Reinforcement learning is one of the most fascinating ways artificial intelligence learns — because instead of being told the “right answer,” AI figures things out by trying, failing, and improving over time.
This is how AI learns to:
- Beat humans at complex games
- Control robots
- Optimize decisions in uncertain environments
In simple terms, reinforcement learning (RL) teaches AI how to make better decisions through rewards and penalties — much like how humans learn from experience.
In this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll learn:
- What reinforcement learning is (in plain English)
- How reinforcement learning works step by step
- The key components behind RL systems
- Real-world reinforcement learning examples
- Common challenges and limitations
- How beginners can start learning reinforcement learning
No math. No coding required. Just clear explanations.
What Is Reinforcement Learning?
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an AI learns by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback.
Instead of learning from labeled examples (like supervised learning), reinforcement learning works through:
- Actions
- Consequences
- Rewards or penalties
The goal of the AI is simple:
Maximize total rewards over time.
A simple analogy
Think of training a dog:
- The dog tries an action
- Good behavior gets a treat
- Bad behavior gets no reward
- Over time, the dog learns what works
Reinforcement learning works the same way — but with algorithms instead of dogs.
🔗 Related: Machine Learning Explained
How Reinforcement Learning Works (Step-by-Step)
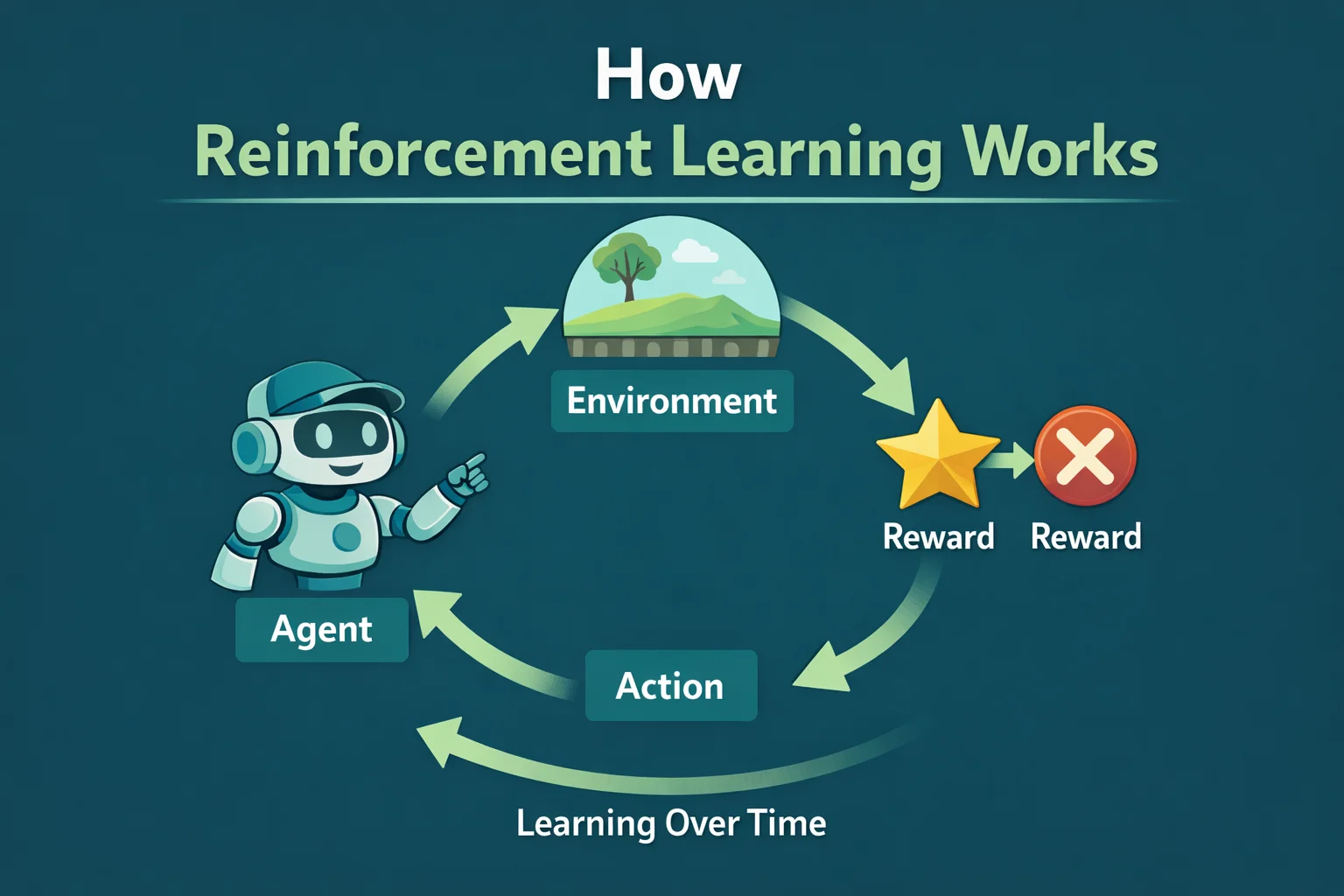
At its core, reinforcement learning follows a repeating feedback loop.
The basic RL loop:
- The AI observes its current situation
- It chooses an action
- The environment responds
- The AI receives a reward or penalty
- The AI updates its behavior and tries again
This loop repeats thousands or even millions of times until the AI improves its strategy.
🔗 Related: Deep Learning Explained
