Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a fascinating part of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on how computers can understand and work with human language. Imagine if computers could read, interpret, and respond to text or speech just like people do—that’s what NLP aims to achieve. This section will give you a clear idea of what NLP is, why it’s important, and how it’s shaping the future of AI.
1. What is NLP?

NLP is a branch of AI that deals with the interaction between computers and human language.
The goal is to teach computers to understand, process, and generate language in a way that makes sense and is useful.
NLP includes a range of tasks like recognizing speech, translating languages, analyzing feelings in text, and chatting with virtual assistants.
By figuring out the structure and meaning of language, NLP makes human-computer communication more natural.
Why is NLP Important?
NLP is crucial because so much of our data is in text form—think of emails, social media posts, and web content.
NLP helps computers make sense of this information, providing answers, recommendations, and even creating content.
It makes interacting with technology easier and more intuitive, which is essential as we rely more on digital communication.
2. How NLP Improves Interaction and Data Understanding

- Better Interaction: NLP helps create chatbots and virtual assistants that can understand and respond to your questions, making tech more user-friendly.
- Understanding Data: Most of the world’s data is in unstructured text. NLP helps analyze this data, providing valuable insights for businesses and researchers.
- Breaking Language Barriers: Tools like Google Translate use NLP to translate text between different languages, making global communication smoother.
The Basics of NLP
NLP combines computer science, AI, and language studies. Here’s a quick look at its core ideas:
- Linguistics: Understanding the structure of language helps build algorithms that process and generate text.
- Computational Techniques: NLP uses algorithms and models to handle tasks like breaking down text, analyzing grammar, and identifying key information.
How NLP Has Evolved
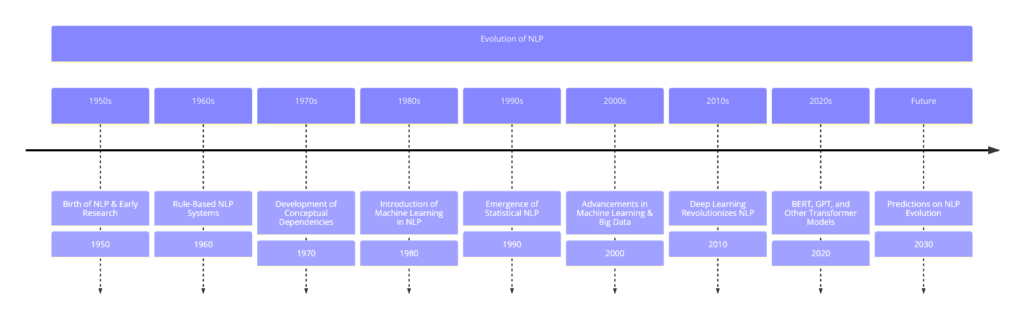
NLP has come a long way from simple rule-based systems to advanced machine learning and deep learning techniques:
- Early Systems: Old NLP systems used fixed rules to process language, which were limited in handling complex language.
- Statistical Methods: Later, NLP used large amounts of text data to find patterns, improving language processing.
- Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Modern NLP uses sophisticated models that learn from data to understand and generate language with great accuracy.
3. Key Models in NLP

Some important models in NLP are:
- Probabilistic Context-Free Grammar (PCFG): Helps parse sentences by considering various possible structures and their probabilities.
- Hidden Markov Model (HMM): Used in speech recognition and tagging parts of speech by modeling sequences of words or sounds.
4. Key Technologies and Algorithms in NLP

NLP uses various technologies and algorithms to understand and generate language:
- Tokenization: Splits text into smaller units like words or phrases.
- Parsing: Analyzes sentence structure to understand grammatical relationships.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifies and classifies key information, like names and dates.
- Sentiment Analysis: Determines the emotional tone of text, such as whether it’s positive or negative.

