Machine Learning Explained (Simple Guide for Beginners)

Introduction — Machine Learning in Plain English
Machine learning is one of the most important parts of artificial intelligence — and it powers almost everything we use today. From Netflix recommendations to Google Maps, self-driving cars, voice assistants, and even ChatGPT, machine learning helps computers learn from data and make smart decisions.
But what exactly is machine learning? And how does it work?
This machine learning explained guide breaks ML down in simple terms. No jargon, no advanced math — just clear explanations, real examples, and an easy way to understand how computers learn in a human-like way. By the end, you’ll understand why machine learning matters, how it works, and where you’re already seeing it in real life every day.
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine learning (ML) is a type of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn from data instead of being manually programmed.
Machine learning is a core part of artificial intelligence, which we explain from the ground up in our AI beginner’s guide.
Simple definition:
Machine learning is the process by which computers learn from examples.
Instead of giving a computer a rule for every situation, we feed it data — and it figures out patterns on its own. That’s why ML is so powerful: it improves over time as it sees more examples.
Real-world machine learning examples you already use:
- Netflix learns what shows you like
- Google Photos recognizes faces
- TikTok figures out your interests
- Spam filters learn what emails are junk
- Self-driving cars identify pedestrians
Machine learning is everywhere — usually without you even noticing.
To understand the broader context of machine learning, check out our beginner’s guide to what artificial intelligence is.
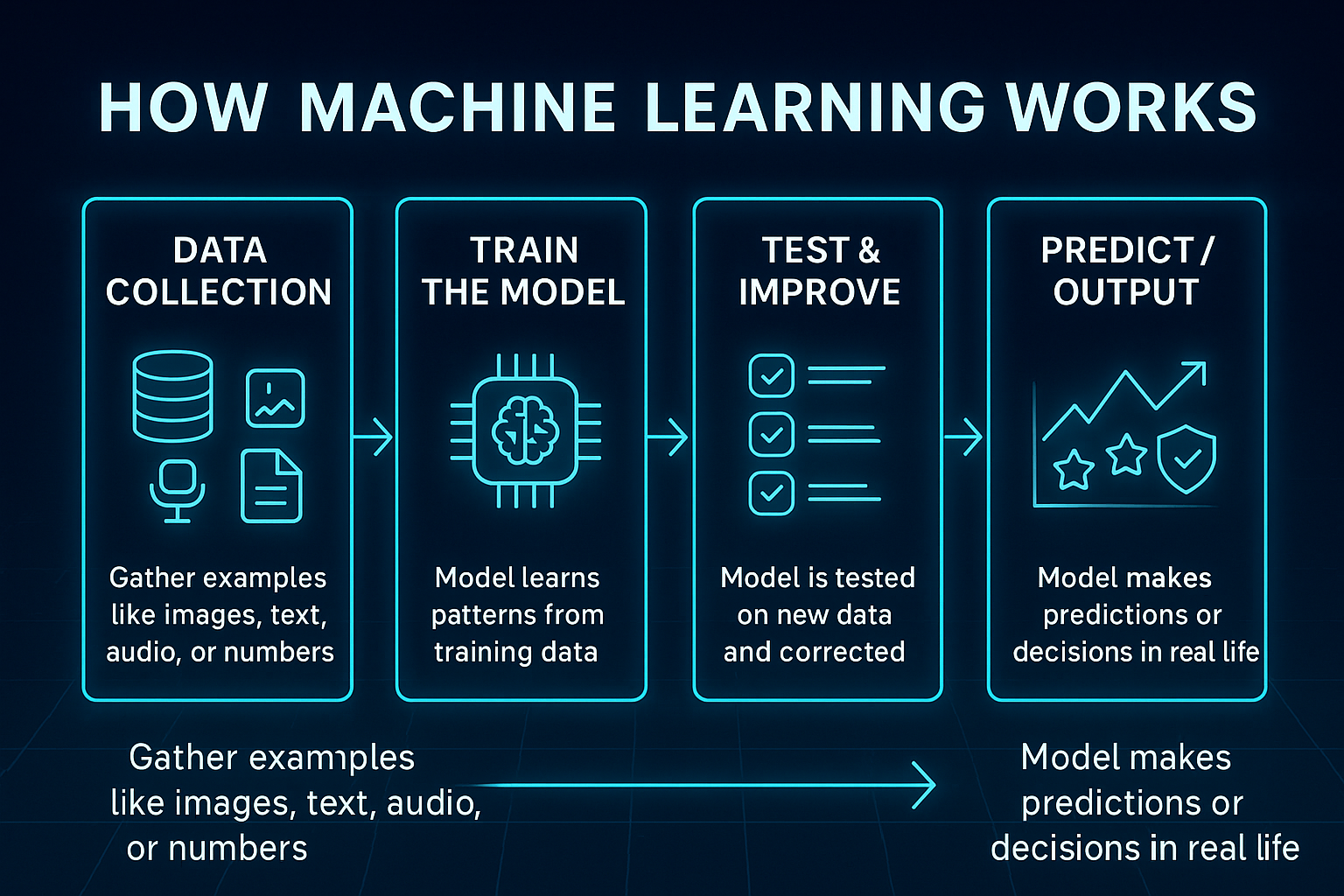
How Machine Learning Works (Simple Breakdown)
Think of machine learning like teaching a child:
- Show them examples
- Let them make guesses
- Correct them when they’re wrong
- Let them practice
- They improve over time
Computers learn in the exact same way — just with data instead of flashcards.