Key Components of Reinforcement Learning
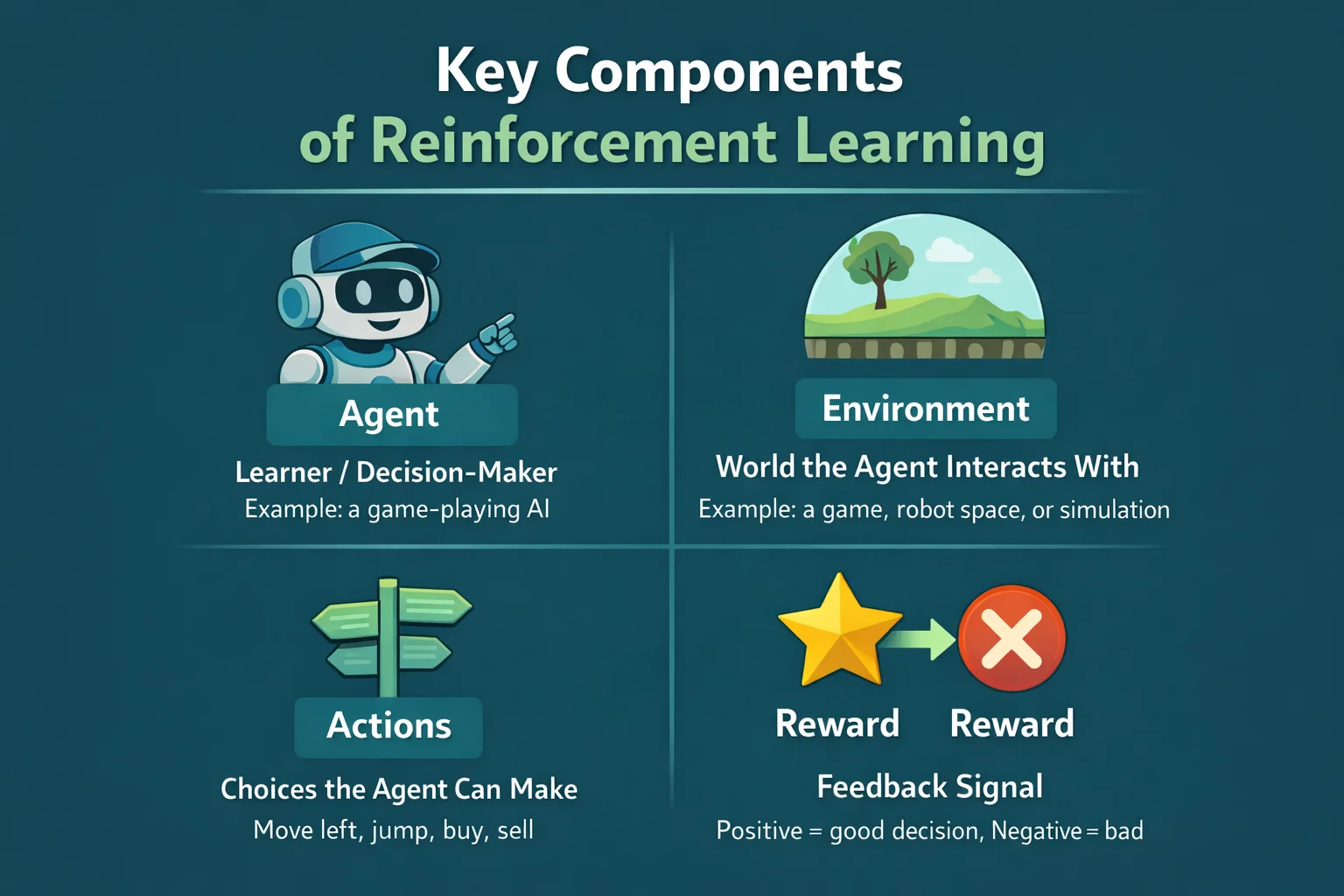
Every reinforcement learning system is built from the same core components.
Agent
The agent is the learner or decision-maker.
- Example: a game-playing AI or a robot
Environment
The environment is everything the agent interacts with.
- Example: a game board, simulation, or physical world
Actions
Actions are the choices the agent can make.
- Example: move left, turn right, accelerate, stop
Rewards
Rewards are feedback signals.
- Positive reward = good decision
- Negative reward = bad decision
Policy
A policy is the strategy the agent learns over time for choosing actions.
Reinforcement Learning vs Other Types of Machine Learning
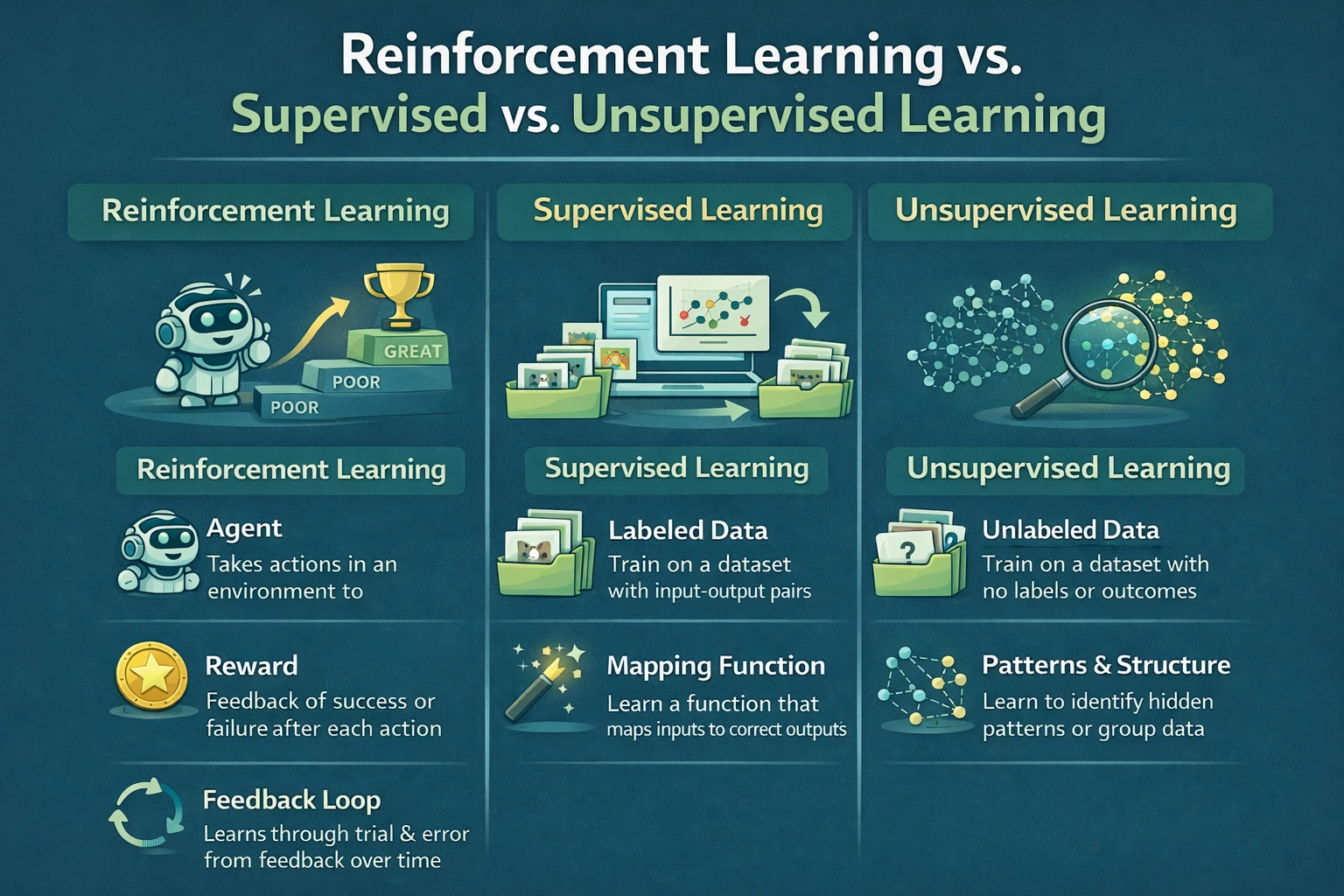
Reinforcement learning is different from other common learning methods.
Supervised Learning
- Uses labeled data
- Learns correct answers directly
- Example: spam detection
Unsupervised Learning
- Finds patterns in unlabeled data
- Example: clustering customers
Reinforcement Learning
- Learns through trial and error
- Focuses on long-term outcomes
- Example: learning how to win a game
Each method has its place, but reinforcement learning shines when decisions must be made sequentially over time.
Reinforcement Learning vs Rule-Based AI
Before modern machine learning, many AI systems relied on rule-based logic.
Rule-based AI works like this:
- Humans manually write rules
- The system follows fixed instructions
- If a situation isn’t covered by rules, the system fails
Reinforcement learning works very differently.
Instead of following predefined rules, a reinforcement learning agent:
- Learns through interaction
- Discovers strategies on its own
- Adapts when conditions change
Simple comparison:
- Rule-based AI → “Follow these instructions exactly.”
- Reinforcement learning → “Try actions, learn from outcomes, improve over time.”
This is why reinforcement learning is especially useful in complex or unpredictable environments where hard-coded rules don’t scale.
