Speech recognition, a cornerstone of artificial intelligence (AI), enables machines to understand and interpret human speech, transforming spoken words into text or commands. This technology bridges communication gaps between humans and computers, allowing for more natural and intuitive interactions. The significance of speech recognition in AI is profound, as it not only enhances user experiences but also opens up a myriad of applications that rely on vocal commands, from virtual assistants to hands-free control systems.

1. Introduction to Speech Recognition
Speech recognition is a key part of artificial intelligence (AI). It allows computers to understand and convert human speech into text or commands.
This makes talking to computers feel more natural and easy. Speech recognition is important because it improves how we interact with technology, like using voice commands for virtual assistants or hands-free systems.
The technology started in the mid-1900s with simple systems that could only recognize a few words.
These early attempts showed both the potential and the challenges of getting machines to understand human speech.
Over time, speech recognition improved a lot, thanks to better computers and new algorithms.
Machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks changed everything.
These technologies helped create models that learn from huge amounts of spoken data, making speech recognition much more accurate and able to understand natural language.
Today, speech recognition can transcribe speech accurately and understand context, intent, and even emotion.
Speech recognition is already making a big impact in society, from personal virtual assistants on phones and smart speakers to helping people with disabilities interact with digital devices.
As the technology gets better, its role in AI and our daily lives will only grow.
In this exploration, we’ll look at the history, core technologies, applications, challenges, and future directions of speech recognition.
It’s a story of continuous innovation, as researchers and engineers push the boundaries of what’s possible, making machines not just see and think but also listen and understand.
2. Historical Development of Speech Recognition
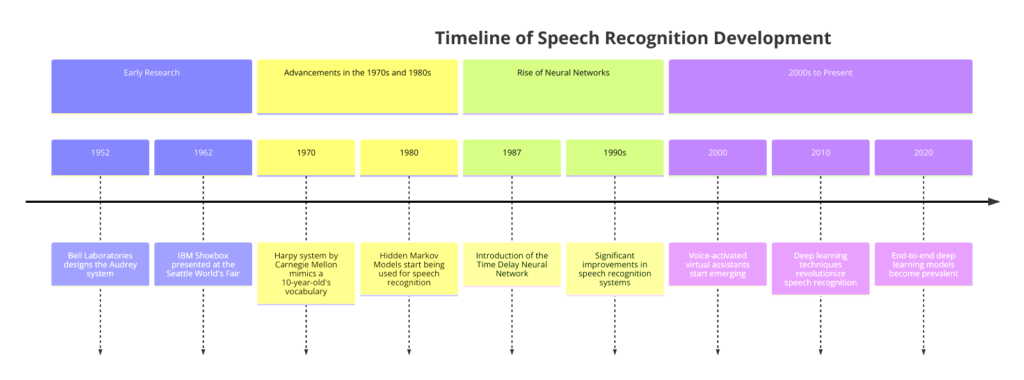
The history of speech recognition is full of important milestones and breakthroughs. It started in the 1950s with Bell Laboratories’ “Audrey,” which could recognize spoken digits.
Though limited, it laid the groundwork for future research.
In the 1960s, IBM’s “Shoebox” could recognize 16 words.
These early systems used analog technology and simple template matching, comparing spoken words to predefined patterns.
In the 1970s and 1980s, speech recognition moved to digital technology, which allowed for more advanced algorithms and larger vocabularies.
Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), introduced in the late 1970s, provided a statistical method for dealing with variations in speech patterns.
The 1990s and early 2000s saw improved algorithms, more computing power, and larger speech databases, leading to systems with speaker independence and better natural language understanding.
The DARPA Speech Recognition Research Workshop, held since the 1980s, has been crucial in driving advancements.
In the 2010s, deep learning and neural networks revolutionized speech recognition. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) significantly improved accuracy and efficiency.
These models could learn directly from raw audio data, reducing error rates.
Key figures like Raj Reddy and Geoffrey Hinton have greatly contributed to the field.
The history of speech recognition shows its complexity and the ingenuity of those dedicated to understanding human speech.
From recognizing digits to today’s advanced systems, speech recognition has come a long way, highlighting both technological evolution and future challenges and opportunities.