Step 1 — Collect Data
Machine learning needs data to learn patterns.
Examples include:
- Images
- Text
- Videos
- Audio recordings
- Website behavior
- Past decisions
If you want an AI to recognize cats → you feed it thousands of cat photos first.
Step 2 — Train the Model
The computer studies the data and tries to find patterns.
For example:
- What do cats usually look like?
- What colors?
- What shapes?
- What features (ears, whiskers, etc.)?
It learns by making millions of tiny adjustments until it “gets” the pattern.
Step 3 — Test & Improve
After training, the model is tested on new data it’s never seen.
If it gets something wrong:
- it corrects itself
- learns from mistakes
- improves accuracy
This repeats until the model becomes highly accurate.
Step 4 — Make Predictions
Once trained, the model can:
- predict the next word in a sentence (ChatGPT)
- recognize objects in photos
- suggest content you might like
- detect fraud on your credit card
This is where machine learning becomes powerful — it turns patterns into real decisions.
Want the beginner breakdown? Read What is generative AI to see how tools like ChatGPT create new content.
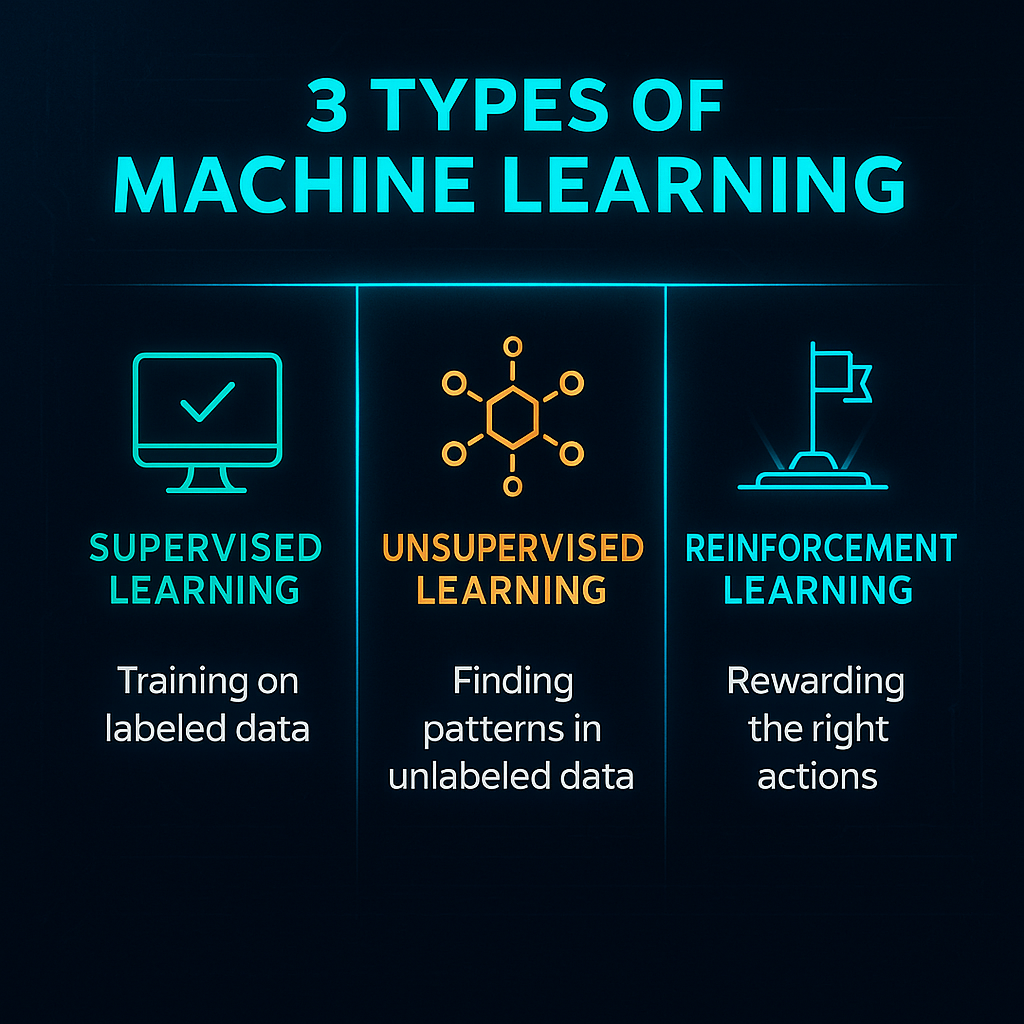
The Main Types of Machine Learning
There are three core types of machine learning. Here’s the simple version.