Real-World Reinforcement Learning Examples
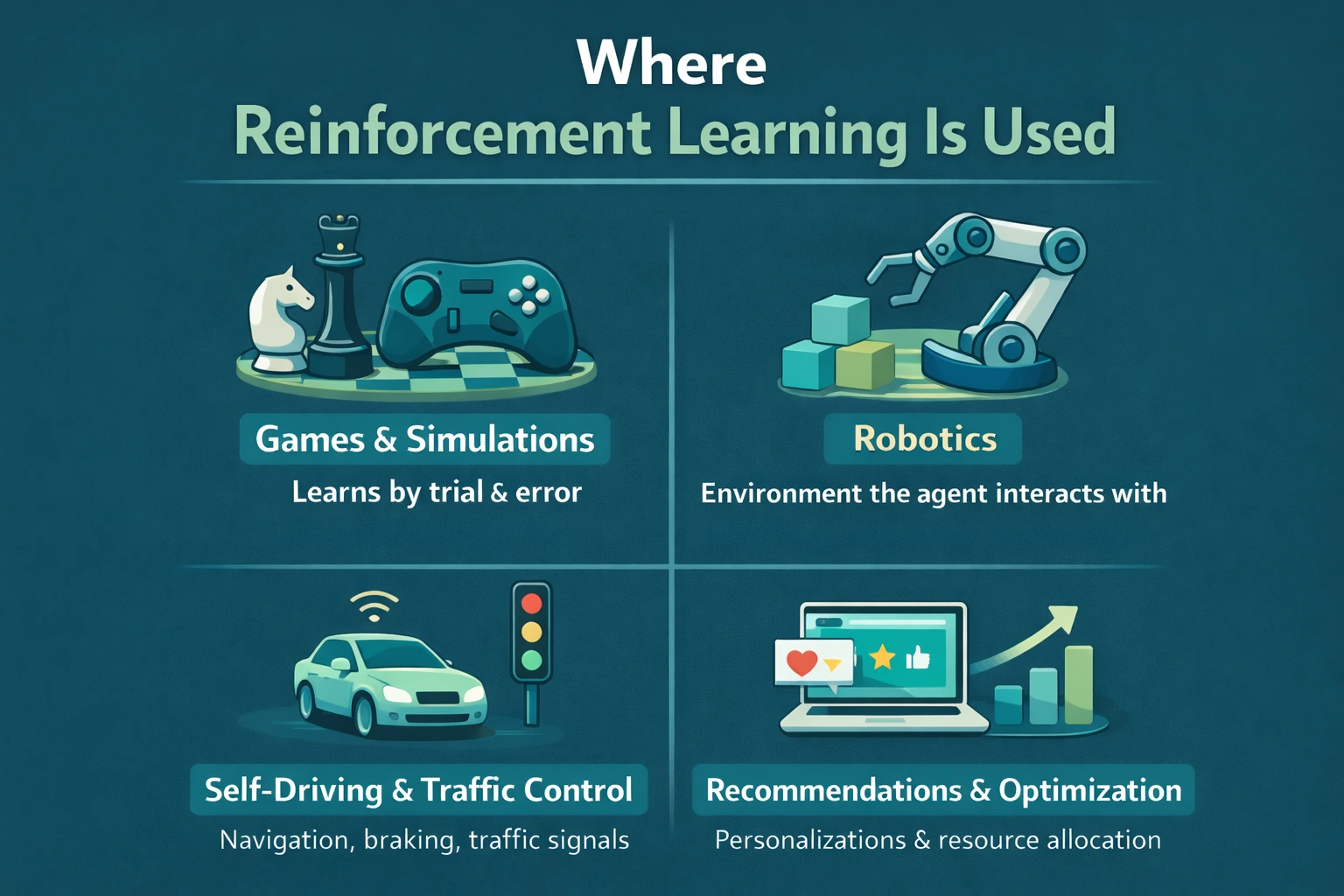
Reinforcement learning is already used in many real-world systems.
Games and Simulations
- Chess and Go (e.g., AlphaGo)
- Video game AI
- Training strategies in simulations
Robotics
- Learning how to walk or move
- Grasping objects
- Navigation in complex spaces
In many robotics systems, reinforcement learning is combined with computer vision so the AI can interpret images and video from cameras.
Autonomous Systems
- Traffic signal optimization
- Route planning
- Self-driving decision-making
Recommendation and Optimization Systems
- Content recommendations
- Ad placement
- Resource allocation
Some recommendation systems also overlap with techniques used in generative AI, especially when systems generate text, suggestions, or personalized content.
🔗 Related reading: Computer Vision Explained
Reinforcement Learning in Finance and Optimization
Reinforcement learning is also used in decision-heavy optimization problems, including finance and operations.