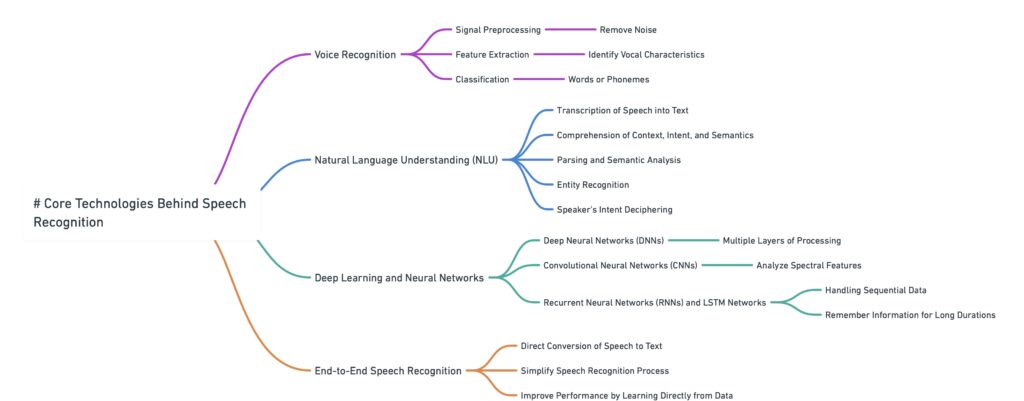
3. Core Technologies Behind Speech Recognition
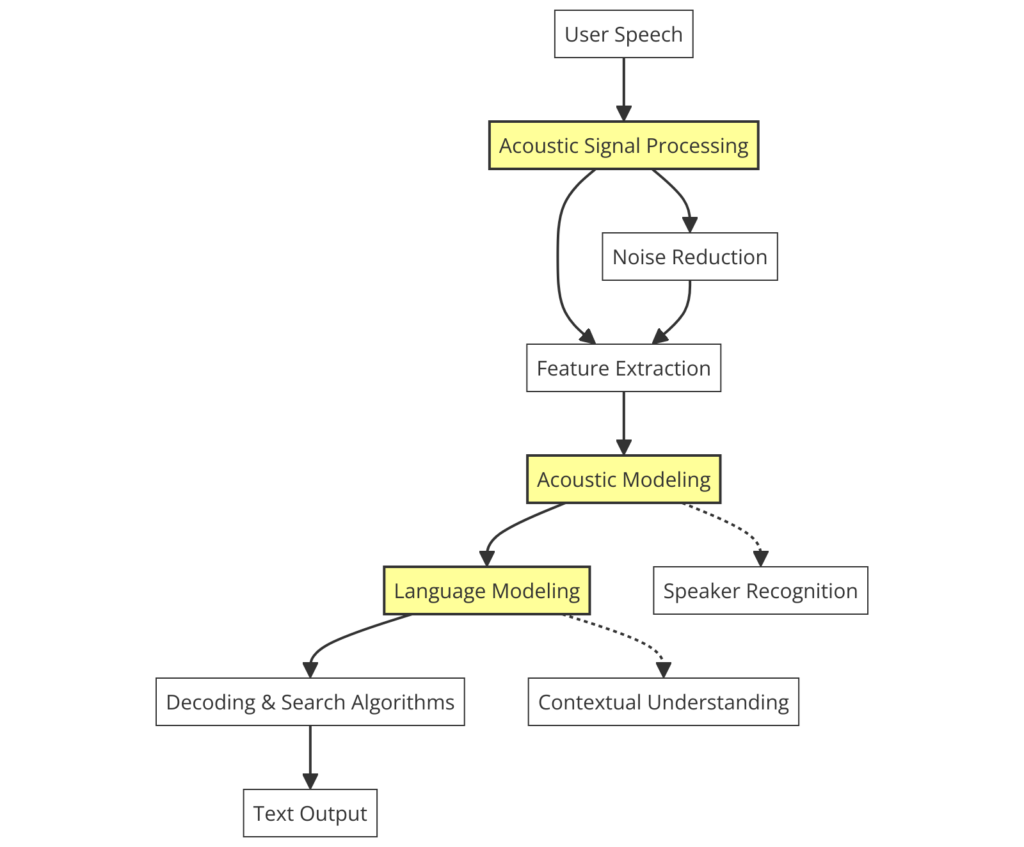
Modern speech recognition relies on several key technologies, which have evolved over time to make machines better at understanding human speech in real-time.