1) Supervised Learning (Most Common)
The model learns from labeled examples.
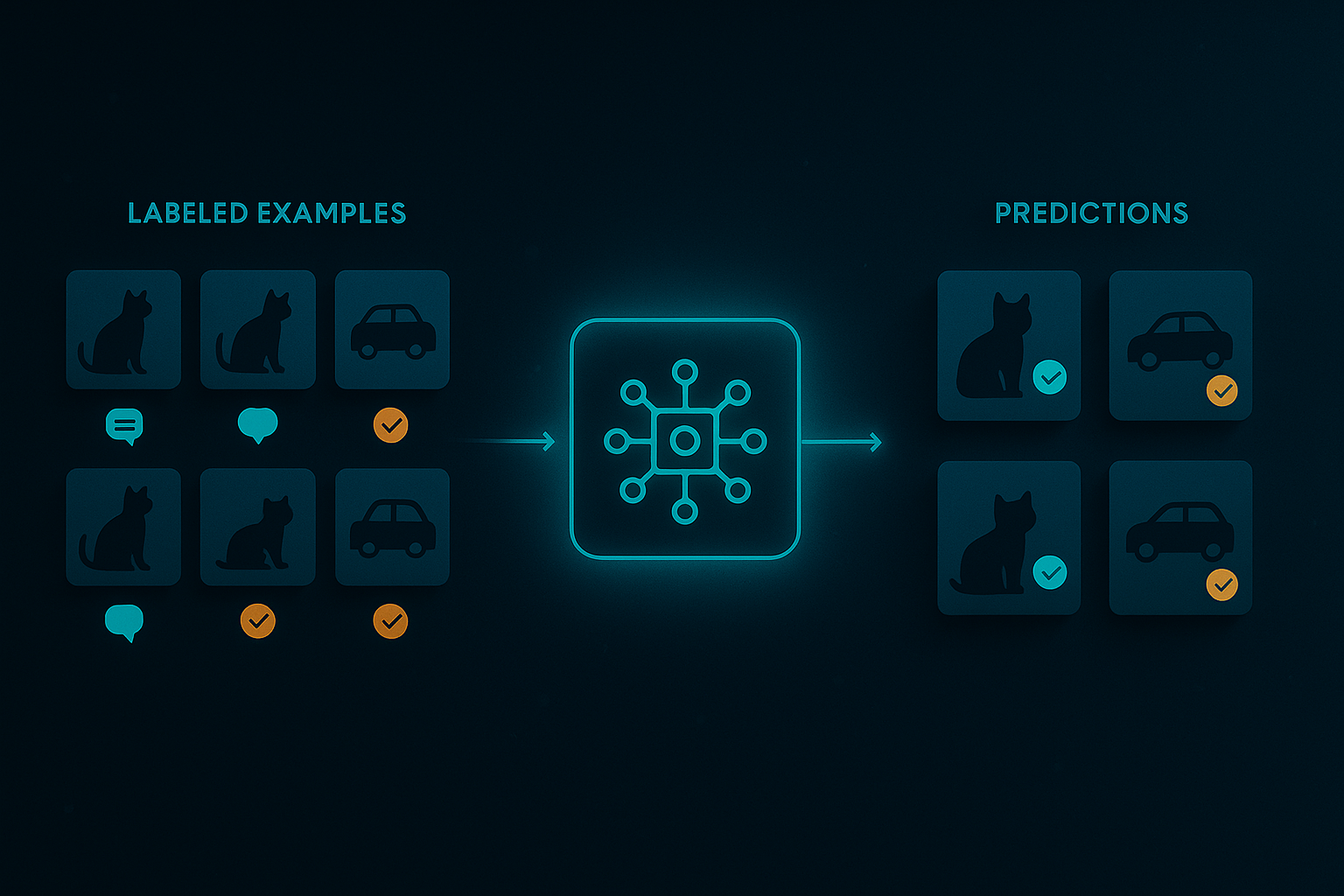
Example:
You show the AI 10,000 photos labeled “cat” or “not cat.” It learns the difference.
