers
1. What are Generative Pre-Trained Transformers (GPT)?
GPTs are a type of AI model known for their ability to generate human-like text, based on deep learning and transformer architecture.
2. How are GPT models used in different industries?
They are used in various applications, from content creation and chatbots to more complex tasks like language translation and data analysis.
Quizzes
Quiz 1: “Identifying GPT Applications” – Match GPT applications to the correct industry.
For each application, match it to the corresponding industry from the list provided.
GPT Applications:
- Content Creation – Generating articles, stories, and creative writing.
- Code Generation – Assisting in writing and debugging software code.
- Language Translation – Translating text between various languages accurately.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants – Providing customer service and support through conversational AI.
- Educational Tools – Creating personalized learning materials and tutoring aids.
- Legal Document Analysis – Reviewing and summarizing legal documents.
- Market Research and Analysis – Generating insights from social media and other textual data.
- Healthcare Assistance – Summarizing medical records and literature for quicker decision-making.
- Game Development – Creating dynamic narratives and dialogues in games.
- Financial Forecasting – Analyzing financial documents and news to predict market trends.
Industries:
A. Healthcare
B. Education
C. Legal
D. Software Development
E. Finance
F. Customer Service
G. Entertainment
H. Marketing
I. Media and Publishing
J. Translation Services
Match:
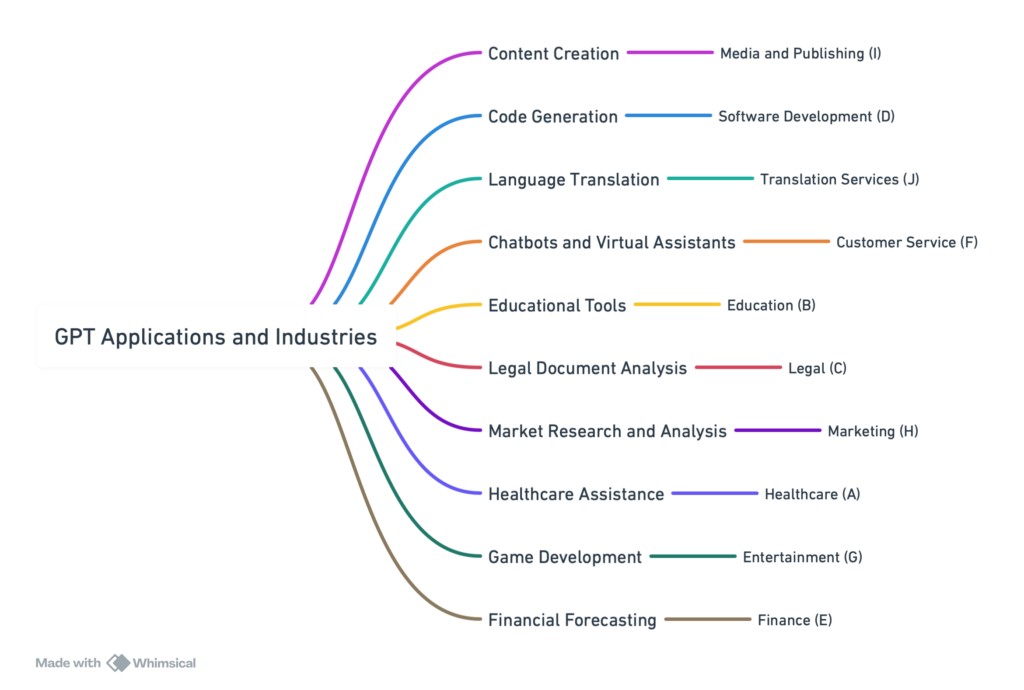
- I. Media and Publishing
- D. Software Development
- J. Translation Services
- F. Customer Service
- B. Education
- C. Legal
- H. Marketing
- A. Healthcare
- G. Entertainment
- E. Finance
These matches illustrate how GPT’s versatile capabilities can be applied across a wide range of industries, offering innovative solutions and enhancing productivity in numerous domains.
Quiz 2: “GPT Milestones” – Test knowledge of the development and evolution of GPT models.
I’ll provide you with statements related to the development and evolution of GPT models. Your task is to determine whether each statement is True or False. Let’s begin!
GPT Milestones Quiz
- GPT-1 was the first to introduce the transformer architecture, which revolutionized natural language processing.
- True / False
- GPT-2 was initially not fully released due to concerns over its potential misuse in generating fake news and misinformation.
- True / False
- GPT-3 has significantly fewer parameters than GPT-2, focusing instead on more efficient algorithms.
- True / False
- Codex, a descendant of GPT-3, is specifically designed to generate computer code and powers GitHub Copilot.
- True / False
- DALL·E, a version of GPT-3, can generate photorealistic images from textual descriptions.
- True / False
- GPT-3 was the first model in the series to be made available via an API, allowing developers to integrate its capabilities into their applications.
- True / False
- GPT-4 is expected to have a smaller model size than GPT-3 but with enhanced reasoning and comprehension abilities.
- True / False (Note: This statement might require speculation based on my last update in April 2023.)
- The introduction of GPT-2 marked the beginning of using large-scale transformer models for natural language generation tasks.
- True / False
- Each version of GPT has been trained exclusively on text data, without incorporating any form of multimodal data during training.
- True / False (As of my last update, consider the role of models like DALL·E in this context.)
- GPT-3 demonstrated the ability to perform specific tasks without the need for task-specific training data, relying instead on its vast training dataset.
- True / False
Here are the correct answers and explanations:
A. Media and Publishing B. Education C. Legal D. Software Development E. Finance F. Customer Service G. Entertainment H. Marketing I. Media and Publishing J. Translation Services