These core technologies include voice recognition, natural language understanding (NLU), and deep learning and neural networks.
Voice Recognition involves converting spoken words into text. It includes steps like removing noise, extracting vocal features, and classifying these features into words or phonemes (the smallest speech units).
Early systems used simple pattern matching, but human speech’s complexity required more advanced methods.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) goes beyond just transcribing speech. It involves understanding the context, intent, and meaning behind words. This is essential for more complex interactions, like those with virtual assistants and chatbots.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks have significantly improved speech recognition. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) help capture speech’s nuances.
- DNNs learn complex speech patterns, improving recognition in noisy environments.
- CNNs, adapted from image processing, analyze speech’s spectral features.
- RNNs and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks handle sequential data like speech, capturing its temporal dynamics.
End-to-End Speech Recognition models convert speech directly to text, bypassing traditional steps and improving performance by learning from data.
These core technologies have transformed human-computer interaction, making AI systems more intuitive and accessible.
Ongoing research continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible with speech recognition, paving the way for more innovative and efficient communication.
4. Applications of Speech Recognition
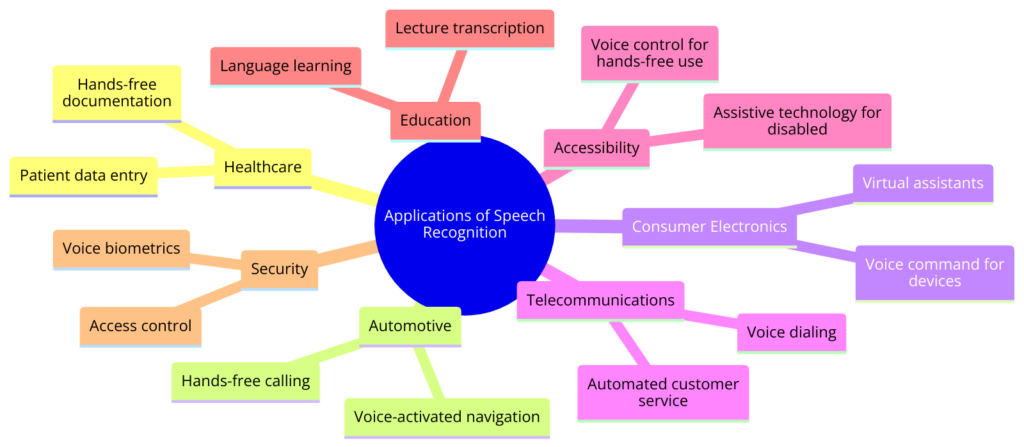
Speech recognition has changed how we interact with digital devices, allowing for more natural and accessible communication. Its applications span many industries, improving efficiency, user experiences, and creating new services.
Virtual Assistants and Smart Home Devices: Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use speech recognition to understand commands, helping with tasks like setting reminders, answering questions, and controlling smart devices. These assistants have become part of many people’s daily routines.
Accessibility Technologies: Speech recognition is vital for people with physical disabilities or those who can’t use traditional input devices. Text-to-speech and speech-to-text applications allow users to control devices using their voice, enhancing digital accessibility.
Automotive Applications: In cars, speech recognition helps drivers stay safe by allowing them to control navigation, make calls, and adjust entertainment options with voice commands, keeping their eyes on the road.
Customer Service and Call Centers: Speech recognition powers interactive voice response (IVR) systems, which handle customer inquiries without human intervention, streamlining service and reducing wait times.
Healthcare Documentation: In healthcare, speech recognition helps transcribe medical notes and records, saving time and improving accuracy.
Language Learning and Translation: Speech recognition aids language learning by providing feedback on pronunciation and fluency. Real-time translation apps break down language barriers, enabling communication between different languages.
Security and Authentication: Voice biometrics, using unique voice characteristics, offer secure authentication methods for accessing devices and information.
Despite its benefits, deploying speech recognition faces challenges like achieving accuracy with different accents, minimizing errors in noisy environments, and addressing privacy concerns.