Used for:
- Email spam detection
- Stock prediction
- Credit risk models
- Image classification
2) Unsupervised Learning
The model finds patterns without labels.
Example:
It groups customers into segments based on behavior, even if nobody told it what the groups are.
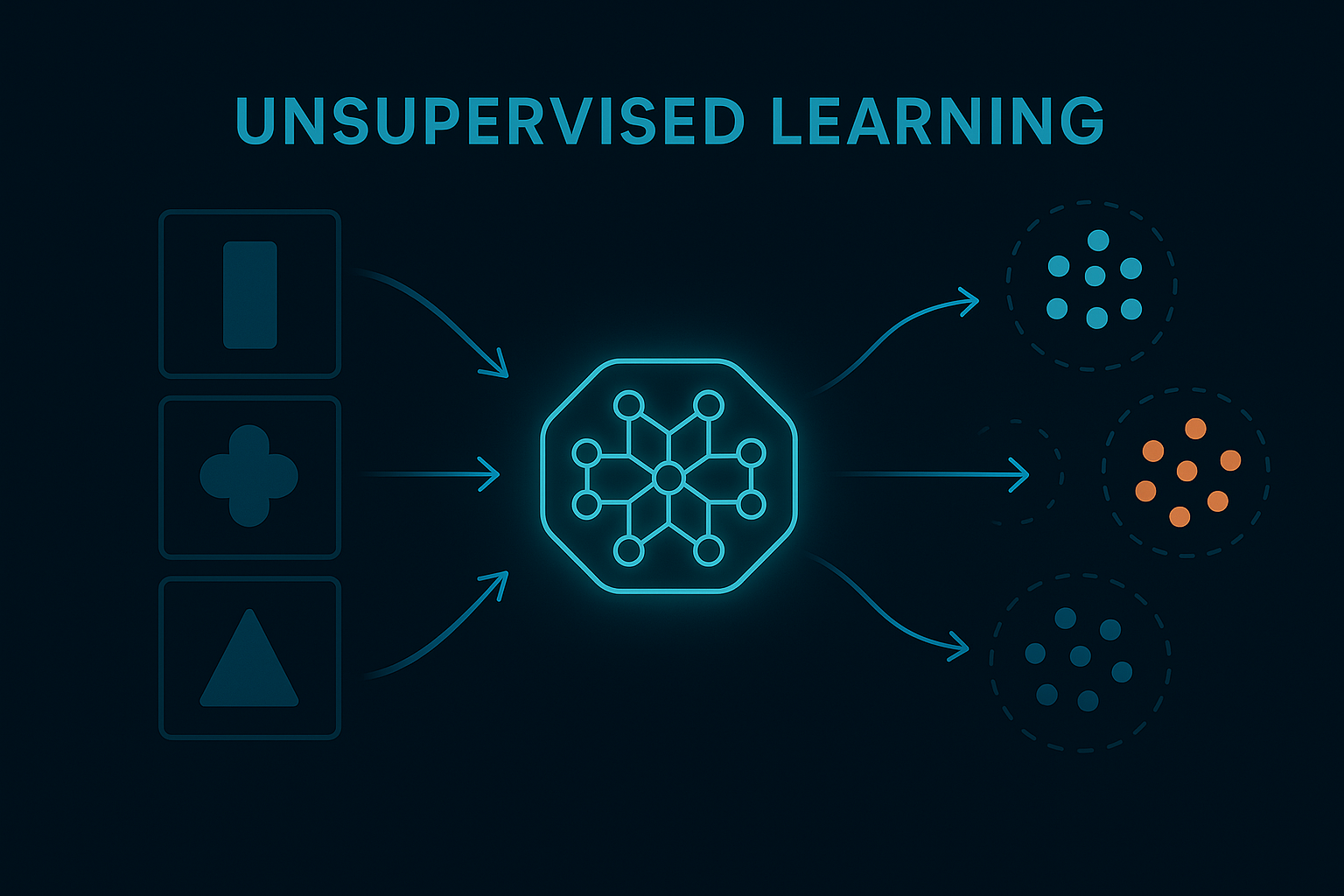
Used for:
- Customer segmentation
- Product recommendations
- Fraud detection
3) Reinforcement Learning
The AI learns through trial and error, like humans do.