5. Challenges in Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP faces several challenges:
- Understanding Nuances: Language can be complex, with idioms, sarcasm, and context affecting meaning. Teaching computers to handle these subtleties is tough.
- Language Diversity: Many languages and dialects are underrepresented in NLP models, creating gaps in language processing.
- Ethical Issues: Ensuring privacy, fairness, and avoiding biases in NLP systems are important concerns.
6. The Future of Natural Language Processing (NLP)

NLP is evolving rapidly, with exciting developments on the horizon:
- Deep Learning: Advanced neural networks will improve language understanding and generation.
- Cross-lingual Models: New models will be able to work with multiple languages more effectively.
- Contextual Understanding: Future systems will better grasp context and emotions in language.
- Ethical AI: There will be more focus on creating fair and unbiased NLP technologies.
7. Conclusion: Reflecting on the Transformative Role of NLP in AI

NLP is a vital part of AI that’s transforming how we interact with technology.
From chatbots to translation tools, NLP is making communication with machines more natural and useful.
As NLP technology advances, it will continue to enhance how we understand and use language, driving innovation and improving our digital experiences.
FAQ & Answers
What is Natural Language Processing in AI?
NLP in AI refers to the technology that enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a useful and meaningful way.
How does NLP impact AI development?
NLP advances AI’s capabilities to process and analyze large volumes of natural language data, enhancing machine-human interactions and data-driven insights.
Quizzes
Quiz 1: “Identify the NLP Technology”
Instructions: Match each description of an NLP technology with its correct name. Some technologies might closely resemble others; choose the best match based on the description.
Descriptions:
- A technology that extracts the emotional tone behind a series of words, used to determine the writer’s or speaker’s attitude towards the subject.
- A model that converts text into meaningful vectors, often used to compare document similarity or improve language models.
- An algorithm that breaks down text into its component parts to understand its grammatical structure, often used in text comprehension and constructing sentences.
- A system that automatically generates human-like text based on a given input, capable of creating stories, completing sentences, or generating code.
- A technique that identifies and extracts structured information from unstructured text, such as names of people, organizations, locations, and dates.
- An approach to answering questions posed in natural language, using a database, document, or the internet as its source for answers.
- A technology that translates text or speech from one language to another, facilitating communication between people who speak different languages.
Names:
A. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
B. Question Answering Systems
C. Text-to-Speech Conversion
D. Sentiment Analysis
E. Machine Translation
F. Text Generation
G. Word Embeddings
H. Syntactic Parsing
Answers:
- D. Sentiment Analysis – This technology assesses the sentiment within a body of text, identifying whether the attitude is positive, negative, or neutral towards the subject.
- G. Word Embeddings – Converts words into high-dimensional vectors that represent their meanings, enabling various NLP tasks like similarity assessment and language modeling.
- H. Syntactic Parsing – Analyzes the grammatical structure of sentences, identifying the various parts of speech and their relationship to one another.
- F. Text Generation – Uses models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) to produce text that mimics human writing styles across various applications.
- A. Named Entity Recognition (NER) – Extracts entities such as person names, organizations, locations, and dates from text, turning unstructured data into structured information.
- B. Question Answering Systems – Provides answers to questions posed in natural language by searching through a pre-defined source of information.
- E. Machine Translation – Translates text or speech from one language to another, using complex models to understand and reproduce the meaning in the target language.
Quiz 2: “Real-world NLP Applications”
Instructions: For each industry mentioned below, select the NLP application that is most commonly used within that sector. Each application can be used in various contexts, but choose the one that best fits the described industry.
Industries:
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Customer Service
- E-commerce
- Legal
- Education
- Travel and Hospitality
NLP Applications:
A. Sentiment Analysis
B. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
C. Machine Translation
D. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
E. Text Generation
F. Language Learning Applications
G. Document Summarization
Answers:
- Healthcare: D. Named Entity Recognition (NER) – In healthcare, NER is used to extract specific information from clinical texts, such as patient symptoms, medication names, dosages, and procedures, facilitating patient care and research.
- Finance: A. Sentiment Analysis – This application is widely used in finance to gauge market sentiment from news articles, social media posts, and financial reports, helping investors make informed decisions.
- Customer Service: B. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants – Many customer service departments use chatbots and virtual assistants to provide quick answers to customer inquiries, improve the customer experience, and reduce response times.
- E-commerce: A. Sentiment Analysis – E-commerce platforms use sentiment analysis to understand customer reviews and feedback, helping them improve product offerings and customer service.
- Legal: G. Document Summarization – NLP is used in the legal industry to summarize long legal documents, contracts, and case files, saving time and making the information more accessible.
- Education: F. Language Learning Applications – NLP powers language learning apps, providing interactive and personalized learning experiences, including grammar correction, vocabulary suggestions, and conversational practice.
- Travel and Hospitality: B. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants – In the travel and hospitality industry, chatbots and virtual assistants are used to handle bookings, answer customer queries about travel arrangements, and provide personalized recommendations, enhancing the customer experience.