Speech recognition’s diverse applications offer innovative solutions across many fields. As technology advances, it will further revolutionize industries and improve human-computer interaction, making technology more accessible and intuitive.

5. Challenges in Speech Recognition
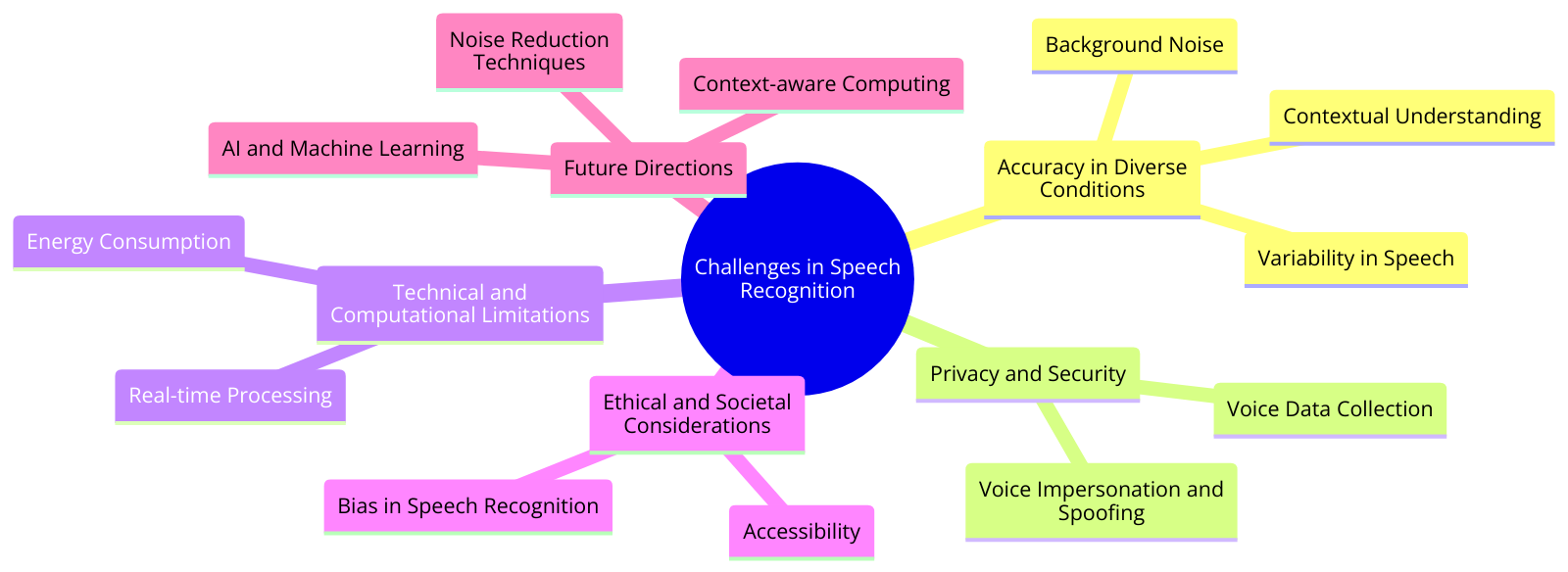
Even though speech recognition has improved a lot, it still faces many challenges. These problems affect how accurate and reliable the technology is and raise privacy and ethical concerns. Solving these issues is crucial for the technology’s growth and acceptance.
Accuracy in Different Conditions:
- Speech Variability: People have different accents, dialects, and speech patterns, making it hard for systems to be accurate for everyone.
- Background Noise: Noisy environments make it difficult for systems to recognize speech correctly.
- Context Understanding: Without context, systems might misinterpret words, especially with homonyms (words that sound the same but have different meanings).
Privacy and Security:
- Voice Data Collection: Collecting and storing voice data raises privacy concerns. People worry their data might be misused.
- Voice Impersonation: As voice-controlled systems grow, there’s a risk of people faking voices to trick systems.
Technical and Computational Limits:
- Real-Time Processing: Speech recognition needs a lot of computing power for real-time use, like with virtual assistants or translation. Balancing speed and accuracy on devices with limited power is challenging.