Example:
An AI becomes great at chess by playing millions of games, learning what wins and what loses.
Used for:
- Robotics
- Gaming AI
- Navigation
- Industrial control systems
Real Examples of Machine Learning in Action
Machine learning shows up in almost every major industry:
✔ Social Media
TikTok, Instagram, Facebook — all use ML to personalize your feed.
✔ Healthcare
ML helps doctors detect diseases early, like cancer in scans.
✔ Finance
ML detects fraud and powers trading bots.
✔ Retail
Amazon predicts what you want to buy before you click.
✔ Transportation
Self-driving cars rely on ML to recognize lanes, signs, and people in real time.
✔ Entertainment
Netflix recommends movies, Spotify recommends songs based on listening patterns.
Tools, Platforms, and Companies Using Machine Learning
Machine learning powers many of the tools people use daily. Here are a few big ones:
Consumer Platforms
- Google Search & YouTube — ranking content and predicting what you’ll click next
- Netflix / Spotify — recommendation engines
- Apple Photos / Google Photos — image recognition for faces and objects
Business & Productivity Tools
- Microsoft Copilot tools — auto-summarizing and drafting docs
- Salesforce AI — predicting churn and customer behavior
- Amazon / Shopify seller tools — demand forecasting
Modern AI Apps
- ChatGPT-style assistants predict and generate text using ML
- AI image tools generate visuals by learning from large datasets
- Voice assistants use ML to understand speech and intent
Benefits of Machine Learning
Machine learning brings major advantages when used responsibly — especially at scale.
- Handles tasks humans can’t do
- Processes huge amounts of data fast
- Improves accuracy over time as it sees more examples
- Automates repetitive tasks
- Enhances personalization (feeds, products, learning, healthcare)
- Powers modern AI tools that feel “smart”
Challenges & Limitations of Machine Learning
Machine learning isn’t magic. It has real limits:
- Needs large amounts of data to learn well
- Can learn bias from information if training data is unfair
- Hard to explain “why” it made a decision (black-box problem)
- Requires computing power
- Can be expensive at scale
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
Machine learning is the broader category.
Deep learning is a more advanced form of ML using neural networks.
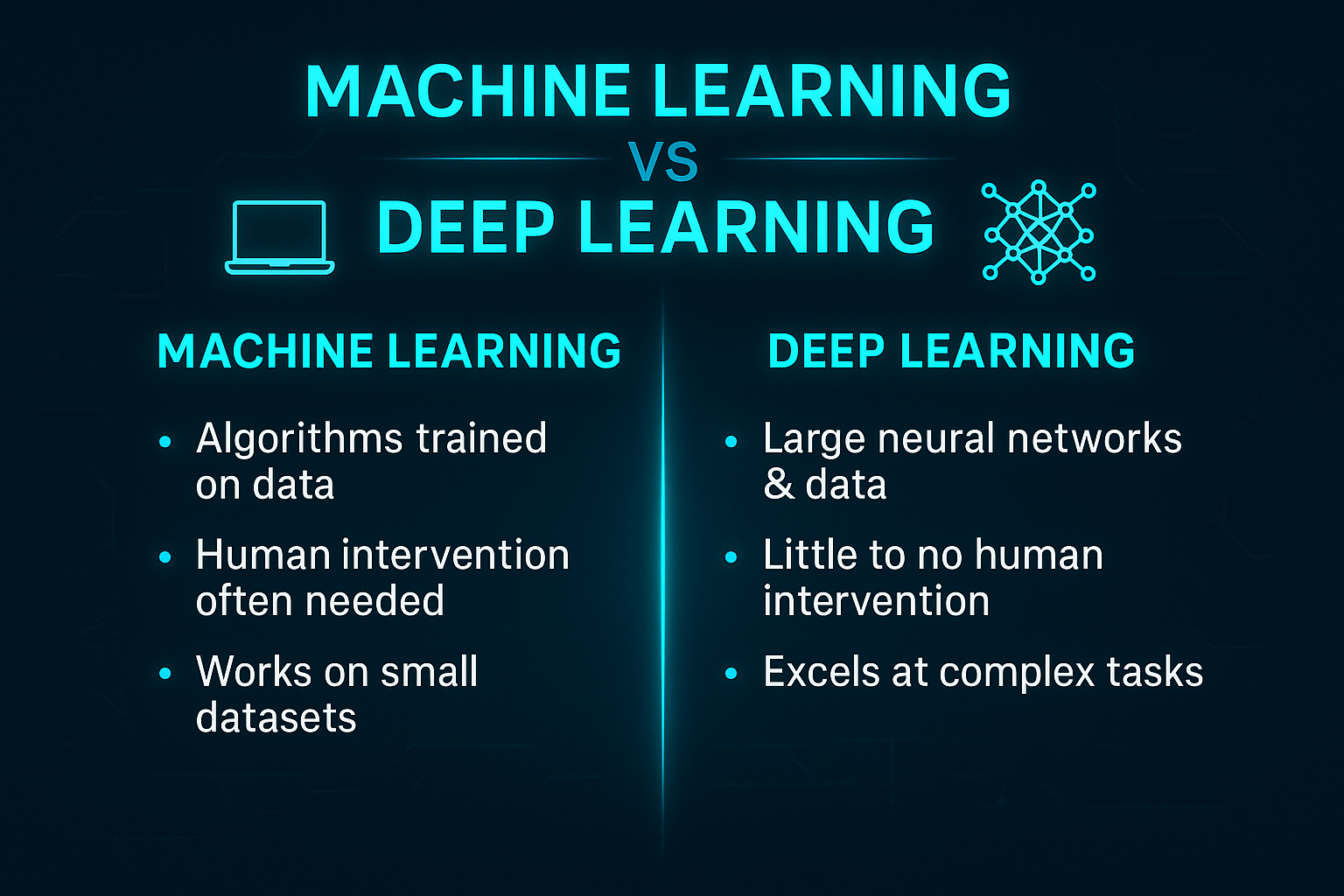
Simple breakdown:
- ML = learns from data
- DL = learns from data using brain-like structures
- DL requires more data & computing power