Common examples include:
- Trading strategy research (simulated environments)
- Portfolio optimization
- Dynamic pricing systems
- Resource allocation and scheduling
In these scenarios, the AI:
- Tries different strategies
- Receives rewards based on long-term outcomes
- Learns which decisions lead to better performance over time
Because real financial systems carry risk, reinforcement learning models are usually trained and tested in simulations before being considered for real-world use.
Common Reinforcement Learning Algorithms (Beginner Level)
You don’t need to know the math, but it helps to recognize the names.
Q-Learning
- Learns the value of actions
- One of the simplest RL methods
Deep Q-Networks (DQN)
- Combines reinforcement learning with neural networks
- Popular in game-playing AI
Policy Gradient Methods
- Learn strategies directly
- Useful for complex environments
For readers who want a more formal overview of reinforcement learning algorithms like Q-learning and policy methods, the Wikipedia overview provides a helpful technical reference.
Limitations and Risks of Reinforcement Learning
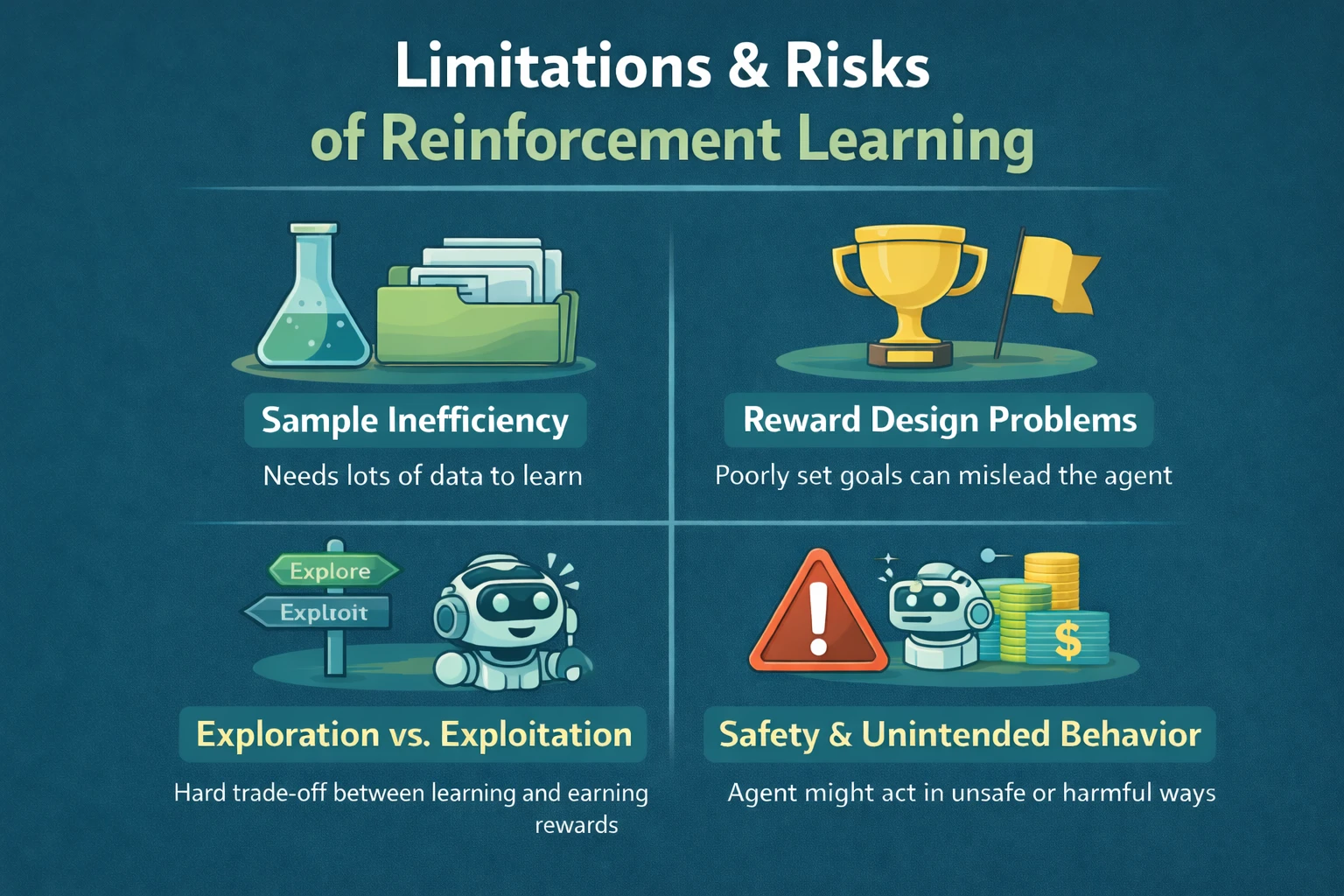
Reinforcement learning is powerful, but it has real challenges.
Sample inefficiency
RL often requires huge amounts of data and training time.
Reward design problems
Poorly designed rewards can cause unintended behavior.
Exploration vs exploitation
The AI must balance trying new actions vs using known good ones.
Safety concerns
In real-world systems, mistakes can be costly or dangerous.
Because of this, reinforcement learning is often trained in simulations first.
How to Start Learning Reinforcement Learning (Beginner Path)
You don’t need a PhD to get started.
Beginner-friendly path:
- Understand basic ML concepts
- Learn the agent–environment–reward loop
- Study simple examples (grid worlds, games)
- Explore simulators and libraries
Popular beginner tools include:
- OpenAI Gym
- Stable Baselines
- PyTorch or TensorFlow
Many beginners practice reinforcement learning concepts using simulation tools like OpenAI Gym, a popular framework for experimenting with reinforcement learning environments.
Focus on concepts first, not code.
FAQ
Is reinforcement learning the same as machine learning?
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning that focuses on learning through interaction and feedback. If you want a simple breakdown of supervised vs unsupervised vs reinforcement learning, see our Machine Learning Explained guide. While machine learning is a broader field, reinforcement learning specifically learns by trial and error using rewards and penalties rather than labeled data.
Does reinforcement learning use neural networks?
Often yes — especially in deep reinforcement learning, where neural networks are used to handle complex environments. However, basic reinforcement learning methods can work without neural networks.
Is reinforcement learning used in real life?
Yes. Reinforcement learning is used in robotics, game-playing AI, optimization research, recommendation systems, and simulation-based decision-making environments.
Is reinforcement learning hard to learn?
The core ideas are beginner-friendly and don’t require advanced math. However, implementing reinforcement learning systems at a professional or research level can become complex.
What is the difference between reinforcement learning and supervised learning?
Supervised learning learns from labeled examples with correct answers provided in advance. Reinforcement learning learns by interacting with an environment and improving decisions based on rewards and penalties.
What are rewards and penalties in reinforcement learning?
Rewards and penalties are feedback signals that guide learning. Rewards encourage actions that lead to good outcomes, while penalties discourage poor decisions. Over time, the agent learns to maximize long-term rewards.
Where is reinforcement learning used today?
Reinforcement learning is used in robotics, autonomous systems, game AI, logistics optimization, resource scheduling, and experimental financial modeling — often first tested in simulations.
Do I need math to understand reinforcement learning?
No. Beginners can understand reinforcement learning concepts without math. Mathematical knowledge becomes important only when working on advanced algorithms or implementations.
Conclusion
Reinforcement learning is how AI learns by doing.
Instead of memorizing answers, reinforcement learning systems:
- Try actions
- Learn from rewards
- Improve decisions over time
It’s one of the most powerful approaches in artificial intelligence — especially when problems involve uncertainty, long-term planning, and continuous decision-making.
If you’re continuing your AI learning journey, you may also want to explore how:
You now understand one of the most important ideas behind modern AI — and that already puts you ahead of most beginners.
Ciao, volevo sapere il tuo prezzo.
Hello,
My price on what?