- Energy Use: Advanced speech recognition algorithms can drain device batteries quickly. Optimizing them for lower energy use is necessary.
Ethical and Societal Concerns:
- Bias: If training data isn’t diverse, systems can be biased, disadvantaging certain groups.
- Accessibility: While speech recognition can help many, relying only on voice commands can exclude people with speech impairments.
Future Directions: Solving these challenges requires combining AI advancements with insights from linguistics and human-computer interaction. Innovations in algorithms, noise reduction, and context-aware computing can help. Ethical and privacy concerns must also be addressed, ensuring speech recognition respects user rights and promotes inclusivity.
The challenges in speech recognition are varied and complex. Addressing them is essential for the technology’s future as a reliable tool in our digital world.
As researchers and developers work on these issues, the future of speech recognition looks promising, with potential for more accurate, secure, and inclusive human-machine interactions.
6. The Future of Speech Recognition
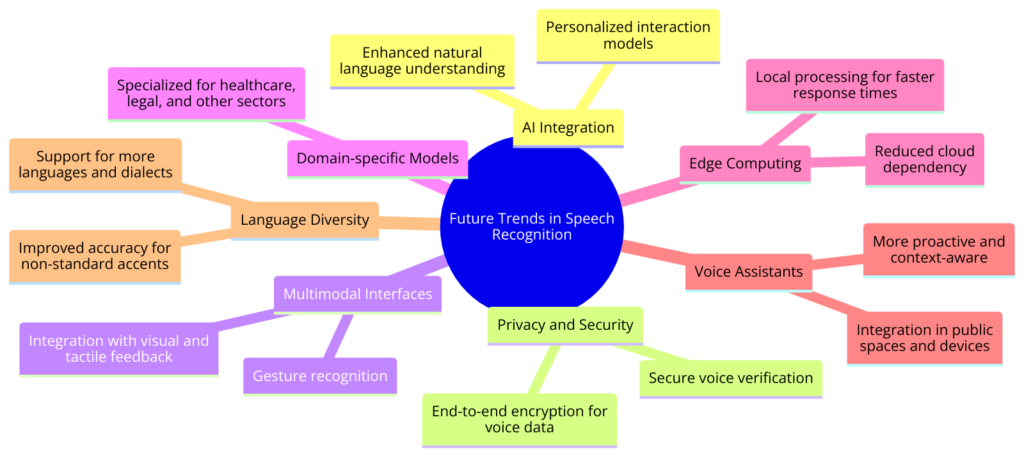
The future of speech recognition technology is full of promise, with improvements expected to make it more accurate, expand its uses, and tackle current problems. Here are some key trends and predictions for the future of this technology:
Technological Advancements:
- Better Accuracy and Context Understanding: Future developments in deep learning and neural networks will make speech recognition more accurate, even in noisy places or with strong accents. Enhanced models will understand context better, reducing errors.
- Edge Computing for Real-Time Processing: Edge computing will allow faster, real-time processing of voice commands on devices, reducing reliance on cloud servers. This will improve response times and address privacy concerns by keeping data local.
Expanded Applications:
- Healthcare Diagnostics and Therapies: Speech recognition will play a bigger role in healthcare, not just for documentation but also in diagnosing conditions like depression or cognitive impairments early.
- Voice-Controlled Environments: Voice-controlled technology will expand to public spaces and workplaces, making interactions with devices more intuitive and hands-free.
Societal Impacts:
- Breaking Down Language Barriers: Advances in real-time translation will help people communicate across different languages and cultures, fostering global connectivity.
- Enhancing Accessibility: Speech recognition will further enhance accessibility for people with disabilities, offering more effective tools for interaction and independence.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
- Ethical AI Practices: Developing standards for ethical AI practices and ensuring transparency in how voice data is used will be crucial. Robust security measures will protect against misuse.
Future Predictions:
- Personalized AI Assistants: Speech recognition will enable highly personalized AI assistants that understand individual preferences, context, and emotions, offering tailored support.
- Voice as a Primary Interface: As speech recognition becomes more reliable, voice will become a primary way to interact with technology, reducing reliance on screens and keyboards.
The future of speech recognition promises significant advancements and deeper integration into daily life.
While technical innovation is important, addressing ethical and privacy challenges is essential for the technology to reach its full potential.
By overcoming these challenges, speech recognition can enrich our lives and open up new possibilities for communication, accessibility, and global understanding.
7. Conclusion
The journey of speech recognition shows how transformative this technology is and how it reflects the broader goals and challenges of AI.
From its early days with simple tools to today’s advanced deep learning models, speech recognition has evolved significantly.
Today, speech recognition is a crucial part of our daily lives, enabling interactions that once seemed like science fiction.
Virtual assistants, accessibility technologies, and voice-controlled devices are just the beginning, showing the technology’s potential to revolutionize industries and create more natural digital interfaces.
However, there are still challenges to overcome, like improving accuracy, understanding different dialects, handling noise, and addressing privacy concerns.
These challenges highlight the complexity of human speech and the need for ongoing innovation.
Looking ahead, speech recognition will likely see further breakthroughs, expanding its impact on society.
Advances in algorithms, language understanding, and integration with new technologies like augmented reality and IoT suggest a future where speech recognition is everywhere and seamlessly integrated into our lives.
As speech recognition becomes more common, it’s important to ensure it enhances communication, respects privacy, and promotes inclusivity.
Ethical use of this technology will be crucial to unlocking its full potential.
In summary, the evolution, current state, and future direction of speech recognition show the dynamic relationship between technology and humanity.
As we refine and expand this technology, we’re not just teaching machines to understand us; we’re also learning about the complexities of human language.
The future of speech recognition offers exciting opportunities for innovation and a chance to redefine our interaction with the digital world and each other.
FAQ & Answers
What is Speech Recognition?
The technology that enables computers to interpret human speech and convert it into text or commands.
How has Speech Recognition technology evolved?
From simple voice commands to understanding complex conversations and accents.
Quiz
Quiz 1: Guess the Application
In our first quiz, “Guess the Application,” we describe various applications of speech recognition technology, and your challenge is to guess which application or tool is being referred to.
Ready to test your knowledge?
Let’s get started!
1. Hands-Free Control
Description: This tool allows users to command their devices without physical touch, employing voice for tasks like opening apps, sending messages, or making calls.
A) Voice-activated assistants
B) Speech-to-text software
C) Audio transcription services
2. From Speech to Text
Description: Favored by writers and students, this application transforms spoken words into written text in real-time.
A) Language translation services
B) Speech-to-text software
C) Voice cloning
3. Breaking Language Barriers
Description: This service turns live or recorded speech from one language to another, easing communication across linguistic divides.
A) Language translation services
B) Voice biometrics
C) Interactive voice response (IVR) systems
4. The Voiceprint Lock
Description: Businesses use this to authenticate identities through unique voice patterns.
A) Voice cloning
B) Voice biometrics
C) Audio transcription services
5. Automate Your Calls
Description: This system manages calls by providing automated responses or routing them based on voice commands.
A) Interactive voice response (IVR) systems
B) Voice-activated assistants
C) Speech-to-text software
Answers
- A) Voice-activated assistants
- B) Speech-to-text software
- A) Language translation services
- B) Voice biometrics
- A) Interactive voice response (IVR) systems
Quiz 2: Timeline Challenge
Our second quiz, “Timeline Challenge,” will test your knowledge on the history of speech recognition.
Can you place these key developments in their correct chronological order?
Let’s find out!
Developments:
- Apple introduces Siri, bringing voice-activated assistants to the mainstream.
- The IBM Shoebox debuts at the 1962 World’s Fair, marking an early milestone in speech recognition.
- Google adds voice search capabilities, revolutionizing how we access information.
- The Hidden Markov Model (HMM) significantly advances speech recognition in the late ’70s and early ’80s.
- Amazon’s Alexa enhances smart homes with voice control.
Correct Order:
- The IBM Shoebox (1962)
- The Hidden Markov Model (Late 1970s/Early 1980s)
- Siri by Apple
- Google’s Voice Search
- Amazon’s Alexa
How did you do? Whether you aced these quizzes or learned something new, we hope you enjoyed exploring the impact and development of speech recognition technology. As we continue to witness advancements in this field, it’s clear that voice recognition will play an increasingly integral role in our digital lives.
Stay tuned for more insights and quizzes on cutting-edge technology!