- DL powers modern AI like ChatGPT, Midjourney, and Siri
Want the beginner breakdown of neural networks? Read Deep Learning 101.
Future Outlook of Machine Learning
Machine learning will keep expanding into nearly every part of life:
- Medicine
- Robotics
- Education
- Finance
- Smart homes
- Creative tools
- Automated driving
We’re still early. The biggest breakthroughs are likely coming within the next decade as models improve, data grows, and AI becomes cheaper and more accessible.
FAQ: Machine Learning Explained
What is machine learning in simple terms?
Machine learning is a type of AI where computers learn from data instead of being manually programmed. They use examples to find patterns and make predictions.
How does machine learning work?
Machine learning works by collecting data, training a model to find patterns, testing and improving that model, then using it to make predictions or decisions in real life.
What are the 3 main types of machine learning?
The three main types are supervised learning (labeled examples), unsupervised learning (pattern finding without labels), and reinforcement learning (trial-and-reward learning).
What is supervised learning?
Supervised learning is when an AI learns from labeled data, like photos tagged “cat” or “not cat,” so it can predict the correct label on new data.
What is unsupervised learning?
Unsupervised learning finds patterns without labels. It groups or clusters data on its own, such as detecting customer segments.
What is reinforcement learning?
Reinforcement learning teaches AI through trial and error. The model learns by taking actions, getting rewards or penalties, and improving over time.
What’s the difference between machine learning and deep learning?
Machine learning is the broader field of learning from data. Deep learning is a powerful type of machine learning that uses large neural networks and usually needs more data and computing power.
Where is machine learning used today?
Machine learning is used in recommendations (Netflix, YouTube), fraud detection, medical imaging, self-driving features, voice assistants, and many other tools.
Conclusion
Machine learning is the engine behind most of today’s artificial intelligence. It helps computers learn from data, make predictions, and automate tasks at a scale humans could never achieve.
Understanding ML puts you ahead in today’s AI-powered world — whether you’re a creator, student, investor, or business owner.
To continue building your AI foundation, explore these beginner guides next: